前言:本文解决的问题
- java中的线程有哪些状态
- 这些状态怎么转换
1 Java中线程的状态
在任何时候JAVA中的线程总处于以下Thread.State枚举类6种状态中的一种:
- New,任何线程被新建后就处于该状态
- Runnable , 当调用start()方法后线程的状态
- Waiting,等待另一个线程执行动作,比如当前线程调用join(),另一线程的状态
- Timed-waiting,正在等待另一个线程执行动作达到指定等待时间的线程处于此状态;比如某一线程调用sleep();
- Termanated,已经退出的线程的状态
注意
线程处于Runnable状态,并不一定是正在运行,而是取决于线程调度器。
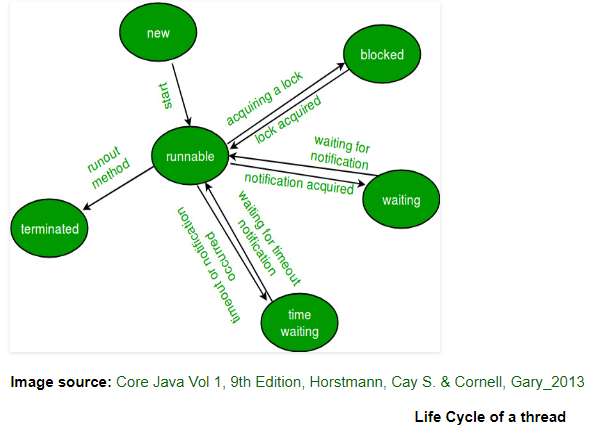
2 状态转换
2.1 NEW
新建一个线程还没执行时,线程就处于NEW状态
obj = new ThreadStateTest();
thread1 = new Thread(obj); //使用new 新建
对应的枚举类为——public static final Thread.State NEW
2.2 RUNNABLE
thread1.start();
当启动star()方法后线程处于该状态——public static final Thread.State RUNNABLE
2.3 BLOCKED
线程A和线程B都需要持有lock对象的锁才能调用方法。如果A持有锁,那么线程B处于BLOCKED;如果线程B持有锁,那么线程A处于public static final Thread.State BLOCKED状态。
2.4 WAITING
thread2.join();
Object的wait方法、Thread的join方法(都是没有时间参数的)和LockSupport.park 都会产生 public static final Thread.State WAITING状态。处于该状态的线程,正在等待另一线程执行特定的操作;比如wait()等待别的线程唤醒,join()等待调用该方法的线程结束。
2.5 TIMED-WAITING
Thread.sleep(200);
和上一状态类似,是一个有等待时间的等待状态public static final Thread.State TIMED_WAITING, 线程处于定时等待状态,不会一直等下去。
2.6 TERMINATED
线程运行结束后(因为run方法正常退出而自然死亡;由于没有捕获的异常终止了run方法而导致不正常死亡),就处于该状态public static final Thread.State TERMINATED。
状态转移总结
从NEW变为RUNNABLE,调用start()方法;当线程处于RUNNABLE,如果没有获得必须的锁,则被阻塞,进入BLOCKED状态;在BLOCKED状态的线程获得锁后变为RUNNABLE;处于RUNNABLE状态的线程当调用sleep(1000)方法时进入TIMED-WAITING状态;当某一线程调用join()方法时,另一线程处于WAITING状态;当线程正常运行结束后处于TERMINATED状态。下面看完整的代码。
3 例子分析
class thread implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1500);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1500);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("State of thread1 while it called join on thread2 -"+
ThreadStateTest.thread1.getState());
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class ThreadStateTest implements Runnable{
public static Thread thread1;
public static ThreadStateTest obj;
public static void main(String[] args) {
obj = new ThreadStateTest();
thread1 = new Thread(obj);
System.out.println("State of thread1 after creating it - "+ thread1.getState());
thread1.start();
System.out.println("State of thread1 after calling .start method on it -"+ thread1.getState());
}
@Override
public void run() {
thread myThread = new thread();
Thread thread2 = new Thread(myThread);
//thread1 created and is currently in the NEW state
System.out.println("State of thread2 after creating it - "+ thread2.getState());
thread2.start();
System.out.println("State of thread2 after calling .start() - "+ thread2.getState());
//moving thread1 to timed waiting state
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
}catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("State of thread2 after calling .sleep method on it - "+thread2.getState());
try {//waiting thread2 to die
thread2.join();
}catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("State of thread 2 when it has finished it's execution - "+ thread2.getState());
}
}
执行结果
State of thread1 after creating it - NEW
State of thread1 after calling .start method on it -RUNNABLE
State of thread2 after creating it - NEW
State of thread2 after calling .start() - RUNNABLE
State of thread2 after calling .sleep method on it - TIMED_WAITING
State of thread1 while it called join on thread2 -WAITING
State of thread 2 when it has finished it's execution - TERMINATED
结果分析
当一个线程新建时,处于NEW状态;当调用.start()后,线程调度器把它变成RUNNABLE状态。当thread2调用.join()方法时,当前正在执行这个命令的线程thread1将会等待thread2灭亡(die),因此thread1的状态时WAITING。
Whenever join() method is called on a thread instance, the current thread executing that statement will wait for this thread to move to Terminataed state.
参考网站
https://fangjian0423.github.io/2016/06/04/java-thread-state/
https://www.journaldev.com/1044/thread-life-cycle-in-java-thread-states-in-java
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/lifecycle-states-of-a-thread-in-java/