1.样本下采样选择
# 下采样取样本数据 X = data.ix[:, data.columns != 'Class'] y = data.ix[:, data.columns == 'Class'] # Number of data points in the minority class number_records_fraud = len(data[data.Class == 1]) fraud_indices = np.array(data[data.Class == 1].index) # Picking the indices of the normal classes normal_indices = data[data.Class == 0].index # Out of the indices we picked, randomly select "x" number (number_records_fraud) random_normal_indices = np.random.choice(normal_indices, number_records_fraud, replace = False) random_normal_indices = np.array(random_normal_indices) # Appending the 2 indices under_sample_indices = np.concatenate([fraud_indices,random_normal_indices]) # Under sample dataset under_sample_data = data.iloc[under_sample_indices,:] X_undersample = under_sample_data.ix[:, under_sample_data.columns != 'Class'] y_undersample = under_sample_data.ix[:, under_sample_data.columns == 'Class'] # Showing ratio print("Percentage of normal transactions: ", len(under_sample_data[under_sample_data.Class == 0])/len(under_sample_data)) print("Percentage of fraud transactions: ", len(under_sample_data[under_sample_data.Class == 1])/len(under_sample_data)) print("Total number of transactions in resampled data: ", len(under_sample_data)) # 下采样后的数据进行训练、验证数据集拆分 from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split # Whole dataset X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size = 0.3, random_state = 0) print("Number transactions train dataset: ", len(X_train)) print("Number transactions test dataset: ", len(X_test)) print("Total number of transactions: ", len(X_train)+len(X_test)) # Undersampled dataset X_train_undersample, X_test_undersample, y_train_undersample, y_test_undersample = train_test_split(X_undersample ,y_undersample ,test_size = 0.3 ,random_state = 0) print("") print("Number transactions train dataset: ", len(X_train_undersample)) print("Number transactions test dataset: ", len(X_test_undersample)) print("Total number of transactions: ", len(X_train_undersample)+len(X_test_undersample))
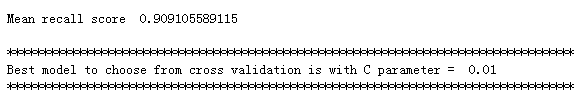
交叉验证选择最优参数:
#Recall = TP/(TP+FN) from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression from sklearn.cross_validation import KFold, cross_val_score from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix,recall_score,classification_report def printing_Kfold_scores(x_train_data,y_train_data): fold = KFold(len(y_train_data),5,shuffle=False) # Different C parameters c_param_range = [0.01,0.1,1,10,100] results_table = pd.DataFrame(index = range(len(c_param_range),2), columns = ['C_parameter','Mean recall score']) results_table['C_parameter'] = c_param_range # the k-fold will give 2 lists: train_indices = indices[0], test_indices = indices[1] j = 0 for c_param in c_param_range: print('-------------------------------------------') print('C parameter: ', c_param) print('-------------------------------------------') print('') recall_accs = [] for iteration, indices in enumerate(fold,start=1): # Call the logistic regression model with a certain C parameter lr = LogisticRegression(C = c_param, penalty = 'l1') # Use the training data to fit the model. In this case, we use the portion of the fold to train the model # with indices[0]. We then predict on the portion assigned as the 'test cross validation' with indices[1] lr.fit(x_train_data.iloc[indices[0],:],y_train_data.iloc[indices[0],:].values.ravel()) # Predict values using the test indices in the training data y_pred_undersample = lr.predict(x_train_data.iloc[indices[1],:].values) # Calculate the recall score and append it to a list for recall scores representing the current c_parameter recall_acc = recall_score(y_train_data.iloc[indices[1],:].values,y_pred_undersample) recall_accs.append(recall_acc) print('Iteration ', iteration,': recall score = ', recall_acc) # The mean value of those recall scores is the metric we want to save and get hold of. results_table.ix[j,'Mean recall score'] = np.mean(recall_accs) j += 1 print('') print('Mean recall score ', np.mean(recall_accs)) print('') best_c = results_table.loc[results_table['Mean recall score'].idxmax()]['C_parameter'] # Finally, we can check which C parameter is the best amongst the chosen. print('*********************************************************************************') print('Best model to choose from cross validation is with C parameter = ', best_c) print('*********************************************************************************') return best_c best_c = printing_Kfold_scores(X_train_undersample,y_train_undersample)

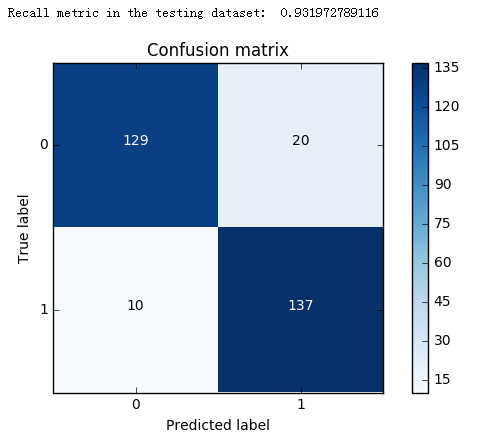
绘制混淆矩阵
def plot_confusion_matrix(cm, classes, title='Confusion matrix', cmap=plt.cm.Blues): """ This function prints and plots the confusion matrix. """ plt.imshow(cm, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap) plt.title(title) plt.colorbar() tick_marks = np.arange(len(classes)) plt.xticks(tick_marks, classes, rotation=0) plt.yticks(tick_marks, classes) thresh = cm.max() / 2. for i, j in itertools.product(range(cm.shape[0]), range(cm.shape[1])): plt.text(j, i, cm[i, j], horizontalalignment="center", color="white" if cm[i, j] > thresh else "black") plt.tight_layout() plt.ylabel('True label') plt.xlabel('Predicted label')
import itertools lr = LogisticRegression(C = best_c, penalty = 'l1') lr.fit(X_train_undersample,y_train_undersample.values.ravel()) y_pred_undersample = lr.predict(X_test_undersample.values) # Compute confusion matrix cnf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test_undersample,y_pred_undersample) np.set_printoptions(precision=2) print("Recall metric in the testing dataset: ", cnf_matrix[1,1]/(cnf_matrix[1,0]+cnf_matrix[1,1])) # Plot non-normalized confusion matrix class_names = [0,1] plt.figure() plot_confusion_matrix(cnf_matrix , classes=class_names , title='Confusion matrix') plt.show()
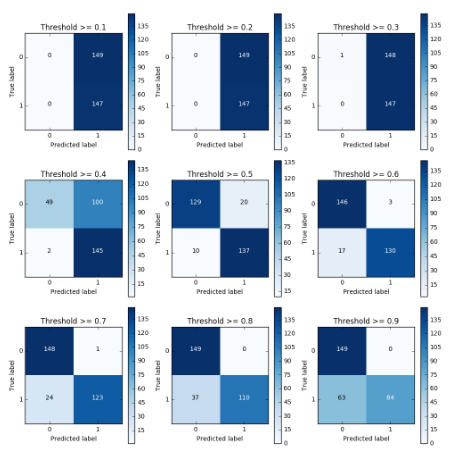
查看不同阈值对应召回率
lr = LogisticRegression(C = 0.01, penalty = 'l1') lr.fit(X_train_undersample,y_train_undersample.values.ravel()) y_pred_undersample_proba = lr.predict_proba(X_test_undersample.values) thresholds = [0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5,0.6,0.7,0.8,0.9] plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) j = 1 for i in thresholds: y_test_predictions_high_recall = y_pred_undersample_proba[:,1] > i plt.subplot(3,3,j) j += 1 # Compute confusion matrix cnf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test_undersample,y_test_predictions_high_recall) np.set_printoptions(precision=2) print("Recall metric in the testing dataset: ", cnf_matrix[1,1]/(cnf_matrix[1,0]+cnf_matrix[1,1])) # Plot non-normalized confusion matrix class_names = [0,1] plot_confusion_matrix(cnf_matrix , classes=class_names , title='Threshold >= %s'%i)