案例子任务一、编写登录欢迎脚本welcome.sh
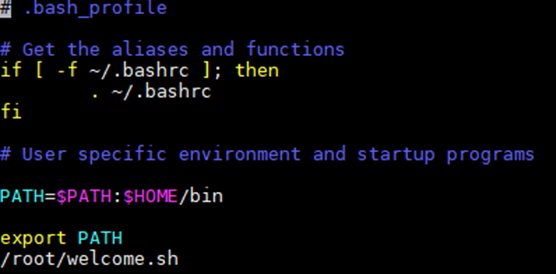
要求:在用户目录/root下编写存储welcome.sh脚本,赋予执行权限,并在~/.bash_profile中调用该脚本,使得在用户登录时显示欢迎信息
#!/bin/sh
#执行whoami命令获取当前登录用户名并保存到username中
username="$(whoami)"
#执行下面带有正则的嵌套语句获取当前登录的IP地址并保存到useip中
useip="$(ifconfig -a|grep -o -e 'inet
[0-9]{1,3}.[0-9]{1,3}.[0-9]{1,3}.[0-9]{1,3}'|grep -v "127.0.0"|awk '{print $2}')"
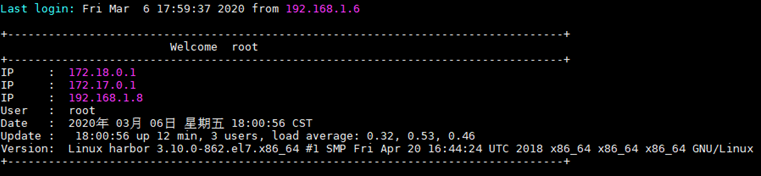
echo -e " "
echo -e "+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+"
echo -e " Welcome $username"
echo -e "+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+"
#由于得到的IP可能不唯一,要进行遍历显示
for i in $useip
do
echo -e "IP : $i"
done
#输出得出的用户名,日期,更新时间,版本信息
echo -e "User : $username"
echo -e "Date : "$(date)
echo -e "Update : "$(uptime)
echo -e "Version: "$(uname -a)
echo -e "+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+"
echo -e " "

案例子任务二 编写status、 start、stop脚本管理系统服务
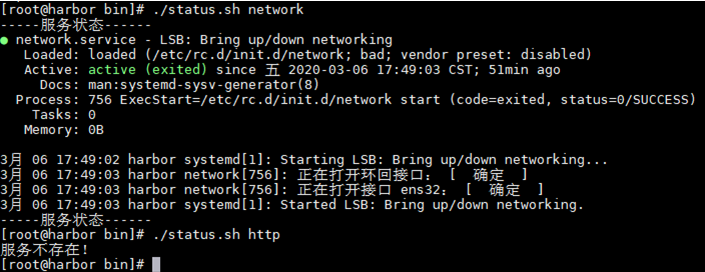
要求:在/root/bin目录下编写status、 start、stop脚本,可以根据脚本后面的服务名称分别显示服务状态、开启服务、停止服务
#!/bin/bash
#查看运行状态
#-f查看文件是否存在
if [ -f "/etc/init.d/$1" ]
then
echo "-----服务状态------"
systemctl status $1
echo "-----服务状态------"
else
echo "服务不存在!"
fi
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#!/bin/bash
#启动服务
#-f查看文件是否存在
if [ -f "/etc/init.d/$1" ]
then
echo "-----正在启动------"
systemctl start $1
echo "-----启动完成------"
else
echo "服务不存在!"
fi
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#!/bin/bash
#关闭服务
#-f查看文件是否存在
if [ -f "/etc/init.d/$1" ]
then
echo "-----正在关闭------"
systemctl stop $1
echo "-----关闭完成------"
else
echo "服务不存在!"
fi
This is end!