转载请注明出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/wenjunwei/p/10779450.html
spring基于注解的缓存
对于缓存声明,spring的缓存提供了一组java注解:
- @Cacheable:触发缓存写入。
- @CacheEvict:触发缓存清除。
- @CachePut:更新缓存(不会影响到方法的运行)。
- @Caching:重新组合要应用于方法的多个缓存操作。
- @CacheConfig:设置类级别上共享的一些常见缓存设置。
@Cacheable注解
顾名思义,@Cacheable可以用来进行缓存的写入,将结果存储在缓存中,以便于在后续调用的时候可以直接返回缓存中的值,而不必再执行实际的方法。 最简单的使用方式,注解名称=缓存名称,使用例子如下:
@Cacheable("books")
public Book findBook(ISBN isbn) {...}
一个方法可以对应两个缓存名称,如下:
@Cacheable({"books", "isbns"})
public Book findBook(ISBN isbn) {...}
@Cacheable的缓存名称是可以配置动态参数的,比如选择传入的参数,如下: (以下示例是使用SpEL声明,如果您不熟悉SpEL,可以阅读Spring Expression Language)
@Cacheable(cacheNames="books", key="#isbn")
public Book findBook(ISBN isbn, boolean checkWarehouse, boolean includeUsed)
@Cacheable(cacheNames="books", key="#isbn.rawNumber")
public Book findBook(ISBN isbn, boolean checkWarehouse, boolean includeUsed)
@Cacheable(cacheNames="books", key="T(someType).hash(#isbn)")
public Book findBook(ISBN isbn, boolean checkWarehouse, boolean includeUsed)
@Cacheable还可以设置根据条件判断是否需要缓存
- condition:取决于给定的参数是否满足条件
- unless:取决于返回值是否满足条件
以下是一个简单的例子:
@Cacheable(cacheNames="book", condition="#name.length() < 32")
public Book findBook(String name)
@Cacheable(cacheNames="book", condition="#name.length() < 32", unless="#result.hardback")
public Book findBook(String name)
@Cacheable还可以设置:keyGenerator(指定key自动生成方法),cacheManager(指定使用的缓存管理),cacheResolver(指定使用缓存的解析器)等,这些参数比较适合全局设置,这里就不多做介绍了。
@CachePut注解
@CachePut:当需要更新缓存而不干扰方法的运行时 ,可以使用该注解。也就是说,始终执行该方法,并将结果放入缓存,注解参数与@Cacheable相同。 以下是一个简单的例子:
@CachePut(cacheNames="book", key="#isbn")
public Book updateBook(ISBN isbn, BookDescriptor descriptor)
通常强烈建议不要对同一方法同时使用@CachePut和@Cacheable注解,因为它们具有不同的行为。可能会产生不可思议的BUG哦。
@CacheEvict注解
@CacheEvict:删除缓存的注解,这对删除旧的数据和无用的数据是非常有用的。这里还多了一个参数(allEntries),设置allEntries=true时,可以对整个条目进行批量删除。 以下是个简单的例子:
@CacheEvict(cacheNames="books")
public void loadBooks(InputStream batch)
//对cacheNames进行批量删除
@CacheEvict(cacheNames="books", allEntries=true)
public void loadBooks(InputStream batch)
@Caching注解
@Caching:在使用缓存的时候,有可能会同时进行更新和删除,会出现同时使用多个注解的情况.而@Caching可以实现。 以下是个简单的例子:
@Caching(evict = { @CacheEvict("primary"), @CacheEvict(cacheNames="secondary", key="#p0") })
public Book importBooks(String deposit, Date date)
@CacheConfig注解
@CacheConfig:缓存提供了许多的注解选项,但是有一些公用的操作,我们可以使用@CacheConfig在类上进行全局设置。 以下是个简单的例子:
@CacheConfig("books")
public class BookRepositoryImpl implements BookRepository {
@Cacheable
public Book findBook(ISBN isbn) {...}
}
可以共享缓存名称,统一配置KeyGenerator,CacheManager,CacheResolver。
实例
来看看我们在springboot中怎么使用redis来作为缓存吧.
为spring cache配置redis作为缓存
1.在pom.xml引入redis依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.springboot集成redis配置文件(在本地启动的redis),在springboot中使用redis,只要配置文件写有redis配置,代码就可以直接使用了。
spring:
redis:
database: 0 # Database index used by the connection factory.
url: redis://user:@127.0.0.1:6379 # Connection URL. Overrides host, port, and password. User is ignored. Example: redis://user:password@example.com:6379
host: 127.0.0.1 # Redis server host.
password: # Login password of the redis server.
port: 6379 # Redis server port.
ssl: false # Whether to enable SSL support.
timeout: 5000 # Connection timeout.
3.redis缓存配置类CacheConfig,这里对spring的缓存进行了配置,包括KeyGenerator,CacheResolver,CacheErrorHandler,CacheManager,还有redis序列化方式。
/**
* @author wwj
*/
@Configuration
public class CacheConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
@Resource
private RedisConnectionFactory factory;
/**
* 自定义生成redis-key
*
* @return
*/
@Override
@Bean
public KeyGenerator keyGenerator() {
return (o, method, objects) -> {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(o.getClass().getName()).append(".");
sb.append(method.getName()).append(".");
for (Object obj : objects) {
sb.append(obj.toString());
}
System.out.println("keyGenerator=" + sb.toString());
return sb.toString();
};
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate() {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(factory);
GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer genericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer();
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(genericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(genericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(genericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return redisTemplate;
}
@Bean
@Override
public CacheResolver cacheResolver() {
return new SimpleCacheResolver(cacheManager());
}
@Bean
@Override
public CacheErrorHandler errorHandler() {
// 用于捕获从Cache中进行CRUD时的异常的回调处理器。
return new SimpleCacheErrorHandler();
}
@Bean
@Override
public CacheManager cacheManager() {
RedisCacheConfiguration cacheConfiguration =
defaultCacheConfig()
.disableCachingNullValues()
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()));
return RedisCacheManager.builder(factory).cacheDefaults(cacheConfiguration).build();
}
}
代码使用
测试@Cacheable方法
@Test
public void findUserTest() {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.println("第" + i + "次");
User user = userService.findUser();
System.out.println(user);
}
}
@Override
@Cacheable(value = {"valueName", "valueName2"}, key = "'keyName1'")
public User findUser() {
System.out.println("执行方法...");
return new User("id1", "张三", "深圳", "1234567", 18);
}
执行结果
只有一次输出了'执行方法...',后面直接从缓存获取,不会再进入方法。
第0次
执行方法...
User{id='id1', name='张三', address='深圳', tel='1234567', age=18}
第1次
User{id='id1', name='张三', address='深圳', tel='1234567', age=18}
第2次
User{id='id1', name='张三', address='深圳', tel='1234567', age=18}
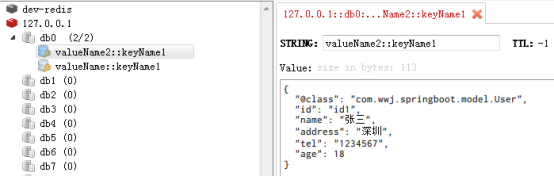
测试@CachePut方法:对缓存进行了修改
@Test
public void updateUserTest() {
userService.updateUser();
User user = userService.findUser();
System.out.println(user);
}
@Override
@CachePut(value = "valueName", key = "'keyName1'")
public User updateUser() {
System.out.println("更新用户...");
return new User("id1", "李四", "北京", "1234567", 18);
}
执行结果
对缓存进行了更新,获取值的时候取了新的值
更新用户...
User{id='id1', name='李四', address='北京', tel='1234567', age=18}

测试@CacheEvict方法:缓存被清空,再次findUser的时候又重新执行了方法。
@Test
public void clearUserTest() {
userService.clearUser();
User user = userService.findUser();
System.out.println(user);
}
@Override
@CacheEvict(value = "valueName",allEntries = true)
public void clearUser() {
System.out.println("清除缓存...");
}
执行结果
这里清除了缓存,为什么还是没有执行方法呢?因为这个方法我们定了两个value值,清了一个还有一个
清除缓存...
User{id='id1', name='张三', address='深圳', tel='1234567', age=18}

最后贴一下代码吧
User.java
package com.wwj.springboot.model;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @author wwj
*/
public class User implements Serializable {
public User() {
}
private String id;
private String name;
private String address;
private String tel;
private Integer age;
//省略get,set,tostring
}
CacheTest.java
package com.wwj.springboot.cache;
import com.wwj.springboot.model.User;
import com.wwj.springboot.service.UserService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* @author wwj
*/
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@EnableCaching
public class CacheTest {
@Resource
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void findUserTest() {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.println("第" + i + "次");
User user = userService.findUser();
System.out.println(user);
}
}
@Test
public void updateUserTest() {
userService.updateUser();
User user = userService.findUser();
System.out.println(user);
}
@Test
public void clearUserTest() {
userService.clearUser();
User user = userService.findUser();
System.out.println(user);
}
}
UserService.java
package com.wwj.springboot.service;
import com.wwj.springboot.model.User;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author wwj
*/
public interface UserService {
/**
* 获取用户
* @return user
*/
User findUser();
/**
* 更新用户信息
* @return user
*/
User updateUser();
/**
* 清除缓存的用户信息
*/
void clearUser();
}
UserServiceImpl.java
package com.wwj.springboot.service.impl;
import com.wwj.springboot.model.User;
import com.wwj.springboot.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheConfig;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author wwj
*/
@Service
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "CacheConfigName")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
@Cacheable(value = {"valueName", "valueName2"}, key = "'keyName1'")
public User findUser() {
System.out.println("执行方法...");
return new User("id1", "张三", "深圳", "1234567", 18);
}
@Override
@CachePut(value = "valueName", key = "'keyName1'")
public User updateUser() {
System.out.println("更新用户...");
return new User("id1", "李四", "北京", "1234567", 18);
}
@Override
@CacheEvict(value = "valueName",allEntries = true)
public void clearUser() {
System.out.println("清除缓存...");
}
}
本文欢迎各位转载,但是转载文章之后必须在文章开头给出原文链接。感谢您的阅读,如果您觉得阅读本文对您有帮助,请点个“推荐”支持一下。