Kafka简介
消息队列(Message Queue)
消息 Message
网络中的两台计算机或者两个通讯设备之间传递的数据。例如说:文本、音乐、视频等内容。
队列 Queue
一种特殊的线性表(数据元素首尾相接),特殊之处在于只允许在首部删除元素和在尾部追加元素。入队、出队。
消息队列 MQ
消息+队列,保存消息的队列。消息的传输过程中的容器;主要提供生产、消费接口供外部调用做数据的存储和获取。
MQ分类
MQ主要分为两类:点对点(p2p)、发布订阅(Pub/Sub) 共同点: 消息生产者生产消息发送到queue中,然后消息消费者从queue中读取并且消费消息。 不同点: p2p模型包括:消息队列(Queue)、发送者(Sender)、接收者(Receiver) 一个生产者生产的消息只有一个消费者(Consumer)(即一旦被消费,消息就不在消息队列中)。比如说打电话。 Pub/Sub包含:消息队列(Queue)、主题(Topic)、发布者(Publisher)、订阅者(Subscriber) 每个消息可以有多个消费者,彼此互不影响。比如我发布一个微博:关注我的人都能够看到。 那么在大数据领域呢,为了满足日益增长的数据量,也有一款可以满足百万级别消息的生成和消费,分布式、持久稳定的产品——Kafka。
Kafka简介
Kafka是分布式的发布—订阅消息系统。它最初由LinkedIn(领英)公司发布,使用Scala语言编写,与2010年12月份开源,成为Apache的顶级项目。
Kafka是一个高吞吐量的、持久性的、分布式发布订阅消息系统。
它主要用于处理活跃的数据(登录、浏览、点击、分享、喜欢等用户行为产生的数据)。
三大特点:
高吞吐量
可以满足每秒百万级别消息的生产和消费——生产消费。QPS
持久性
有一套完善的消息存储机制,确保数据的高效安全的持久化——中间存储。
分布式
基于分布式的扩展和容错机制;Kafka的数据都会复制到几台服务器上。当某一台故障失效时,生产者和消费者转而使用其它的机器——整体健壮性。
Kafka组件
一个MQ需要哪些部分?生产、消费、消息类别、存储等等。 对于kafka而言,kafka服务就像是一个大的水池。不断的生产、存储、消费着各种类别的消息。那么kafka由何组成呢? > Kafka服务: > Topic:主题,Kafka处理的消息的不同分类。 > Broker:消息代理,Kafka集群中的一个kafka服务节点称为一个broker,主要存储消息数据。存在硬盘中。每个topic都是有分区的。 > Partition:Topic物理上的分组,一个topic在broker中被分为1个或者多个partition,分区在创建topic的时候指定。 > Message:消息,是通信的基本单位,每个消息都属于一个partition > Kafka服务相关 > Producer:消息和数据的生产者,向Kafka的一个topic发布消息。 > Consumer:消息和数据的消费者,定于topic并处理其发布的消息。 > Zookeeper:协调kafka的正常运行。
Broker
Broker:配置文件server.properties 1、为了减少磁盘写入的次数,broker会将消息暂时buffer起来,当消息的个数达到一定阀值或者过了一定的时间间隔时,再flush到磁盘,这样减少了磁盘IO调用的次数。 配置:Log Flush Policy #log.flush.interval.messages=10000 一个分区的消息数阀值 #log.flush.interval.ms=1000 2、kafka的消息保存一定时间(通常为7天)后会被删除。 配置:Log Retention Policy log.retention.hours=168 #log.retention.bytes=1073741824 log.retention.check.interval.ms=300000
Producer
Producer:配置文件:producer.properties 1、自定义partition Producer也根据用户设置的算法来根据消息的key来计算输入哪个partition:partitioner.class 2、异步或者同步发送 配置项:producer.type 异步或者同步发送 同步是指:发送方发出数据后,等接收方发回响应以后才发下一个数据的通讯方式。 异步是指:发送方发出数据后,不等接收方发回响应,接着发送下个数据的通讯方式。 3、批量发送可以很有效的提高发送效率。 Kafka producer的异步发送模式允许进行批量发送,先将消息缓存在内存中,然后一次请求批量发送出去。 具体配置queue.buffering.max.ms、queue.buffering.max.messages。 默认值分别为5000和10000
Consumer
consumers:配置文件:consumer.properties 1、每个consumer属于一个consumer group,可以指定组id。group.id 2、消费形式: 组内:组内的消费者消费同一份数据;同时只能有一个consumer消费一个Topic中的1个partition;一个consumer可以消费多个partitions中的消息。
所以,对于一个topic,同一个group中推荐不能有多于partitions个数的consumer同时消费,否则将意味着某些consumer将无法得到消息。 组间:每个消费组消费相同的数据,互不影响。 3、在一个consumer多个线程的情况下,一个线程相当于一个消费者。 例如:partition为3,一个consumer起了3个线程消费,另一个后来的consumer就无法消费。 (这是Kafka用来实现一个Topic消息的广播(发给所有的Consumer)和单播(发给某一个Consumer)的手段。一个Topic可以对应多个Consumer Group。
如果需要实现广播,只要每个Consumer有一个独立的Group就可以了。要实现单播只要所有的Consumer在同一个Group里。
用Consumer Group还可以将Consumer进行自由的分组而不需要多次发送消息到不同的Topic。)
topic、partition、message
1、每个partition在存储层面是append log文件。新消息都会被直接追加到log文件的尾部,每条消息在log文件中的位置称为offset(偏移量)。 2、每条Message包含了以下三个属性: 1°、offset 对应类型:long 此消息在一个partition中序号。可以认为offset是partition中Message的id 2°、MessageSize 对应类型:int32 此消息的字节大小。 3°、data 是message的具体内容。 3、越多的partitions意味着可以容纳更多的consumer,有效提升并发消费的能力。 4、总之:业务区分增加topic、数据量大增加partition。
Kafka安装配置
解压: [uplooking@uplooking01 ~]$ tar -zxvf soft/kafka_2.10-0.10.0.1.tgz -C app/ 重命名:[uplooking@uplooking01 ~]$ mv app/kafka_2.10-0.10.0.1/ app/kafka 添加KAFKA_HOME至环境变量:~/.bash_profile export KAFKA_HOME=/home/uplooking/app/kafka export PATH=$PATH:$KAFKA_HOME/bin source ~/.bash_profile 配置相关参数:$KAFKA_HOME/config/server.properties 主要参数:broker.id、log.dirs、zookeeper.connect broker.id=10 log.dirs=/home/uplooking/data/kafka [kafka数据的存放目录] zookeeper.connect=uplooking01:2181,uplooking02:2181,uplooking03:2181 kafka实例broker监听默认端口9092,配置listeners=PLAINTEXT://:9092 启动: $KAFKA_HOME/bin/kafka-server-start.sh [-daemon] $KAFKA_HOME/config/server.properties -daemon 可选,表示后台启动kafka服务
当然,kafka的配置文件也非常重要,有必要对其中的内容学习一下,这里给出其配置文件的说明:
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more # contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with # this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. # The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0 # (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with # the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at # # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 # # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and # limitations under the License. # see kafka.server.KafkaConfig for additional details and defaults ############################# Server Basics ############################# ################################################################################## # broker就是一个kafka的部署实例,在一个kafka集群中,每一台kafka都要有一个broker.id # 并且,该id唯一,且必须为整数 ################################################################################## broker.id=10 ############################# Socket Server Settings ############################# # The address the socket server listens on. It will get the value returned from # java.net.InetAddress.getCanonicalHostName() if not configured. # FORMAT: # listeners = security_protocol://host_name:port # EXAMPLE: # listeners = PLAINTEXT://your.host.name:9092 #listeners=PLAINTEXT://:9092 # Hostname and port the broker will advertise to producers and consumers. If not set, # it uses the value for "listeners" if configured. Otherwise, it will use the value # returned from java.net.InetAddress.getCanonicalHostName(). #advertised.listeners=PLAINTEXT://your.host.name:9092 ################################################################################## #The number of threads handling network requests # 默认处理网络请求的线程个数 3个 ################################################################################## num.network.threads=3 ################################################################################## # The number of threads doing disk I/O # 执行磁盘IO操作的默认线程个数 8 ################################################################################## num.io.threads=8 ################################################################################## # The send buffer (SO_SNDBUF) used by the socket server # socket服务使用的进行发送数据的缓冲区大小,默认100kb ################################################################################## socket.send.buffer.bytes=102400 ################################################################################## # The receive buffer (SO_SNDBUF) used by the socket server # socket服务使用的进行接受数据的缓冲区大小,默认100kb ################################################################################## socket.receive.buffer.bytes=102400 ################################################################################## # The maximum size of a request that the socket server will accept (protection against OOM) # socket服务所能够接受的最大的请求量,防止出现OOM(Out of memory)内存溢出,默认值为:100m # (应该是socker server所能接受的一个请求的最大大小,默认为100M) ################################################################################## socket.request.max.bytes=104857600 ############################# Log Basics (数据相关部分,kafka的数据称为log)############################# ################################################################################## # A comma seperated list of directories under which to store log files # 一个用逗号分隔的目录列表,用于存储kafka接受到的数据 ################################################################################## log.dirs=/home/uplooking/data/kafka ################################################################################## # The default number of log partitions per topic. More partitions allow greater # parallelism for consumption, but this will also result in more files across # the brokers. # 每一个topic所对应的log的partition分区数目,默认1个。更多的partition数目会提高消费 # 并行度,但是也会导致在kafka集群中有更多的文件进行传输 # (partition就是分布式存储,相当于是把一份数据分开几份来进行存储,即划分块、划分分区的意思) ################################################################################## num.partitions=1 ################################################################################## # The number of threads per data directory to be used for log recovery at startup and flushing at shutdown. # This value is recommended to be increased for installations with data dirs located in RAID array. # 每一个数据目录用于在启动kafka时恢复数据和在关闭时刷新数据的线程个数。如果kafka数据存储在磁盘阵列中 # 建议此值可以调整更大。 ################################################################################## num.recovery.threads.per.data.dir=1 ############################# Log Flush Policy (数据刷新策略)############################# # Messages are immediately written to the filesystem but by default we only fsync() to sync # the OS cache lazily. The following configurations control the flush of data to disk. # There are a few important trade-offs(平衡) here: # 1. Durability 持久性: Unflushed data may be lost if you are not using replication. # 2. Latency 延时性: Very large flush intervals may lead to latency spikes when the flush does occur as there will be a lot of data to flush. # 3. Throughput 吞吐量: The flush is generally the most expensive operation, and a small flush interval may lead to exceessive seeks. # The settings below allow one to configure the flush policy to flush data after a period of time or # every N messages (or both). This can be done globally and overridden on a per-topic basis. # kafka中只有基于消息条数和时间间隔数来制定数据刷新策略,而没有大小的选项,这两个选项可以选择配置一个 # 当然也可以两个都配置,默认情况下两个都配置,配置如下。 # The number of messages to accept before forcing a flush of data to disk # 消息刷新到磁盘中的消息条数阈值 #log.flush.interval.messages=10000 # The maximum amount of time a message can sit in a log before we force a flush # 消息刷新到磁盘生成一个log数据文件的时间间隔 #log.flush.interval.ms=1000 ############################# Log Retention Policy(数据保留策略) ############################# # The following configurations control the disposal(清理) of log segments(分片). The policy can # be set to delete segments after a period of time, or after a given size has accumulated(累积). # A segment will be deleted whenever(无论什么时间) *either* of these criteria(标准) are met. Deletion always happens # from the end of the log. # 下面的配置用于控制数据片段的清理,只要满足其中一个策略(基于时间或基于大小),分片就会被删除 # The minimum age of a log file to be eligible for deletion # 基于时间的策略,删除日志数据的时间,默认保存7天 log.retention.hours=168 # A size-based retention policy for logs. Segments are pruned from the log as long as the remaining # segments don't drop below log.retention.bytes. 1G # 基于大小的策略,1G #log.retention.bytes=1073741824 # The maximum size of a log segment file. When this size is reached a new log segment will be created. # 数据分片策略 log.segment.bytes=1073741824 # The interval at which log segments are checked to see if they can be deleted according # to the retention policies 5分钟 # 每隔多长时间检测数据是否达到删除条件 log.retention.check.interval.ms=300000 ############################# Zookeeper ############################# # Zookeeper connection string (see zookeeper docs for details). # This is a comma separated host:port pairs, each corresponding to a zk # server. e.g. "127.0.0.1:3000,127.0.0.1:3001,127.0.0.1:3002". # You can also append an optional chroot string to the urls to specify the # root directory for all kafka znodes. zookeeper.connect=uplooking01:2181,uplooking02:2181,uplooking03:2181 # Timeout in ms for connecting to zookeeper zookeeper.connection.timeout.ms=6000
另外需要注意的是,kafka启动后,会在zookeeper中创建相关的节点:
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 1] ls / [controller, brokers, zookeeper, yarn-leader-election, hadoop-ha, admin, isr_change_notification, consumers, config, hbase] [zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 5] get /brokers/ids/10 {"jmx_port":-1,"timestamp":"1521936591128","endpoints":["PLAINTEXT://uplooking01:9092"],"host":"uplooking01","version":3,"port":9092} cZxid = 0xa000000c1 ctime = Sun Mar 25 08:09:50 CST 2018 mZxid = 0xa000000c1 mtime = Sun Mar 25 08:09:50 CST 2018 pZxid = 0xa000000c1 cversion = 0 dataVersion = 0 aclVersion = 0 ephemeralOwner = 0x6762543b71390005 dataLength = 133 numChildren = 0
Kafka操作
topic操作
创建Topic:
kafka-topics.sh --create --topic hadoop --zookeeper uplooking01:2181,uplooking02:2181,uplooking03:2181 --partitions 1 --replication-factor 1 kafka-topics.sh --create --topic hive --zookeeper uplooking01:2181 --partitions 1 --replication-factor 1 kafka-topics.sh --create --topic hbase --zookeeper uplooking01:2181 --partitions 3 --replication-factor 1 创建topic过程的问题,replication-factor个数不能超过broker的个数 bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --topic sqoop --zookeeper uplooking01:2181 --partitions 3 --replication-factor 3 Error while executing topic command : replication factor: 3 larger than available brokers: 1 另外,在创建topic后,可以在/home/uplooking/data/kafka目录查看到分区的目录, 有多少个分区就会相应创建多少个目录。
uplooking01:2181,uplooking02:2181,uplooking03:2181 可以只写一个,为了做笔记方便,后面只写一个。
查看Topic列表:
kafka-topics.sh --list --zookeeper uplooking01:2181
查看某一个具体的Topic:
kafka-topics.sh --describe xxx --zookeeper uplooking01:2181 Topic:xxx PartitionCount:3 ReplicationFactor:1 Configs: Topic: xxx Partition: 0 Leader: 10 Replicas: 10 Isr: 10 Topic: xxx Partition: 1 Leader: 10 Replicas: 10 Isr: 10 Topic: xxx Partition: 2 Leader: 10 Replicas: 10 Isr: 10 PartitionCount:topic对应的partition的个数 ReplicationFactor:topic对应的副本因子,说白就是副本个数 Partition:partition编号,从0开始递增 Leader:当前partition起作用的breaker.id Replicas: 当前副本数据坐在的breaker.id,是一个列表,排在最前面的起作用 Isr:当前kakfa集群中可用的breaker.id列表
修改Topic:
不能修改replication-factor,以及只能对partition个数进行增加,不能减少 kafka-topics.sh --alter --topic hive --zookeeper uplooking01:2181 --partitions 3 partition由3变为2的时,抛出的异常: ERROR kafka.admin.AdminOperationException: The number of partitions for a topic can only be increased
删除Topic:
kafka-topics.sh --delete --topic hbase --zookeeper uplooking01:2181 Topic hbase is marked for deletion. Note: This will have no impact if delete.topic.enable is not set to true. 彻底删除一个topic,需要在server.properties中配置delete.topic.enable=true,否则只是标记删除 配置完成之后,需要重启kafka服务。
生产者消费者案例
使用kafka提供的标准生产消费脚本。
生产数据:
kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list uplooking01:9092 --topic hadoop 生产数据的时候需要指定:当前数据流向哪个broker,以及哪一个topic
消费数据:
kafka-console-consumer.sh --topic hadoop --zookeeper uplooking01:2181 说明:该消费语句,只能获取最新的数据,要想历史数据,需要添加选项--from-beginning /kafka-console-consumer.sh --topic hadoop --zookeeper uplooking01:2181 --from-beginning 在消费数据的时候,只需要指定topic,以及topic的元数据信息即可(在ZK中存放),所以这里需要使用zk
消费者--黑名单(blacklist)和白名单(whitelist)选项:
--blacklist 后面跟需要过滤的topic的列表,使用","隔开,意思是除了列表中的topic之外,都能接收其它topic的数据 --whitelist 后面跟需要过滤的topic的列表,使用","隔开,意思是除了列表中的topic之外,都不能接收其它topic的数据 eg: kafka-console-consumer.sh --zookeeper uplooking01:2181 --from-beginning --blacklist hadoop,hive kafka-console-consumer.sh --zookeeper uplooking01:2181 --from-beginning --whitelist hadoop,flume
kafka分布式环境搭建与概念验证
kafka中没有主从节点的概念,因此只需要将kafka安装目录拷贝到其它节点上即可,不过需要注意的是,需要修改broker Id为唯一的:
scp -r /home/uplooking/app/kafka/ uplooking@uplooking02:/home/uplooking/app
scp -r /home/uplooking/app/kafka/ uplooking@uplooking03:/home/uplooking/app
为了方便后面理解kafka的相关概念,这里将uplooking01、uplooking02、uplooking03的brokerId分别修改为101、102、103.
在三个节点上分别启动kafka:
kafka-server-start.sh -daemon app/kafka/config/server.properties
创建一个topic:
kafka-topics.sh --create --topic hadoop --partitions 3 --replication-factor 3 --zookeeper uplooking01:2181,uplooking02:2181,uplooking03:2181
查看该topic的详细信息:
[uplooking@uplooking01 ~]$ kafka-topics.sh --describe hbase --zookeeper uplooking01:2181,uplooking02:2181,uplooking03:2181 Topic:hadoop PartitionCount:3 ReplicationFactor:3 Configs: Topic: hadoop Partition: 0 Leader: 101 Replicas: 101,102,103 Isr: 101,102,103 Topic: hadoop Partition: 1 Leader: 102 Replicas: 102,103,101 Isr: 102,103,101 Topic: hadoop Partition: 2 Leader: 103 Replicas: 103,101,102 Isr: 103,101,102 再查看前面的解释: PartitionCount:topic对应的partition的个数 ReplicationFactor:topic对应的副本因子,说白就是副本个数 Partition:partition编号,从0开始递增 Leader:当前partition起作用的breaker.id Replicas: 当前副本数据坐在的breaker.id,是一个列表,排在最前面的起作用 Isr:当前kakfa集群中可用的breaker.id列表 这样就很容易理解了。
这意味着,三个分区在三个节点上都有保存数据的,可以分别在每个节点上查看相关的分区数据信息:
[uplooking@uplooking01 kafka]$ ll 总用量 24 -rw-rw-r-- 1 uplooking uplooking 0 3月 25 19:33 cleaner-offset-checkpoint drwxrwxr-x 2 uplooking uplooking 4096 3月 25 19:33 hadoop-0 drwxrwxr-x 2 uplooking uplooking 4096 3月 25 19:33 hadoop-1 drwxrwxr-x 2 uplooking uplooking 4096 3月 25 19:33 hadoop-2 -rw-rw-r-- 1 uplooking uplooking 56 3月 25 19:33 meta.properties -rw-rw-r-- 1 uplooking uplooking 37 3月 25 19:48 recovery-point-offset-checkpoint -rw-rw-r-- 1 uplooking uplooking 37 3月 25 19:49 replication-offset-checkpoint
为了进一步理解相关概念,可以尝试把uplooking01上的kafka关掉,然后再查看topic的详细信息:
[uplooking@uplooking01 ~]$ kafka-topics.sh --describe hadoop --zookeeper uplooking01:2181,uplooking02:2181,uplooking03:2181 Topic:hadoop PartitionCount:3 ReplicationFactor:3 Configs: Topic: hadoop Partition: 0 Leader: 102 Replicas: 101,102,103 Isr: 102,103 Topic: hadoop Partition: 1 Leader: 102 Replicas: 102,103,101 Isr: 102,103 Topic: hadoop Partition: 2 Leader: 103 Replicas: 103,101,102 Isr: 103,102
然后个人分析如下:
前面提到:业务区分增加topic、数据量大增加partition。 所以partition分区,是为了把数据分散来存放,这好比日志需要每天分割一样,也是避免单个存储位置数据量过多。 显然,至于我们的每个消息存放在哪个分区,kafka本身是有机制去进行计算的: int hashCode = Math.abs("ttt".hashCode()); int partition = hashCode % 50; 具体这里就不进行讨论了。 另外,因为设置了3个副本因子,所以3个分区的数据在3个节点上都会有保存,同时为了起到负载均衡的作用,kafka 会为每个分区设置一个leader节点来专门进行该分区数据的相关操作。 现在再去看前面kafka组件的理论知识,就很容易理解了。
Kafka和Flume的整合
整合场景说明
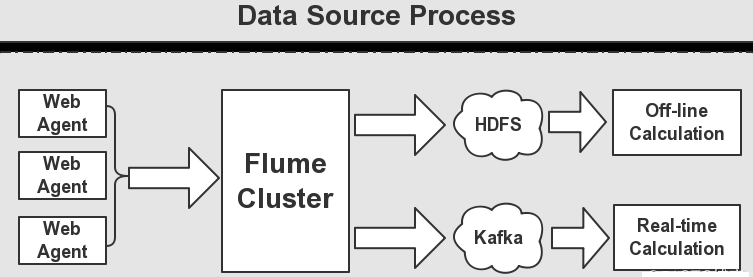
如上图所示,一般的,Kafka生产的数据,是由Flume的Sink提供的,这里我们需要用到Flume集群,
通过Flume集群将Agent的日志收集分发到 Kafka(供实时计算处理)和HDFS(离线计算处理)。
这里,我们使用Flume作为日志收集系统,将收集到的数据输送到Kafka中间件,以供Storm去实时消费计算,整个流程从各个Web节点 上,
通过Flume的Agent代理收集日志,然后汇总到Flume集群,在由Flume的Sink将日志输送到Kafka集群,完成数据的生产流程。
整合案例
先创建一个topic:
[uplooking@uplooking01 ~]$ kafka-topics.sh --create --topic flume-kafka --partitions 3 --replication-factor 3 --zookeeper uplooking01:2181,uplooking02:2181,uplooking03:2181 Created topic "flume-kafka". [uplooking@uplooking01 ~]$ kafka-topics.sh --describe flume-kafka --zookeeper uplooking01:2181,uplooking02:2181,uplooking03:2181 Topic:flume-kafka PartitionCount:3 ReplicationFactor:3 Configs: Topic: flume-kafka Partition: 0 Leader: 101 Replicas: 101,102,103 Isr: 101,102,103 Topic: flume-kafka Partition: 1 Leader: 102 Replicas: 102,103,101 Isr: 102,103,101 Topic: flume-kafka Partition: 2 Leader: 103 Replicas: 103,101,102 Isr: 103,101,102
启动kafka消费者:
[uplooking@uplooking01 ~]$ kafka-console-consumer.sh --topic flume-kafka --zookeeper uplooking01:2181,uplooking02:2181,uplooking03:2181
Flume的配置文件,这里为监听一个目录下的文件变化:
######################################################### ## ##主要作用是监听目录中的新增文件,采集到数据之后,输出到kafka ## 注意:Flume agent的运行,主要就是配置source channel sink ## 下面的a1就是agent的代号,source叫r1 channel叫c1 sink叫k1 ######################################################### a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 #对于source的配置描述 监听目录中的新增文件 a1.sources.r1.type = spooldir a1.sources.r1.spoolDir = /home/uplooking/data/flume/source a1.sources.r1.fileHeader = true a1.sources.r1.fileHeaderKey = filepath a1.sources.r1.fileSuffix = .OK a1.sources.r1.deletePolicy = immediate #对于sink的配置描述 使用kafka做数据的消费 a1.sinks.k1.type = org.apache.flume.sink.kafka.KafkaSink a1.sinks.k1.topic = flume-kafka a1.sinks.k1.brokerList = uplooking01:9092,uplooking02:9092,uplooking03:9092 a1.sinks.k1.requiredAcks = 1 a1.sinks.k1.batchSize = 20 #对于channel的配置描述 使用内存缓冲区域做数据的临时缓存 a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 #通过channel c1将source r1和sink k1关联起来 a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
启动Flume:
flume-ng agent --conf conf --name a1 --conf-file conf/flume-kafka.conf
向被侦听目录中添加hello文件,其内容如下:
hello he
hello me
hello you
添加后查看kafka消费者端的输出:
[uplooking@uplooking01 ~]$ kafka-console-consumer.sh --topic flume-kafka --zookeeper uplooking01:2181,uplooking02:2181,uplooking03:2181 hello he hello me hello you
这样就完成了Kafka和Flume的整合。