中介者模式
定义:用一个中介对象来封装一系列的对象交互,中介者使各对象不需要显式的相互引用,从而使耦合松散,而且可以独立的改变他们之间的交互。
使用场景:多个类相互耦合,形成了网状结构。比如想租房,不用和每个房东联系,而是跟一个中介联系就行。

缺点:中介者模式把多个对象之间的相互依赖改成了中介和多个房东对象的依赖,如果房东对象太多,中介者就会变得臃肿,难以维护。
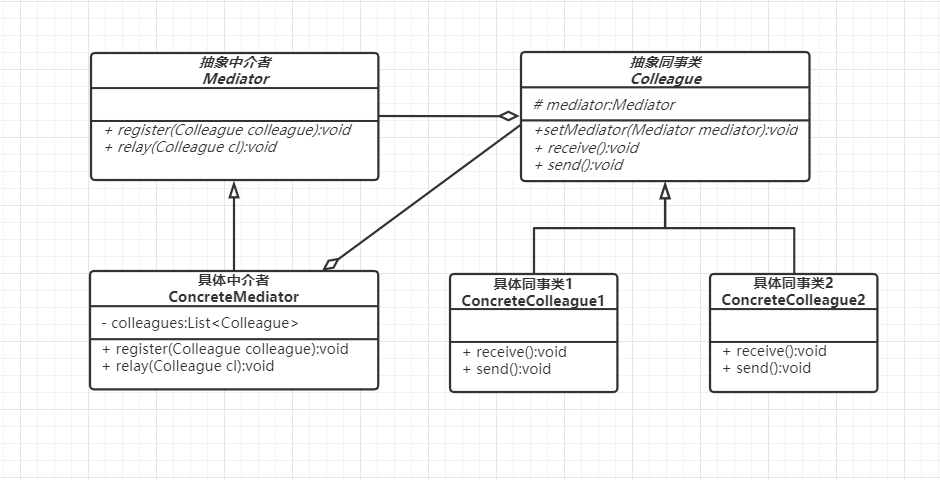
优点:
- 避免多个同事类之间的过度耦合。
- 可以将对象间一对多的关联关系转为一对一的关联关系
一般只有同事类的关系混乱不堪时才引用中介者模式
代码示例:模拟用户在聊天室发发消息,聊天室就是作为一个中介的存在。
/**
* 抽象中介类
*/
public abstract class Mediator {
public abstract void register(Colleague colleague);
public abstract void relay(Colleague colleague);
}
/**
* 中介类
*/
public class ConcreteMediator extends Mediator {
private List<Colleague> colleagues=new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public void register(Colleague colleague) {
if(!colleagues.contains(colleague)){
colleague.setMediator(this);
colleagues.add(colleague);
}
}
@Override
public void relay(Colleague colleague) {
colleagues.forEach(c->{
if(!c.equals(colleague)){
c.receive();
}
});
}
}
public abstract class Colleague {
protected Mediator mediator;
public abstract void receive();
public abstract void send();
public void setMediator(Mediator mediator) {
this.mediator = mediator;
}
}
public class User1 extends Colleague {
@Override
public void receive() {
System.out.println("用户1接收到消息");
}
@Override
public void send() {
System.out.println("用户1发送消息");
//中介转发
this.mediator.relay(this);
}
}
public class User2 extends Colleague {
@Override
public void receive() {
System.out.println("用户2接收到消息");
}
@Override
public void send() {
System.out.println("用户2发送消息");
//中介转发
this.mediator.relay(this);
}
}
public class User3 extends Colleague {
@Override
public void receive() {
System.out.println("用户3接收到消息");
}
@Override
public void send() {
System.out.println("用户3发送消息");
//中介转发
this.mediator.relay(this);
}
}
模式的扩展
在实际开发中,通常采用以下两种方法简化中介模式。
- 不定义中介接口,把具体的中介对象实现为单例
- 同事对象不持有中介类,需要的时候直接获取中介者对象并调用。

用简化后的模式改写上面的代码示例:
public class SimpleMediator {
private static final SimpleMediator smd=new SimpleMediator();
private List<Colleague> colleagues=new ArrayList<>();
private SimpleMediator(){}
public static SimpleMediator getInstance(){
return smd;
}
public void register(Colleague colleague){
if(!colleagues.contains(colleague)){
colleagues.add(colleague);
}
}
public void relay(Colleague colleague) {
colleagues.forEach(c->{
if(!c.equals(colleague)){
c.receive();
}
});
}
}
public abstract class Colleague {
public abstract void receive();
public abstract void send();
}
public class User1 extends Colleague {
public User1(){
SimpleMediator.getInstance().register(this);
}
@Override
public void receive() {
System.out.println("用户1接收到消息");
}
@Override
public void send() {
System.out.println("用户1发送消息");
//中介转发
SimpleMediator.getInstance().relay(this);
}
}
public class User2 extends Colleague {
public User2(){
SimpleMediator.getInstance().register(this);
}
@Override
public void receive() {
System.out.println("用户2接收到消息");
}
@Override
public void send() {
System.out.println("用户2发送消息");
//中介转发
SimpleMediator.getInstance().relay(this);
}
}
public class User3 extends Colleague {
public User3(){
SimpleMediator.getInstance().register(this);
}
@Override
public void receive() {
System.out.println("用户3接收到消息");
}
@Override
public void send() {
System.out.println("用户3发送消息");
//中介转发
SimpleMediator.getInstance().relay(this);
}
}
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, CloneNotSupportedException {
Colleague user1=new User1();
Colleague user2=new User2();
Colleague user3=new User3();
user1.send();
}
//用户1发送消息
//用户2接收到消息
//用户3接收到消息