笔记:Python3 Ansible
一、Ansible
Ansible特点:
不需要安装客户端,通过sshd去通信
基于模块工作,模块可以任何语言开发
不仅支持命令行使用模块,也支持编写yaml格式的playbook
支持sudo
有提供UI(浏览器图形化)www.ansible.com/tower 10台主机以内免费
开源UI https://github.com/alaxli/ansible_ni
文档 http://download.csdn.net/detail/liyang23456/7741185
Ansible安装:
两台机器 172.7.15.106 172.7.15.111
只需要在106机器上安装ansible即可
yum install –y epel-release
yum install –y ansible
Ansible配置密钥
106上操作,生成密钥
ssh-keygen –t rsa 直接回车即可,不用设置密钥密码
把公钥(id_rsa.pub)内容放到对方机器(111)的/root/.ssh/authorized_keys里面
scp .ssh/id_rsa.pub 172.7.15.111:/root/.ssh/authorized_keys
本机也要操作
cat /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> /root/.ssh/authorized_keys
106和111上操作
chmod 600 /root/.ssh/authorized_keys
关闭selinux和iptables,并保存
setenforce 0
iptables –F; /etc/init.d/iptables save
Ansible 更改配置文件
vim /etc/ansible/hosts //增加
[testhost]
127.0.0.1
172.7.15.111
说明: testhost为主机组名字,自定义的。下面两个IP为组内的机器IP
Ansible 远程执行命令
ansible testhost –m command –a ‘w’
这样就可以批量执行命令了。这里的testhost为主机组名,-m后边是模块名字,-a后面是命令。当然我们也可以直接写一个ip,针对某一台机器来执行命令。
ansible 127.0.0.1 –m command –a ‘hostname’
错误:”msg”: Aborting, target uses selinux but python bindings (libselinux-python) aren’t installed!”
解决: yum install –y libselinux-python
还有一个模块就是shell同样也可以实现
ansible testhost –m shell –a ‘w
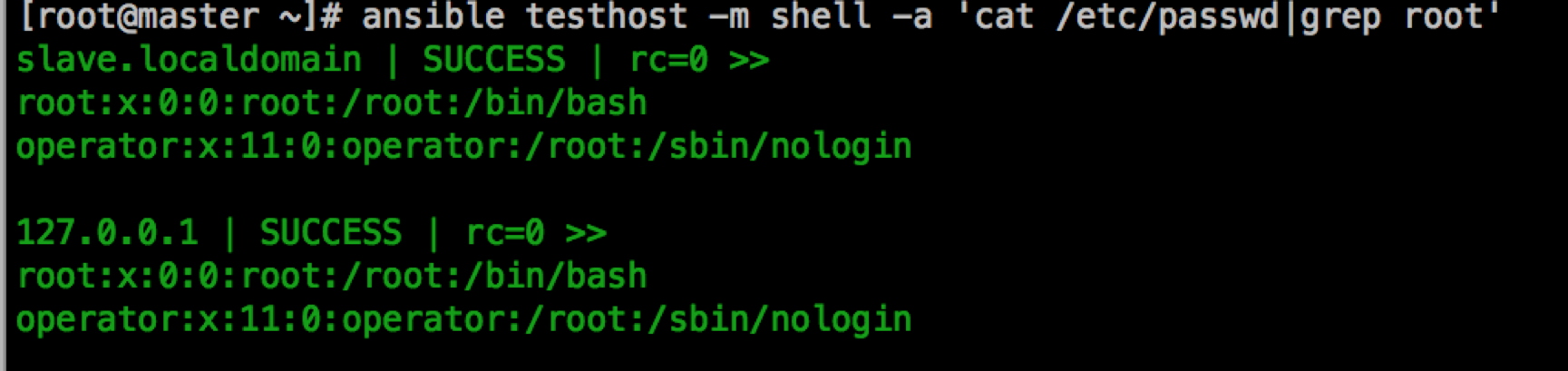
command模块不支持管道过滤,而shell模块支持管道过滤
command模块能实现的功能,shell模块也能实现,而shell模块能实现的功能,command模块不一定能实现
Ansible 拷贝文件或目录
ansible slave.localdomain -m copy -a "src=/etc/ansible dest=/tmp/ansibletest owner=root group=root mode=0755"
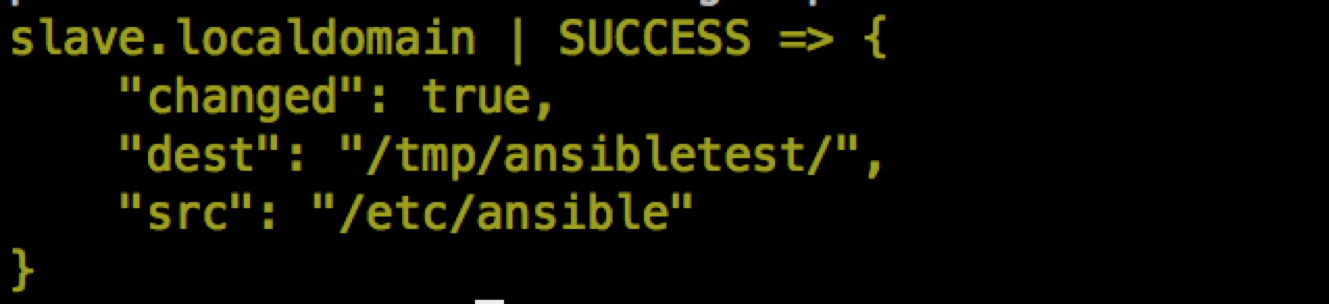


注意: 源目录会放到目标目录下面去,如果目标指定的目录不存在,它会自动创建。如果拷贝的是文件,dest指定的名字和源如果不同,并且它不是已经存在的目录,相当于拷贝过去后又重命名。但相反,如果dest是目标机器上已经存在的目录,则会直接把文件拷贝到该目录下面。
ansible slave.localdomain -m copy -a "src=/etc/passwd dest=/tmp/123"

这里的/tmp/123和源机器上的/etc/passwd是一致的,但如果目标机器上已经有/tmp/123目录,则会再/tmp/123目录下建立passwd文件
Ansible 远程执行脚本
首先创建一个shell脚本
vim /tmp/test.sh //加入以下内容
#!/bin/bash
echo `date` > /tmp/ansible_test.txt
然后把该脚本分发到各个机器上
ansible testhost -m copy -a "src=/tmp/test.sh dest=/tmp/test.sh mode=0755"
最后是批量执行该shell脚本
ansible testhost -m shell -a "/bin/sh /tmp/test.sh"

远程执行命令,查看shell脚本执行后输出的结果

shell模块,还支持远程执行命令并且带管道
ansible testhost -m shell -a "cat /etc/passwd |wc -l"
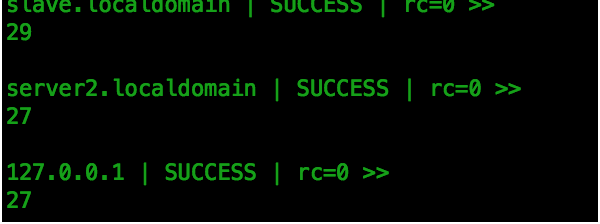
Ansible 实现任务计划
ansible testhost -m cron -a "name='test cron' job='/bin/touch /tmp/1212.txt' weekday=0"

若要删除该cron只需要加一个字段state=absent
ansible testhost -m cron -a "name='test cron' state=absent"

其他的时间表示:分钟minute 小时hour 日期day 月份month
Ansible 安装rpm包/管理服务
ansible server2.localdomain -m yum -a "name=httpd"
在name后面还可以加上state=installed
ansible server2.localdomain -m service -a "name=httpd state=started enabled=yes"

这里的name是centos系统里的服务名,可以通过chkconfig –list查看到。
Ansible文件的使用
ansible-doc –l 列出所有的模块
ansible-doc cron 查看指定的模块的文档
Ansible playbook的使用
相当于把模块写入到配置文件里面,例:
vim /etc/ansible/test.yml
---
- hosts: slave.localdomain //可以指定主机组testhost
remote_user: root
tasks:
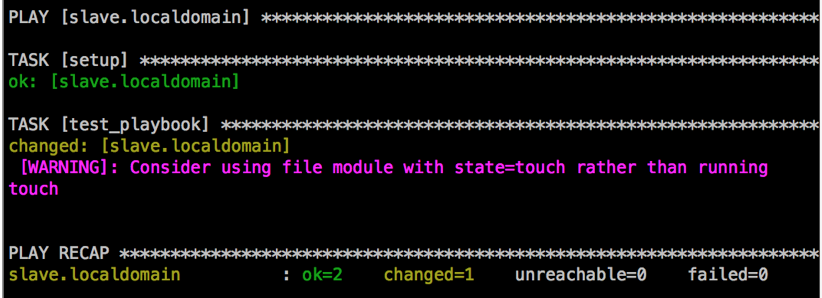
- name: test_playbook
shell: touch /tmp/lishiming.txt
说明: hosts参数指定了对哪些主机进行操作;
user参数指定了使用什么用户登录远程主机操作;
tasks指定了一个任务,其下面的name参数同样是对任务的描述,在执行过程中会打印出来。
执行: ansible-playbook test.yml
再来一个创建用户的例子:
vim /etc/ansible/create_user.yml
---
- name: create_user
hosts: slave.localdomain
user: root
gather_facts: false
vars:
- user: "test"
tasks:
- name: create user
user: name="{{user}}"
说明: name参数对该playbook实现的功能做一个概述,后面执行过程中,会打印name变量的值,可以省略;gather_facts参数指定了在以下任务部分执行前,是否先执行setup模块获取主机相关信息,这在后面的tasks会使用到setup获取的信息时用到;vars参数,指定了变量,这里指定一个user变量,其值为test,需要注意的是,变量值一定要用引号引住;user提定了调用user模块,name是user模块里的一个参数,而增加的用户名字调用了上面user变量的值。
ansible-playbook create_user.yml

Ansible playbook 中的循环
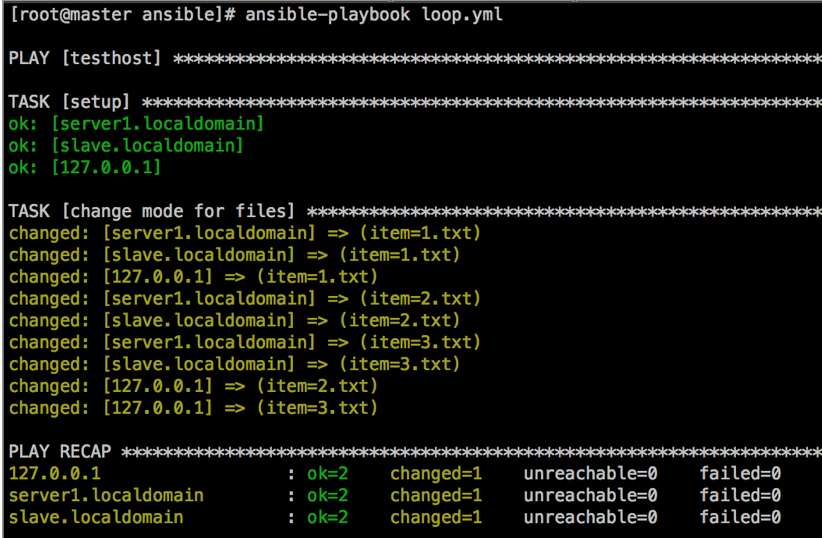
vim /etc/ansible/loop.yml
---
- hosts: testhost
user: root
tasks:
- name: change mode for files
file: path=/tmp/{{item}} mode=600 owner=root group=root
with_items:
- 1.txt
- 2.txt
- 3.txt
批量远程执行更改权限,注意:客户机要保证有1.txt,2.txt,3.txt文件存在
Ansible playbook条件判断
vim /etc/ansible/when.yml
---
- hosts: testhost
remote_user: root
gather_facts: True
tasks:
- name: use when
shell: touch /tmp/when.txt
when: facter_ipaddress == "10.211.55.15"

Ansible playbook 中的handlers
执行task之后,服务器发生变化之后要执行一些操作,比如我们修改了配置文件后,需要重启一下服务
vim /etc/ansible/handlers.yml
---
- hosts: testhost
name: handlers test
user: root
tasks:
- name: copy file
copy: src=/etc/passwd dest=/tmp/aaa.txt
notify: test handlers
handlers:
- name: test handlers
shell: echo "11111" >> /tmp/aaa.txt
说明: 只有copy模块真正执行后,才会去调用下面的handlers相关的操作。也就是说如果1.txt和2.txt内容是一样的,并不会去执行handlers里面的shell相关命令。这种比较适合配置文件发生更改后,重启服务的操作。

通过rsync将服务端上的passwd文件同步到客户端aaa.txt文件,目标文件aaa.txt与服务端的passwd文件内容是一致的

服务端执行ansible-playbook命令同步,客户端文件aaa.txt文件内容不会更改,因为task执行不成功,所以不会执行handlers下面的操作
