数据流之画板数据保存成文件
首先介绍一下有关于数据流的一些小常识:
1.数据流是针对Java的8种基本数据类型的读写操作。
8种基本数据类型:
整数:byte,short,int,long
浮点型:float,double
字符型:char
布尔型:boolean
2.数据流的输入输出举例:
public class DataDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { DataDemo dd=new DataDemo(); Boolean flag=dd.writeData("src/DataIO0826/DataDemo.txt"); if(flag) System.out.println("写入数据成功"); else System.out.println("写入数据失败"); flag=dd.redaData("src/DataIO0826/DataDemo.txt"); if(flag) System.out.println("读取数据成功"); else System.out.println("读取数据失败"); } /** * @param path要写入数据的文件全路径 * @return 返回true表示写入成功;返回false表示写入失败 */ public Boolean writeData(String path) { OutputStream os=null;// 输出流 DataOutputStream ts=null;// 数据输出流 Boolean flag=false; try { // 根据路径实例化一个输出流 os = new FileOutputStream(path); // 根据os实例化一个数据输出流 ts = new DataOutputStream(os); /* * 向文件中写入数据。有8种基本数据类型的读写操作。 整数:byte,short,int,long * 浮点型:float,double * 字符型:char * 布尔型:boolean */ try { ts.writeBoolean(true);//写入布尔型数据 ts.writeByte(1000);//写入字节型数据 ts.writeInt(100);//写入整型数据 ts.writeLong(10000);//写入长整型数据 ts.writeShort(10); ts.writeDouble(15.63); ts.writeFloat(15.0f); ts.writeChar('d'); ts.writeUTF("王文雅 is reading!"); /* //ts.writeChars("wenya"); String str = "王文雅 is reading book!"; byte [] a = str.getBytes(); /* * writeInt:Writes the specified 32-bit int in big-endian order * 表示:写到指定的32位整数在高位优先顺序 */ /* ts.writeInt(a.length); //遍历数组,然后一个一个输出来 for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++){ ts.writeByte(a[i]); }*/ flag=true; } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if (os != null) os.close(); if (ts != null) ts.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return flag; } /** * @param path要读取数据的文件全路径 * @return 返回true表示读取成功;返回false表示读取失败 */ public Boolean redaData(String path) { InputStream is=null;// 输出流 DataInputStream ti=null;// 数据输出流 Boolean flag=false; try { // 根据路径实例化一个输出流 is = new FileInputStream(path); // 根据os实例化一个数据输出流 ti = new DataInputStream(is); /* * 读取文件中的疏浚。有8种基本数据类型的读写操作。 整数:byte,short,int,long * 浮点型:float,double * 字符型:char * 布尔型:boolean */ try { Boolean b =ti.readBoolean(); System.out.println(b); byte by=ti.readByte(); /* * 这里读取的结果是:-24。因为一个字节的大小是 8位 ,范围是: -128 - 127 * 256*3=768,1000-768=232;232-256=-24. */ System.out.println(by); int in=ti.readInt(); System.out.println(in); long l=ti.readLong(); System.out.println(l); short s=ti.readShort(); System.out.println(s); double d=ti.readDouble(); System.out.println(d); Float f=ti.readFloat(); System.out.println(f); char c=ti.readChar(); System.out.println(c); String li=ti.readUTF();//第三种方法 System.out.println(li); flag=true; // String li=ti.readLine(); // System.out.println(li); /* * 输出的结果是: w e n y a .每一个字符前面都有空格。 * 因为一个字符的存储是两个字节,一个字母是一个字节,然后,一个字节中是从地位到高位, * 所以每一个字符前面都有空格。 */ /* int size = ti.readInt();//获得有字符串的大小 byte [] a = new byte[size]; for(int k=0;k<a.length;k++) { a[k] = ti.readByte(); } String str = new String(a); System.out.println(str);*/ } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if (is != null) is.close(); if (ti != null) ti.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return flag; } }
3.注意的bug:
如果用ts.writeChars("wenya");的方式写入字符串数据,用String li=ti.readLine(); System.out.println(li);的方式读取字符串数据,结果将会是:
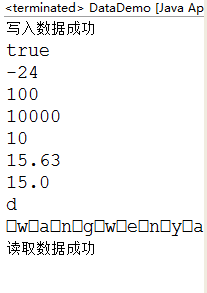
原因是:
因为一个字符的存储是两个字节,一个字母是一个字节,然后,一个字节中是从低位到高位, 所以每一个字符前面都有空格。
4.解决的办法有两个:
1.把字符一个一个输出来:
String str = "王文雅 is reading book!";
byte [] a = str.getBytes();
ts.writeInt(a.length); for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++){ ts.writeByte(a[i]); }
2.用ts.writeUTF("王文雅 is reading!");这种方法,一步到位。
同时我们要注意到字符型数据的输出是:-24,原因是:
这里读取的结果是:-24。因为一个字节的大小是 8位 ,范围是: -128 - 127 ;256*3=768,1000-768=232;232-256=-24.
附带一张8种数据类型的范围表:

接下来是数据流的应用:把画图板所有的画图用数据流存储起来,相当于保存的作用。
在通信的自定义通信协议上,数据流的也是必须要用到的。
今天主要讲的是用数据流把画板数据保存成文件。