转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/barrenlake/p/5349949.html#
1、为什么引入Backpressure
默认情况下,Spark Streaming通过Receiver以生产者生产数据的速率接收数据,计算过程中会出现 batch processing time > batch interval 的情况,其中 batch processing time 为实际计算一个批次花费时间, batch interval为Streaming应用设置的批处理间隔。这意味着Spark Streaming的数据接收速率高于Spark从队列中移除数据的速率,也就是数据处理能力低,在设置间隔内不能完全处理当前接收速率接收的数据。如果这种情况持续过长的时间,会造成数据在内存中堆积,导致Receiver所在Executor内存溢出等问题(如果设置StorageLevel包含disk, 则内存存放不下的数据会溢写至disk, 加大延迟)。Spark 1.5以前版本,用户如果要限制Receiver的数据接收速率,可以通过设置静态配制参数“spark.streaming.receiver.maxRate”的值来实现,此举虽然可以通过限制接收速率,来适配当前的处理能力,防止内存溢出,但也会引入其它问题。比如:producer数据生产高于maxRate,当前集群处理能力也高于maxRate,这就会造成资源利用率下降等问题。为了更好的协调数据接收速率与资源处理能力,Spark Streaming 从v1.5开始引入反压机制(back-pressure),通过动态控制数据接收速率来适配集群数据处理能力。
2、Backpressure
Spark Streaming Backpressure: 根据JobScheduler反馈作业的执行信息来动态调整Receiver数据接收率。通过属性“spark.streaming.backpressure.enabled”来控制是否启用backpressure机制,默认值false,即不启用。
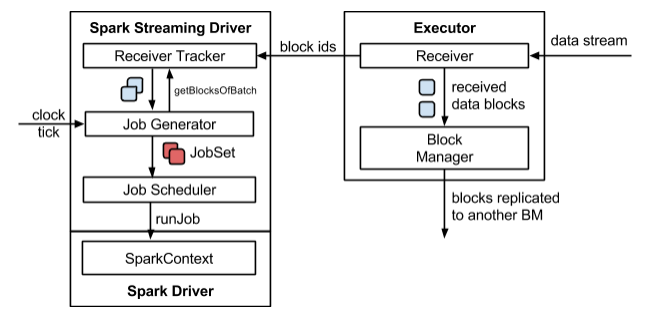
2.1 Streaming架构如下图所示(详见Streaming数据接收过程文档和Streaming 源码解析)
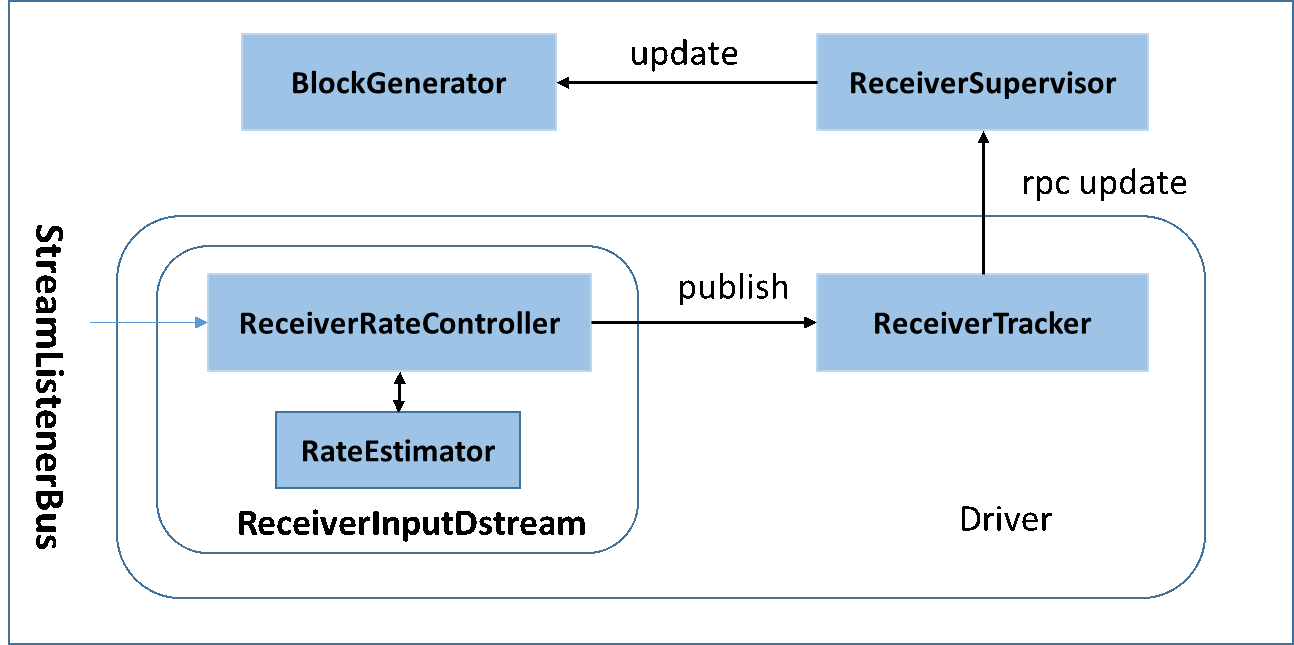
2.2 BackPressure执行过程如下图所示:
在原架构的基础上加上一个新的组件RateController,这个组件负责监听“OnBatchCompleted”事件,然后从中抽取processingDelay 及schedulingDelay信息. Estimator依据这些信息估算出最大处理速度(rate),最后由基于Receiver的Input Stream将rate通过ReceiverTracker与ReceiverSupervisorImpl转发给BlockGenerator(继承自RateLimiter).
3、BackPressure 源码解析
3.1 RateController类体系
RatenController 继承自StreamingListener. 用于处理BatchCompleted事件。核心代码为:
** * A StreamingListener that receives batch completion updates, and maintains * an estimate of the speed at which this stream should ingest messages, * given an estimate computation from a `RateEstimator` */ private[streaming] abstract class RateController(val streamUID: Int, rateEstimator: RateEstimator) extends StreamingListener with Serializable { …… …… /** * Compute the new rate limit and publish it asynchronously. */ private def computeAndPublish(time: Long, elems: Long, workDelay: Long, waitDelay: Long): Unit = Future[Unit] { val newRate = rateEstimator.compute(time, elems, workDelay, waitDelay) newRate.foreach { s => rateLimit.set(s.toLong) publish(getLatestRate()) } } def getLatestRate(): Long = rateLimit.get() override def onBatchCompleted(batchCompleted: StreamingListenerBatchCompleted) { val elements = batchCompleted.batchInfo.streamIdToInputInfo for { processingEnd <- batchCompleted.batchInfo.processingEndTime workDelay <- batchCompleted.batchInfo.processingDelay waitDelay <- batchCompleted.batchInfo.schedulingDelay elems <- elements.get(streamUID).map(_.numRecords) } computeAndPublish(processingEnd, elems, workDelay, waitDelay) } }
3.2 RateController的注册
JobScheduler启动时会抽取在DStreamGraph中注册的所有InputDstream中的rateController,并向ListenerBus注册监听. 此部分代码如下:
def start(): Unit = synchronized { if (eventLoop != null) return // scheduler has already been started logDebug("Starting JobScheduler") eventLoop = new EventLoop[JobSchedulerEvent]("JobScheduler") { override protected def onReceive(event: JobSchedulerEvent): Unit = processEvent(event) override protected def onError(e: Throwable): Unit = reportError("Error in job scheduler", e) } eventLoop.start() // attach rate controllers of input streams to receive batch completion updates for { inputDStream <- ssc.graph.getInputStreams rateController <- inputDStream.rateController } ssc.addStreamingListener(rateController) listenerBus.start() receiverTracker = new ReceiverTracker(ssc) inputInfoTracker = new InputInfoTracker(ssc) receiverTracker.start() jobGenerator.start() logInfo("Started JobScheduler") }
3.3 BackPressure执行过程分析
BackPressure 执行过程分为BatchCompleted事件触发时机和事件处理两个过程
3.3.1 BatchCompleted触发过程
对BatchedCompleted的分析,应该从JobGenerator入手,因为BatchedCompleted是批次处理结束的标志,也就是JobGenerator产生的作业执行完成时触发的,因此进行作业执行分析。
Streaming 应用中JobGenerator每个Batch Interval都会为应用中的每个Output Stream建立一个Job, 该批次中的所有Job组成一个Job Set.使用JobScheduler的submitJobSet进行批量Job提交。此部分代码结构如下所示
/** Generate jobs and perform checkpoint for the given `time`. */ private def generateJobs(time: Time) { // Set the SparkEnv in this thread, so that job generation code can access the environment // Example: BlockRDDs are created in this thread, and it needs to access BlockManager // Update: This is probably redundant after threadlocal stuff in SparkEnv has been removed. SparkEnv.set(ssc.env) // Checkpoint all RDDs marked for checkpointing to ensure their lineages are // truncated periodically. Otherwise, we may run into stack overflows (SPARK-6847). ssc.sparkContext.setLocalProperty(RDD.CHECKPOINT_ALL_MARKED_ANCESTORS, "true") Try { jobScheduler.receiverTracker.allocateBlocksToBatch(time) // allocate received blocks to batch graph.generateJobs(time) // generate jobs using allocated block } match { case Success(jobs) => val streamIdToInputInfos = jobScheduler.inputInfoTracker.getInfo(time) jobScheduler.submitJobSet(JobSet(time, jobs, streamIdToInputInfos)) case Failure(e) => jobScheduler.reportError("Error generating jobs for time " + time, e) } eventLoop.post(DoCheckpoint(time, clearCheckpointDataLater = false)) }
其中,sumitJobSet会创建固定数量的后台线程(具体由“spark.streaming.concurrentJobs”指定),去处理Job Set中的Job. 具体实现逻辑为:
def submitJobSet(jobSet: JobSet) { if (jobSet.jobs.isEmpty) { logInfo("No jobs added for time " + jobSet.time) } else { listenerBus.post(StreamingListenerBatchSubmitted(jobSet.toBatchInfo)) jobSets.put(jobSet.time, jobSet) jobSet.jobs.foreach(job => jobExecutor.execute(new JobHandler(job))) logInfo("Added jobs for time " + jobSet.time) } }
其中JobHandler用于执行Job及处理Job执行结果信息。当Job执行完成时会产生JobCompleted事件. JobHandler的具体逻辑如下面代码所示:
private class JobHandler(job: Job) extends Runnable with Logging { import JobScheduler._ def run() { try { val formattedTime = UIUtils.formatBatchTime( job.time.milliseconds, ssc.graph.batchDuration.milliseconds, showYYYYMMSS = false) val batchUrl = s"/streaming/batch/?id=${job.time.milliseconds}" val batchLinkText = s"[output operation ${job.outputOpId}, batch time ${formattedTime}]" ssc.sc.setJobDescription( s"""Streaming job from <a href="$batchUrl">$batchLinkText</a>""") ssc.sc.setLocalProperty(BATCH_TIME_PROPERTY_KEY, job.time.milliseconds.toString) ssc.sc.setLocalProperty(OUTPUT_OP_ID_PROPERTY_KEY, job.outputOpId.toString) // Checkpoint all RDDs marked for checkpointing to ensure their lineages are // truncated periodically. Otherwise, we may run into stack overflows (SPARK-6847). ssc.sparkContext.setLocalProperty(RDD.CHECKPOINT_ALL_MARKED_ANCESTORS, "true") // We need to assign `eventLoop` to a temp variable. Otherwise, because // `JobScheduler.stop(false)` may set `eventLoop` to null when this method is running, then // it's possible that when `post` is called, `eventLoop` happens to null. var _eventLoop = eventLoop if (_eventLoop != null) { _eventLoop.post(JobStarted(job, clock.getTimeMillis())) // Disable checks for existing output directories in jobs launched by the streaming // scheduler, since we may need to write output to an existing directory during checkpoint // recovery; see SPARK-4835 for more details. PairRDDFunctions.disableOutputSpecValidation.withValue(true) { job.run() } _eventLoop = eventLoop if (_eventLoop != null) { _eventLoop.post(JobCompleted(job, clock.getTimeMillis())) } } else { // JobScheduler has been stopped. } } finally { ssc.sc.setLocalProperty(JobScheduler.BATCH_TIME_PROPERTY_KEY, null) ssc.sc.setLocalProperty(JobScheduler.OUTPUT_OP_ID_PROPERTY_KEY, null) } } } }
当Job执行完成时,向eventLoop发送JobCompleted事件。EventLoop事件处理器接到JobCompleted事件后将调用handleJobCompletion 来处理Job完成事件。handleJobCompletion使用Job执行信息创建StreamingListenerBatchCompleted事件并通过StreamingListenerBus向监听器发送。实现如下:
private def handleJobCompletion(job: Job, completedTime: Long) { val jobSet = jobSets.get(job.time) jobSet.handleJobCompletion(job) job.setEndTime(completedTime) listenerBus.post(StreamingListenerOutputOperationCompleted(job.toOutputOperationInfo)) logInfo("Finished job " + job.id + " from job set of time " + jobSet.time) if (jobSet.hasCompleted) { jobSets.remove(jobSet.time) jobGenerator.onBatchCompletion(jobSet.time) logInfo("Total delay: %.3f s for time %s (execution: %.3f s)".format( jobSet.totalDelay / 1000.0, jobSet.time.toString, jobSet.processingDelay / 1000.0 )) listenerBus.post(StreamingListenerBatchCompleted(jobSet.toBatchInfo)) } job.result match { case Failure(e) => reportError("Error running job " + job, e) case _ => } }
3.3.2、BatchCompleted事件处理过程
StreamingListenerBus将事件转交给具体的StreamingListener,因此BatchCompleted将交由RateController进行处理。RateController接到BatchCompleted事件后将调用onBatchCompleted对事件进行处理。
override def onBatchCompleted(batchCompleted: StreamingListenerBatchCompleted) { val elements = batchCompleted.batchInfo.streamIdToInputInfo for { processingEnd <- batchCompleted.batchInfo.processingEndTime workDelay <- batchCompleted.batchInfo.processingDelay waitDelay <- batchCompleted.batchInfo.schedulingDelay elems <- elements.get(streamUID).map(_.numRecords) } computeAndPublish(processingEnd, elems, workDelay, waitDelay) }
onBatchCompleted会从完成的任务中抽取任务的执行延迟和调度延迟,然后用这两个参数用RateEstimator(目前存在唯一实现PIDRateEstimator,proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller, PID控制器)估算出新的rate并发布。代码如下:
/** * Compute the new rate limit and publish it asynchronously. */ private def computeAndPublish(time: Long, elems: Long, workDelay: Long, waitDelay: Long): Unit = Future[Unit] { val newRate = rateEstimator.compute(time, elems, workDelay, waitDelay) newRate.foreach { s => rateLimit.set(s.toLong) publish(getLatestRate()) } }
其中publish()由RateController的子类ReceiverRateController来定义。具体逻辑如下(ReceiverInputDStream中定义):
/** * A RateController that sends the new rate to receivers, via the receiver tracker. */ private[streaming] class ReceiverRateController(id: Int, estimator: RateEstimator) extends RateController(id, estimator) { override def publish(rate: Long): Unit = ssc.scheduler.receiverTracker.sendRateUpdate(id, rate) }
publish的功能为新生成的rate 借助ReceiverTracker进行转发。ReceiverTracker将rate包装成UpdateReceiverRateLimit事交ReceiverTrackerEndpoint
/** Update a receiver's maximum ingestion rate */ def sendRateUpdate(streamUID: Int, newRate: Long): Unit = synchronized { if (isTrackerStarted) { endpoint.send(UpdateReceiverRateLimit(streamUID, newRate)) } }
ReceiverTrackerEndpoint接到消息后,其将会从receiverTrackingInfos列表中获取Receiver注册时使用的endpoint(实为ReceiverSupervisorImpl),再将rate包装成UpdateLimit发送至endpoint.其接到信息后,使用updateRate更新BlockGenerators(RateLimiter子类),来计算出一个固定的令牌间隔。
/** RpcEndpointRef for receiving messages from the ReceiverTracker in the driver */ private val endpoint = env.rpcEnv.setupEndpoint( "Receiver-" + streamId + "-" + System.currentTimeMillis(), new ThreadSafeRpcEndpoint { override val rpcEnv: RpcEnv = env.rpcEnv override def receive: PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = { case StopReceiver => logInfo("Received stop signal") ReceiverSupervisorImpl.this.stop("Stopped by driver", None) case CleanupOldBlocks(threshTime) => logDebug("Received delete old batch signal") cleanupOldBlocks(threshTime) case UpdateRateLimit(eps) => logInfo(s"Received a new rate limit: $eps.") registeredBlockGenerators.asScala.foreach { bg => bg.updateRate(eps) } } })
其中RateLimiter的updateRate实现如下:
/** * Set the rate limit to `newRate`. The new rate will not exceed the maximum rate configured by * {{{spark.streaming.receiver.maxRate}}}, even if `newRate` is higher than that. * * @param newRate A new rate in events per second. It has no effect if it's 0 or negative. */ private[receiver] def updateRate(newRate: Long): Unit = if (newRate > 0) { if (maxRateLimit > 0) { rateLimiter.setRate(newRate.min(maxRateLimit)) } else { rateLimiter.setRate(newRate) } }
setRate的实现 如下:
public final void setRate(double permitsPerSecond) { Preconditions.checkArgument(permitsPerSecond > 0.0 && !Double.isNaN(permitsPerSecond), "rate must be positive"); synchronized (mutex) { resync(readSafeMicros()); double stableIntervalMicros = TimeUnit.SECONDS.toMicros(1L) / permitsPerSecond; //固定间隔 this.stableIntervalMicros = stableIntervalMicros; doSetRate(permitsPerSecond, stableIntervalMicros); } }
到此,backpressure反压机制调整rate结束。
4.流量控制点
当Receiver开始接收数据时,会通过supervisor.pushSingle()方法将接收的数据存入currentBuffer等待BlockGenerator定时将数据取走,包装成block. 在将数据存放入currentBuffer之时,要获取许可(令牌)。如果获取到许可就可以将数据存入buffer, 否则将被阻塞,进而阻塞Receiver从数据源拉取数据。
/** * Push a single data item into the buffer. */ def addData(data: Any): Unit = { if (state == Active) { waitToPush() //获取令牌 synchronized { if (state == Active) { currentBuffer += data } else { throw new SparkException( "Cannot add data as BlockGenerator has not been started or has been stopped") } } } else { throw new SparkException( "Cannot add data as BlockGenerator has not been started or has been stopped") } }
其令牌投放采用令牌桶机制进行, 原理如下图所示:
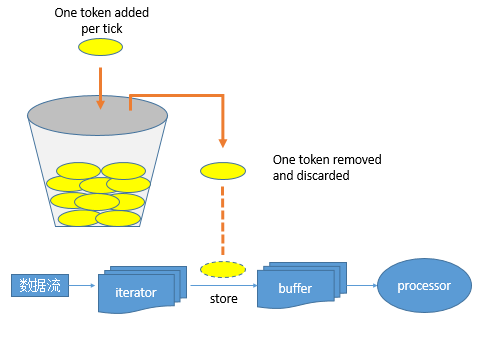
令牌桶机制: 大小固定的令牌桶可自行以恒定的速率源源不断地产生令牌。如果令牌不被消耗,或者被消耗的速度小于产生的速度,令牌就会不断地增多,直到把桶填满。后面再产生的令牌就会从桶中溢出。最后桶中可以保存的最大令牌数永远不会超过桶的大小。当进行某操作时需要令牌时会从令牌桶中取出相应的令牌数,如果获取到则继续操作,否则阻塞。用完之后不用放回。
Streaming 数据流被Receiver接收后,按行解析后存入iterator中。然后逐个存入Buffer,在存入buffer时会先获取token,如果没有token存在,则阻塞;如果获取到则将数据存入buffer. 然后等价后续生成block操作。