一、python打开文件
#=====================python 文件打开方式 open()===================== # open(fileName,type) type="r" 以只读方式打开文件 ,该文件必须存在 file_r=open("E:\python\hello.txt","r"); # open(fileName,type) type="w" #1、以只写方式打开文件 ,该文件如果不存在就创建文件 #2、如果该文件存在并且有内容,则会清空内容 file_w=open("E:\python\hello_w.txt","w"); # open(fileName,type) type="a" 以追加的方式打开文件 file_a=open("E:\python\hello_w.txt","a"); # open(fileName,type) type="r+" 或 type="w+" 以读写的方式打开文件 file_rr=open("E:\python\hello_w.txt","r+"); # open(fileName,type) type="a+" 以追加和读写的方式打开文件 file_aa=open("E:\python\hello_w.txt","a+");
二、python读取文件
#=====================python 文件读取方式 read()===================== # read() 读取全部 read(size) 读取指定数量的字符 def readTest(): file_r=open("E:\python\hello.txt","r"); str=file_r.read(); print(str); file_r.close(); #readline() 读取一行 readline(size) 读取一行中的size个字符(无论size是否大于一行的字符个数,总返回一行中的字符个数) def readLineTest(): file_r=open("E:\python\hello.txt","r"); str=file_r.readline(2); print(str); file_r.close(); # readLines() 读取全部文件(io.DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE),返回每一行所组成的列表(如果文件很大会很占用内存空间) def readLinesTest(): file_r=open("E:\python\hello.txt","r"); str=file_r.readlines(18); print(str); file_r.close(); #iter: 使用迭代器读取文件 def IterTest(): file_r=open("E:\python\hello.txt","r"); iter_f=iter(file_r);#将文件转为迭代器, lines=0; for line in iter_f: print(line); lines+=1; print(lines); file_r.close();
三、python写入文件
在介绍文件写入时,先了解一个文件缓存区的概念。
cpu在操作物理内存中的数据(读写)速度是很耗时的,我们的计算机为了提高运行效率,我们的计算机cup内核会对数据参数一个高速缓存区,cup会先操作高速缓存区中的数据,然会在某一时刻将高速缓存区中的数据写入到物理内存中。
所以在文件写入时我们不得不提两个方法 close() 与flush();
#=====================文件关闭 close()====================
# 将缓存数据写入磁盘
# 在linux系统中每个进程打开文件的个数是有限的(如果超过该限度,再打开文件就会失败)所以在每次使用完文件后一定要关闭该文件
#===================== flush()====================
# 将缓存数据写入磁盘
关于cpu缓存代码演示:
创建一个空文件hello.txt
def writerTest(): file=open("E:\python\hello.txt","w"); file.write("hello Word");
结果:hello.txt 还是为空
使用:close()会flush()方法
def writerTest(): file=open("E:\python\hello.txt","w"); #将数据写入磁盘文件中,但一般我们的cup会有一个文件缓存区,数据一般会先写入cpu的文件缓存区中。 #如果写入字符的数据量大于或等于cpu的文件缓存区大小,那cpu会将该数据自动写入到次磁盘文件中,剩余的字符我们还是需要 #调用flush() 或 close() 方法才能将数据全部写入磁盘文件中。 file.write("hello Word"); #调用flush() 告诉cpu将文件缓存区中的数据写入磁盘文件中,或者直接调用 close()f方法 file.flush(); file.close();
结果:打开hello.txt 内容为 hello Word
writerLines(str):写多行到文件
def writerLinesTest(): file=open("E:\python\hello.txt","w"); file.writelines("hello Word"); file.writelines(("hello_1","hello_2","hello_3")); file.writelines(["hello_4","hello_5","hello_6"]); file.close();
四、文件指针
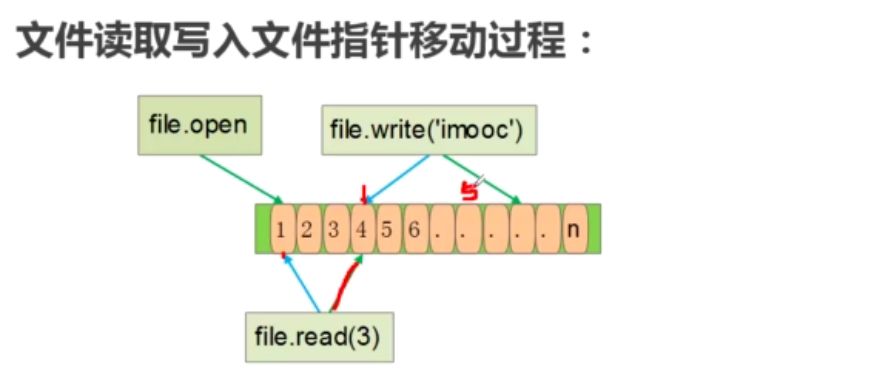
#===================文件指针===================
#文件读写的问题
#写入文件后,必须打开才能读取写入的内容;读取文件后,无法重新再次读取读过的内容
#文件读取原理
#python在进行文件读取过程中,会产生一个文件指针,该指针会记录当前文件被读取的位置。
#如何操作文件指针
#seek(offert,whence):移动文件指针 offset:偏移量可以为负数。whence:偏移相对位置
#os.SEEK_SET:相对文件起始位置
#os.SEEK_CUR:相对文件当前位置
#os.SEEK_END:相对文件结尾位置
#如果文件指针的偏移量大于文件字符个数程序将报错
import os; def seekTest(): file=open("E:\python\hello.txt","r+"); str=file.read(3);#读取三个字符 print(str); index=file.tell();#获取当前文件指针的位置 print(index);# 3 #需求:将文件指针移动到起始位置 file.seek(0,os.SEEK_SET); index=file.tell(); print(index);#0 #需求:将文件指针移动到结尾位置 file.seek(0,os.SEEK_END); index=file.tell(); print(index);#9 file.close();
注意:
Python3不允许非二进制打开的文件,相对于文件末尾的定位,这是文档的原文:
In text files (those opened without a b in the mode
string), only seeks relative to the beginning of the file are allowed
(the exception being seeking to the very file end with seek(0, 2)).(https://docs.python.org/3.2/tutorial/inputoutput.html#methods-of-file-objects)