初始化IOC容器
Spring初始化的时候会优先初始化自定义的类,下面这个就是
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping#0
类的结构图
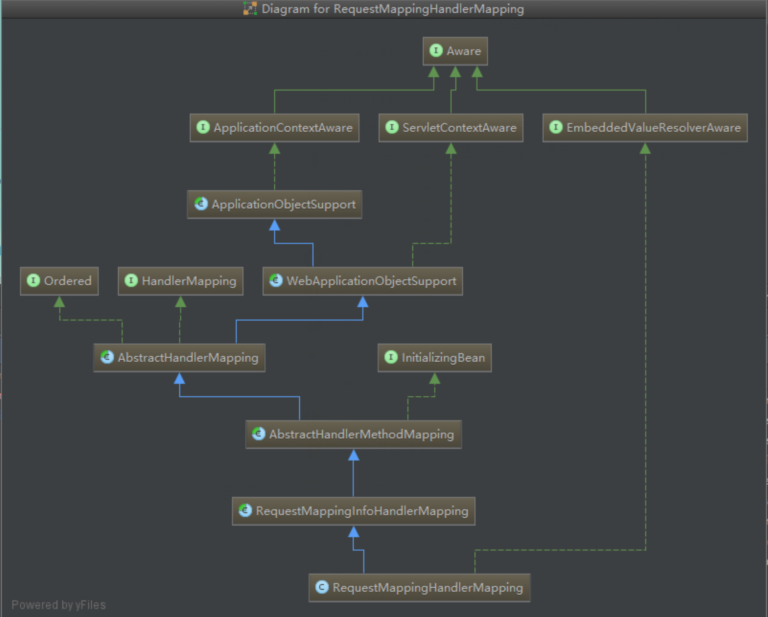
根据这个结构图可以发现,RequestMappingHandlerMapping这个功能还是非常强大的.毕竟注册路由这个功能还是需要依赖IOC容器的,所以它已经实现了ApplicationContextAware持有了上下文的对象.拥有了这个对象,就可以很方便的去容器中查找controller中的所有对象和方法了.
ioc 实例话这个类的时候 会经过一个 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory - invokeInitMethods 的方法, 这个方法会判断这个类是否实现InitializingBean这个类的方法,如果是则调用它的afterPropertiesSet方法。
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() throws Exception {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw pae.getException();
}
}
else {
// 调用这个初始化中接口的方法
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
}
if (mbd != null) {
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
if (initMethodName != null && !(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
}
}
这时候RequestMappingHandlerMapping类会委托给父类去处理这个afterPropertiesSet方法。
获取MVC中的ioc容器里面注册的对象,并且进行循环遍历
判断isHandler注册的对象中的类是否包含@Controller或者@RequestMapping等注解,满足则会对类的方法进行遍历
进行注册到AbstractHandlerMethodMapping中的handlerMethods、urlMap中,一个是以方法做为key[RequestMappingInfo],一个是以url作为key进行存储
注册完毕之后,前端发送过来的请求就会从urlMap这里面进行查找
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
// 父类又会交给一个initHandlerMethods处理
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
// 初始化方法处理
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking for request mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext());
}
// 查询父类是否有处理HandlerMethods方法的上下文,如果没有则获取MVC容器中的所有对象
String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) :
getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
// 遍历对象
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 类名前缀是否包含scopedTarget.
// isHandler 这个方法很关键
// 判断该类是否包含Controller或者RequestMapping注解
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX) &&
isHandler(getApplicationContext().getType(beanName))){
// 处理包含handle中的方法
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
// 注意这个类是在子类RequestMappingHandlerMapping中
@Override
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return ((AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) != null) ||
(AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class) != null));
}
/**
* Look for handler methods in a handler.
* @param handler the bean name of a handler or a handler instance
*/
protected void detectHandlerMethods(final Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType =
(handler instanceof String ? getApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
// Avoid repeated calls to getMappingForMethod which would rebuild RequestMappingInfo instances
final Map<Method, T> mappings = new IdentityHashMap<Method, T>();
final Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
// 查找该类中的所有和handler相关的方法
Set<Method> methods = HandlerMethodSelector.selectMethods(userType, new MethodFilter() {
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method) {
T mapping = getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
if (mapping != null) {
mappings.put(method, mapping);
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
});
// 把上面遍历出来的方法进行相应的注册
for (Method method : methods) {
registerHandlerMethod(handler, method, mappings.get(method));
}
}
// 这里是实际注册handler的方法,在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping中
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
// 创建一个HandlerMethod对象,并且HandlerMethod这个对象持有整个工厂的引用
HandlerMethod newHandlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
// 判断是否存在重复的handler,如果存在则报错
HandlerMethod oldHandlerMethod = this.handlerMethods.get(mapping);
if (oldHandlerMethod != null && !oldHandlerMethod.equals(newHandlerMethod)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous mapping found. Cannot map '" + newHandlerMethod.getBean() +
"' bean method
" + newHandlerMethod + "
to " + mapping + ": There is already '" +
oldHandlerMethod.getBean() + "' bean method
" + oldHandlerMethod + " mapped.");
}
// 不存在则将这个handle注册到handlerMethods中, 这里是根据方法的标识作为key
this.handlerMethods.put(mapping, newHandlerMethod);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Mapped "" + mapping + "" onto " + newHandlerMethod);
}
// 这里就是根据RequestMapping的value作为key进行存储 .. 也就url进行存储
Set<String> patterns = getMappingPathPatterns(mapping);
for (String pattern : patterns) {
if (!getPathMatcher().isPattern(pattern)) {
this.urlMap.add(pattern, mapping);
}
}
if (this.namingStrategy != null) {
String name = this.namingStrategy.getName(newHandlerMethod, mapping);
updateNameMap(name, newHandlerMethod);
}
}
调用过程
其实最终也会交给AbstractHandlerMethodMapping方法进行处理,因为上面注册的时候就已经把url注册到urlMap中了,不过有几点需要注意
1. 它的匹配规则
- 如果注册的时候是//urlPath , 但是你前端传递过来的时候是/urlPath, 这时候urlMap是匹配不到的,这时候它会从方法匹配中去查找,需要注意的是方法匹配需要遍历所有注册过的方法,相当于全局查找
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<Match>();
// 从urlMap注册中查找对应匹配的handler
List<T> directPathMatches = this.urlMap.get(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
// 如果查找不到,就从方法注册的map中进行遍历匹配
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
// No choice but to go through all mappings...
// 从方法为key的map中查找就涉及到一个优先级匹配的规则了
addMatchingMappings(this.handlerMethods.keySet(), matches, request);
}
// 如果取出来的匹配的url不为空,可能是1个或者多个的时候
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
// 获取一个比较器 , 注意这里的比较器最终的实现规则是在AntPatternComparator 类中, 这是一个内部类 -> AntPathMatcher
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
// 进行规则排序
Collections.sort(matches, comparator);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found " + matches.size() + " matching mapping(s) for [" + lookupPath + "] : " + matches);
}
// 获取上面排序之后的第一个,也就是优先级最高的
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
// 如果存在多个,则会将第二个和第一个进行比较 , 如果得到的优先级规则是相等的,则抛异常
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous handler methods mapped for HTTP path '" + request.getRequestURL() + "': {" +
m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
// 返回优先级最好的handler
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
}
else {
return handleNoMatch(handlerMethods.keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
这里会涉及到一个匹配规则,spring是如何做的呢?
addMatchingMappings这个里面会进行一个循环匹配所有URL
遍历的时候会得到这个key的RequestMappingInfo对象.RequestMappingInfo对象持有(PatternsRequestCondition对象)拥有匹配url的规则
PatternsRequestCondition对象又会交给AntPathMatcher , 这里的持有对象都是在初始化中如果没有指定Spring给你默认的,相当于实际匹配的规则都是在AntPathMatcher里面去操作的
AntPathMatcher操作思路:
1. 他定义了一个ConcurrentHashMap对象stringMatcherCache,key是url中的每一个/后面的对象
/a/b/{c} 它承装的就是三个对象 a、b、{c}都是它的key,value就是一个AntPathStringMatcher对象,这个对象会处理{c}这种情况,转化成对应的类似*这种正则匹配
2. 上层经过解析到达AntPathMatcher 对象时是url中的一段一段path,然后从stringMatcherCache去找有没有对应的AntPathStringMatcher,如果没有则实例化一个,然后根据这个进行match,匹配则返回true
整体的匹配思路:
前端传递一个: /a/b/c
程序会将这个url解析成3段去匹配 【a、b、c】
2.先拿a去AntPathMatcher的matchStrings方法去进行匹配,而AntPathMatcher会转交给AntPathStringMatcher,通过则返回true
这里会涉及到一个优先级的问题:
比如后端定义了3个url :
1. /a/b/{c}
2. /a/b/*
3. /a/b/**
这三个都满足上面的匹配条件,这时候Spring会要优先选取一个最好的handle去处理.
这里最终处理的是
AntPathMatcher的内部类AntPatternComparator实现了一个compare方法
/**
优先级排序规则
1. 需要注意的是返回 1 的 表示正序 -1 表示倒序
*/
protected static class AntPatternComparator implements Comparator<String> {
private final String path;
public AntPatternComparator(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
/**
* Compare two patterns to determine which should match first, i.e. which
* is the most specific regarding the current path.
* @return a negative integer, zero, or a positive integer as pattern1 is
* more specific, equally specific, or less specific than pattern2.
*/
@Override
public int compare(String pattern1, String pattern2) {
PatternInfo info1 = new PatternInfo(pattern1);
PatternInfo info2 = new PatternInfo(pattern2);
// 如果pattern1 > pattern2 则会将 pattern2 放在前面 (优先级较高), 反则不动
// 再通俗一点讲 1表示Info2的优先级上调 , -1表示 info1的优先级上调
// 如果是参数(pattern)里面是null 或者 是 /**
if (info1.isLeastSpecific() && info2.isLeastSpecific()) {
return 0;
}
// 优先级降低
else if (info1.isLeastSpecific()) {
return 1;
}
// 优先级上升
else if (info2.isLeastSpecific()) {
return -1;
}
// 具体匹配
boolean pattern1EqualsPath = pattern1.equals(path);
boolean pattern2EqualsPath = pattern2.equals(path);
if (pattern1EqualsPath && pattern2EqualsPath) {
return 0;
}
else if (pattern1EqualsPath) {
return -1;
}
else if (pattern2EqualsPath) {
return 1;
}
// 如果第一个前缀不是/**和后缀不是/**结尾
if (info1.isPrefixPattern() && info2.getDoubleWildcards() == 0) {
return 1;
}
else if (info2.isPrefixPattern() && info1.getDoubleWildcards() == 0) {
return -1;
}
// TotalCount=(包含"{"的次数) +("*出现的次数") + "("**出现的次数")"
if (info1.getTotalCount() != info2.getTotalCount()) {
return info1.getTotalCount() - info2.getTotalCount();
}
//"\{[^/]+?\}"替换后的长度
if (info1.getLength() != info2.getLength()) {
return info2.getLength() - info1.getLength();
}
//*次数比较
if (info1.getSingleWildcards() < info2.getSingleWildcards()) {
return -1;
}
else if (info2.getSingleWildcards() < info1.getSingleWildcards()) {
return 1;
}
// { 出现的次数
if (info1.getUriVars() < info2.getUriVars()) {
return -1;
}
else if (info2.getUriVars() < info1.getUriVars()) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
}
根据上面定义的优先级进行排序.之后会将优先级也就是list中的下标为0的作为最好的handle进行处理
总结
初始化逻辑:
1. 在IOC容器已经初始化容器的时候,会加载Spring的一个内置对象RequestMappingHandlerMapping,而这个对象又实现了InitializingBean方法.这时候就会触发afterPropertiesSet方法的调用
2. 而这个方法里面则是会对ioc容器中的所有对象进行遍历,找到类中包含@Controller或者@RequestMapping等注解的类
3. 将上面符合的类的方法进行遍历并且注册到Map中,这个map又分为一个url为key的map和方法对象为key的map
4. 这时候HandlerMethod已经初始化完成
调用逻辑:
1. 当前端发送一个url请求的时候,会被springMvc拦截到
2. 会根据当前的url进行handler匹配,第一个匹配是根据url进行全路径匹配,这个匹配容器封装在了一个叫UrlMap中,如果匹配到直接返回map中的handlerMethod对象
3. 如果上面没有匹配到,这时候会从一个封装方法的Map中去进行正则匹配,这里匹配是将所有的Controller中的路由方法进行匹配,这里会先将url按照/进行拆分成多个String进行全路径匹配,匹配到直接返回。
4. 如果匹配不到,则开始进行一系列的正则匹配..具体的匹配规则可以参考上面的AntPatternComparator类,这里会将正则匹配到的url进行一个排序,最前面的优先级最高.
5. 这里就会将优先级最高的进行反射调用
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/lkx444368875/article/details/78949631