目录
VGGNet网络结构
论文中还讨论了其他结构
参考资料
2014年,牛津大学计算机视觉组(Visual Geometry Group)和Google DeepMind公司的研究员一起研发出了新的深度卷积神经网络:VGGNet,并取得了ILSVRC2014比赛分类项目的第二名(第一名是GoogLeNet,也是同年提出的)和定位项目的第一名。
VGGNet探索了卷积神经网络的深度与其性能之间的关系,成功地构筑了16~19层深的卷积神经网络,证明了增加网络的深度能够在一定程度上影响网络最终的性能,使错误率大幅下降,同时拓展性又很强,迁移到其它图片数据上的泛化性也非常好。到目前为止,VGG仍然被用来提取图像特征。
VGGNet可以看成是加深版本的AlexNet,都是由卷积层、全连接层两大部分构成。
|
VGGNet网络结构 |
VGGNet比AlexNet的网络层数多,不再使用尺寸较大的卷积核,如11*11、7*7、5*5,而是只采用了尺寸为3*3的卷积核,VGG-16的卷积神经网络结构如下:

对应代码为:

import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np # 输入 x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 224, 224, 3]) # 第1层:与64个3*3*3的核,步长=1,SAME卷积 w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 3, 64]), dtype=tf.float32, name='w1') conv1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(x, w1, [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME')) # 结果为224*224*64 # 第2层:与64个3*3*64的核,步长=1,SAME卷积 w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 64, 64]), dtype=tf.float32, name='w2') conv2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(conv1, w2, [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME')) # 结果为224*224*64 # 池化1 pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv2, [1, 2, 2, 1], [1, 2, 2, 1], 'VALID') # 结果为112*112*64 # 第3层:与128个3*3*64的核,步长=1,SAME卷积 w3 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 64, 128]), dtype=tf.float32, name='w3') conv3 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(pool1, w3, [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME')) # 结果为112*112*128 # 第4层:与128个3*3*128的核,步长=1,SAME卷积 w4 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 128, 128]), dtype=tf.float32, name='w4') conv4 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(conv3, w4, [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME')) # 结果为112*112*128 # 池化2 pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv4, [1, 2, 2, 1], [1, 2, 2, 1], 'VALID') # 结果为56*56*128 # 第5层:与256个3*3*128的核,步长=1,SAME卷积 w5 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 128, 256]), dtype=tf.float32, name='w5') conv5 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(pool2, w5, [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME')) # 结果为56*56*256 # 第6层:与256个3*3*256的核,步长=1,SAME卷积 w6 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 256, 256]), dtype=tf.float32, name='w6') conv6 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(conv5, w6, [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME')) # 结果为56*56*256 # 第7层:与256个3*3*256的核,步长=1,SAME卷积 w7 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 256, 256]), dtype=tf.float32, name='w7') conv7 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(conv6, w7, [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME')) # 结果为56*56*256 # 池化3 pool3 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv7, [1, 2, 2, 1], [1, 2, 2, 1], 'VALID') # 结果为28*28*256 # 第8层:与512个3*3*256的核,步长=1,SAME卷积 w8 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 256, 512]), dtype=tf.float32, name='w8') conv8 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(pool3, w8, [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME')) # 结果为28*28*512 # 第9层:与512个3*3*512的核,步长=1,SAME卷积 w9 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 512, 512]), dtype=tf.float32, name='w9') conv9 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(conv8, w9, [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME')) # 结果为28*28*512 # 第10层:与512个3*3*512的核,步长=1,SAME卷积 w10 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 512, 512]), dtype=tf.float32, name='w10') conv10 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(conv9, w10, [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME')) # 结果为28*28*512 # 池化4 pool4 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv10, [1, 2, 2, 1], [1, 2, 2, 1], 'VALID') # 结果为14*14*512 # 第11层:与512个3*3*256的核,步长=1,SAME卷积 w11 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 512, 512]), dtype=tf.float32, name='w11') conv11 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(pool4, w11, [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME')) # 结果为14*14*512 # 第12层:与512个3*3*512的核,步长=1,SAME卷积 w12 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 512, 512]), dtype=tf.float32, name='w12') conv12 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(conv11, w12, [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME')) # 结果为14*14*512 # 第13层:与512个3*3*512的核,步长=1,SAME卷积 w13 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 512, 512]), dtype=tf.float32, name='w13') conv13 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(conv12, w13, [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME')) # 结果为14*14*512 # 池化5 pool5 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv13, [1, 2, 2, 1], [1, 2, 2, 1], 'VALID') # 结果为7*7*512 # 拉伸为25088 pool_l5_shape = pool5.get_shape() num = pool_l5_shape[1].value * pool_l5_shape[2].value * pool_l5_shape[3].value flatten = tf.reshape(pool5, [-1, num]) # 结果为25088*1 # 第14层:与4096个神经元全连接 fcW1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([num, 4096]), dtype=tf.float32, name='fcW1') fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(flatten, fcW1)) # 第15层:与4096个神经元全连接 fcW2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4096, 4096]), dtype=tf.float32, name='fcW2') fc2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(fc1, fcW2)) # 第16层:与1000个神经元全连接+softmax输出 fcW3 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4096, 1000]), dtype=tf.float32, name='fcW3') out = tf.matmul(fc2, fcW3) out=tf.nn.softmax(out) session = tf.Session() session.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) result = session.run(out, feed_dict={x: np.ones([1, 224, 224, 3], np.float32)}) # "打印最后的输出尺寸" print(np.shape(result))
|
论文中还讨论了其他结构 |
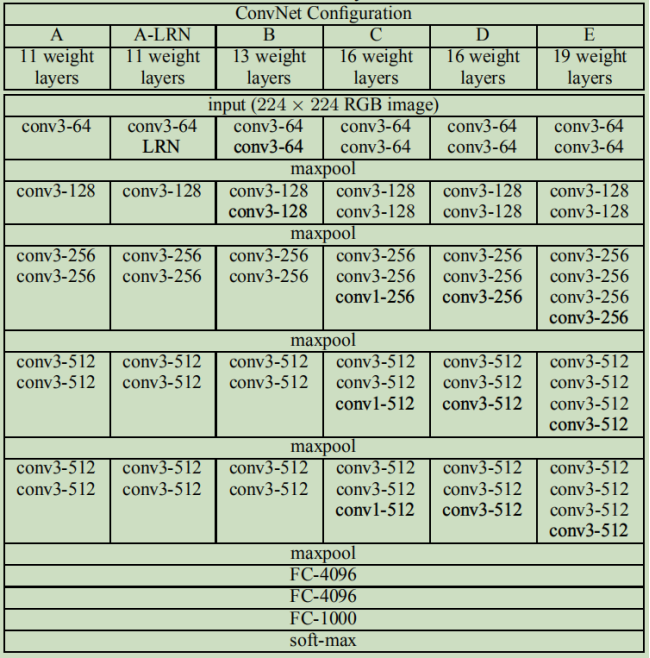
|
参考资料 |
吴恩达深度学习
VGGNet-Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition
《图解深度学习与神经网络:从张量到TensorFlow实现》_张平
《深-度-学-习-核-心-技-术-与-实-践》
大话CNN经典模型:VGGNet
https://my.oschina.net/u/876354/blog/1634322
