django rest framework用户认证
- 进入rest framework的Apiview
-
1 @classmethod 2 def as_view(cls, **initkwargs): 3 """ 4 Store the original class on the view function. 5 6 This allows us to discover information about the view when we do URL 7 reverse lookups. Used for breadcrumb generation. 8 """ 9 if isinstance(getattr(cls, 'queryset', None), models.query.QuerySet): 10 def force_evaluation(): 11 raise RuntimeError( 12 'Do not evaluate the `.queryset` attribute directly, ' 13 'as the result will be cached and reused between requests. ' 14 'Use `.all()` or call `.get_queryset()` instead.' 15 ) 16 cls.queryset._fetch_all = force_evaluation 17 18 view = super().as_view(**initkwargs) 19 view.cls = cls 20 view.initkwargs = initkwargs 21 22 # Note: session based authentication is explicitly CSRF validated, 23 # all other authentication is CSRF exempt. 24 return csrf_exempt(view)
django的类视图是调用内部的as_view方法来实现CBV,在第18行调用了父类的as_view,父类的as_view调用了dispatch方法,这里在ApiView自定义了dispatch
-
1 def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs): 2 """ 3 `.dispatch()` is pretty much the same as Django's regular dispatch, 4 but with extra hooks for startup, finalize, and exception handling. 5 """ 6 self.args = args 7 self.kwargs = kwargs 8 request = self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs) 9 self.request = request 10 self.headers = self.default_response_headers # deprecate? 11 12 try: 13 self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs) 14 15 # Get the appropriate handler method 16 if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names: 17 handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(), 18 self.http_method_not_allowed) 19 else: 20 handler = self.http_method_not_allowed 21 22 response = handler(request, *args, **kwargs) 23 24 except Exception as exc: 25 response = self.handle_exception(exc) 26 27 self.response = self.finalize_response(request, response, *args, **kwargs) 28 return self.response
和django的dispatch类似,第8,9行对request进行了封装
-
1 def initialize_request(self, request, *args, **kwargs): 2 """ 3 Returns the initial request object. 4 """ 5 parser_context = self.get_parser_context(request) 6 7 return Request( 8 request, 9 parsers=self.get_parsers(), 10 authenticators=self.get_authenticators(), 11 negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(), 12 parser_context=parser_context 13 )
封装函数内部返回的是Request对象
-
1 class Request: 2 """ 3 Wrapper allowing to enhance a standard `HttpRequest` instance. 4 5 Kwargs: 6 - request(HttpRequest). The original request instance. 7 - parsers_classes(list/tuple). The parsers to use for parsing the 8 request content. 9 - authentication_classes(list/tuple). The authentications used to try 10 authenticating the request's user. 11 """ 12 13 def __init__(self, request, parsers=None, authenticators=None, 14 negotiator=None, parser_context=None): 15 assert isinstance(request, HttpRequest), ( 16 'The `request` argument must be an instance of ' 17 '`django.http.HttpRequest`, not `{}.{}`.' 18 .format(request.__class__.__module__, request.__class__.__name__) 19 ) 20 21 self._request = request 22 self.parsers = parsers or () 23 self.authenticators = authenticators or () 24 self.negotiator = negotiator or self._default_negotiator() 25 self.parser_context = parser_context 26 self._data = Empty 27 self._files = Empty 28 self._full_data = Empty 29 self._content_type = Empty 30 self._stream = Empty 31 32 if self.parser_context is None: 33 self.parser_context = {} 34 self.parser_context['request'] = self 35 self.parser_context['encoding'] = request.encoding or settings.DEFAULT_CHARSET 36 37 force_user = getattr(request, '_force_auth_user', None) 38 force_token = getattr(request, '_force_auth_token', None) 39 if force_user is not None or force_token is not None: 40 forced_auth = ForcedAuthentication(force_user, force_token) 41 self.authenticators = (forced_auth,)
Request对象的初始化函数,它将原生django的request对象赋值给self._request,所以在ApiView视图中想使用原生的request要用request._request来使用
- 查看self.authenticators
- self.authenticators等于传进来的authenticators
- 在ApiView内部定义了get_authenticators方法,它会被authenticators来接受
1 def get_authenticators(self): 2 """ 3 Instantiates and returns the list of authenticators that this view can use. 4 """ 5 return [auth() for auth in self.authentication_classes]
这个方法回去self.authentication_classes里面找定义好的对象再将其实例化
- 定义自定义验证类
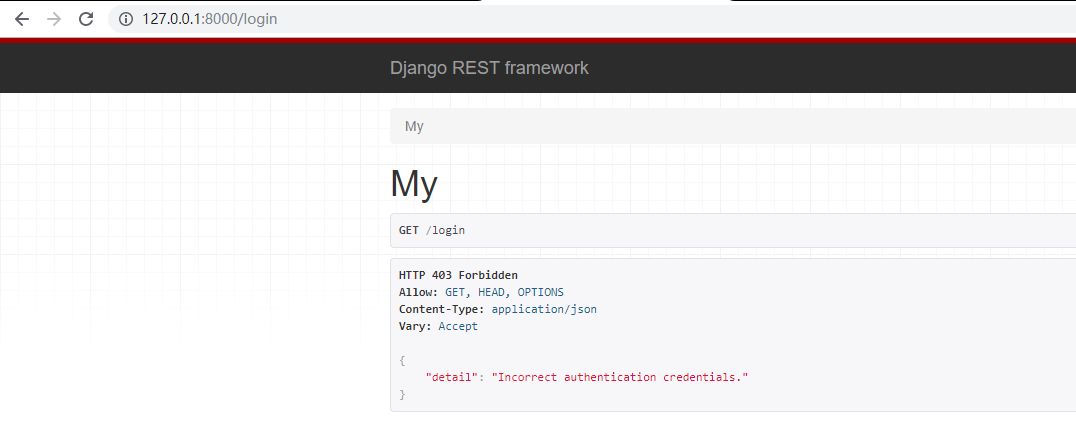
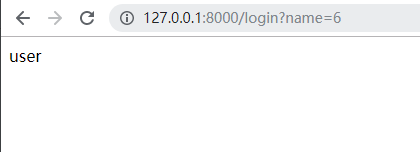
from rest_framework.views import APIView from django.http import HttpResponse from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed class MyAuthentication(BaseAuthentication): def authenticate(self, request): if not request._request.GET.get('name'): raise AuthenticationFailed return ('user', None) def authenticate_header(self, request): pass class MyView(APIView): authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication] def get(self, request):
user = request.user return HttpResponse(user)验证类继承BaseAuthentication(不继承也可以,但都要实现authenticate)方法,在authenticate里面实现用户的认证,最后返回一个元祖,第一个元素为user对象,该对象被request.user接受, 第二个元素会被request.auth捕捉
- 效果
-