本文将从纯xml模式、xml和注解结合、纯注解的方式讲解Spring IOC容器的配置和相关应用。
纯XML模式
实例化Bean的三种方式:
- 使用无参构造函数
默认情况下,会使用反射调用无参构造函数来创建对象。
<bean id="connectionUtils" class="com.mmc.ioc.utils.ConnectionUtils"></bean>
- 使用静态方法创建
在实际开发中,我们使用的方法有时候不是通过构造函数创建出来的,他可能在创建的时候会做很多额外的操作。此时会提供一个创建对象的方法,如果这个方法是static修饰的,就是用这种配置方式。
<bean id="druidUtils" class="com.mmc.ioc.utils.DruidUtils" factory-method="getInstance"></bean>
- 使用实例化方法创建
当方法不是静态的时候,用这种方式
<bean id="connectionUtils" class="com.mmc.ioc.utils.ConnectionUtils"></bean>
<bean id="account" factory-bean="connectionUtils" factory-method="createAccount"></bean>
bean的作用范围和声明周期

常用的是singleton【默认】(单例模式)和prototype(原型模式或多例模式)。通过scope属性可以进行配置
<bean id="account" factory-bean="connectionUtils" factory-method="createAccount" scope="singleton"></bean>
不同作用范围的生命周期
单例模式:singleton
对象创建:当创建容器时,对象就被创建
对象活着:只要容器在,对象一直活着
对象死亡:当容器销毁,对象就被销毁
总结:单例模式的bean对象生命周期与容器相同
多例模式:prototype
对象创建:当使用对象时,创建新的对象实例
对象活着:只要对象在使用中,就一直活着
对象死亡:当对象长时间不用时,被垃圾回收器回收
总结:多例模式的bean对象,spring框架只负责创建,不负责销毁。
Bean的标签属性
- id属性: ⽤于给bean提供⼀个唯⼀标识。在⼀个标签内部,标识必须唯⼀。
- class属性:⽤于指定创建Bean对象的全限定类名。
- name属性:⽤于给bean提供⼀个或多个名称。多个名称⽤空格分隔。
- factory-bean属性:⽤于指定创建当前bean对象的⼯⼚bean的唯⼀标识。当指定了此属性之后,
class属性失效。 - factory-method属性:⽤于指定创建当前bean对象的⼯⼚⽅法,如配合factory-bean属性使⽤,
则class属性失效。如配合class属性使⽤,则⽅法必须是static的。 - scope属性:⽤于指定bean对象的作⽤范围。通常情况下就是singleton。当要⽤到多例模式时,
可以配置为prototype。 - init-method属性:⽤于指定bean对象的初始化⽅法,此⽅法会在bean对象装配后调⽤。必须是
⼀个⽆参⽅法。 - destory-method属性:⽤于指定bean对象的销毁⽅法,此⽅法会在bean对象销毁前执⾏。它只
能为scope是singleton时起作⽤。
DI依赖注入
- 按照注入的方式分类
- 构造函数注入:就是利用带参构造函数实现对类成员的属性赋值
<bean id="account" class="com.mmc.ioc.bean.Account">
<constructor-arg name="cardNo" value="123"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="money" value="23"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="name" value="aa"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
- set方法注入:通过类成员的set方法实现数据注入
<bean id="account" class="com.mmc.ioc.bean.Account">
<property name="name" value="mmc"></property>
<property name="cardNo" value="abc"></property>
<property name="money" value="22"></property>
</bean>
- 按照注入的数据类型分类
- 基本数据类型和String
- 其他Bean类型
- 复杂类型(集合类型)
基本类型使用value,其他bean类型使用ref,复杂类型使用对应的array、map、set标签
<bean id="user" class="com.mmc.ioc.bean.User">
<property name="id" value="1"></property>
<property name="account" ref="account"></property>
<property name="list">
<array>
<value>aa</value>
<value>bb</value>
</array>
</property>
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="a" value="1"></entry>
<entry key="b" value="2"></entry>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
web.xml
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<!--配置spring ioc容器的配置文件-->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--使用监听器启动Spring的IOC容器-->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
</web-app>
xml与注解结合的方式
注意:实际开发中,纯xml模式使用已经很少了,引入注解功能,不需要引入额外的jar包。xml+注解结合模式中,xml文件依然存在,所以Spring IOC容器的启动仍然从加载xml开始。
一般来说第三方jar包里面的bean定义在xml里面,自己开发的bean使用注解。
将第三方jar包的bean放入容器
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
">
<!--包扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.mmc.ioc"></context:component-scan>
<!--引入配置文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
xml中标签与注解的对应
| xml形式 | 注解 |
|---|---|
| 标签 | @Component,注解加在类上。默认情况下bean的id为类名(首字母小写)。另外,针对分层代码开发提供了@Componenet的三种别名@Controller、 |
| @Service、@Repository分别⽤于控制层类、服务层类、dao层类的bean定义,这 | |
| 四个注解的⽤法完全⼀样,只是为了更清晰的区分⽽已 | |
| 标签的scope属性 | @Scope("prototype") |
DI依赖注入的注解实现方式
- @Autowired(推荐使用)
@Autowired为Spring提供的注解。策略是按类型注入
public class TransferServiceImpl implements TransferService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
}
如上代码所示,这样装配会去spring容器中找到类型为AccountDao的bean,然后将其中如。但如果一个类型有多个bean怎么办呢?可以配合@Qualifier("bean的id")使用。
public class TransferServiceImpl implements TransferService {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("jdbcAccountDao")
private AccountDao accountDao;
}
- @Resource
@Resource注解由j2EE提,如果指定了name或type就会根据指定的来,如果都没有指定就自动按照ByName方式装配。
注意:@Resource在Jdk11中已经移除,如果要使用,需要单独引入jar包。
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
在Servlet类里面获取applicationContext
public class TransferServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(this.getServletContext());
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = (ProxyFactory) webApplicationContext.getBean("proxyFactory");
transferService= (TransferService) proxyFactory.getJdkProxy(webApplicationContext.getBean("transferService"));
}
}
纯注解模式
将xml配置改为java代码:
在配置类上声明@Configuration,表明是配置类。
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.mmc.ioc")
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
public class SpringConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
private String driverClass;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
DruidDataSource druidDataSource=new DruidDataSource();
druidDataSource.setDriverClassName(driverClass);
druidDataSource.setUrl(url);
druidDataSource.setUsername(username);
druidDataSource.setPassword(password);
return druidDataSource;
}
}
如果还有其他配置类,可以通过@Import引入进来。
web.xml配置如下:
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<!--告诉ContextLoaderListener是注解方式启动ioc容器-->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextClass</param-name>
<param-value>org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--配置spring ioc容器的配置文件-->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>com.mmc.ioc.SpringConfig</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--使用监听器启动Spring的IOC容器-->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
</web-app>
高级特性
延迟加载
xml方式:
<bean id="testBean" calss="cn.lagou.LazyBean" lazy-init="true" />
也可以在容器层次配置默认释放延迟加载,如:
<beans default-lazy-init="true">
<!-- no beans will be eagerly pre-instantiated... -->
</beans>
注解方式:
@Lazy注解
@Bean
@Lazy
public DataSource dataSource(){
}
FactoryBean
Spring中的Bean有两种,一种是普通bean,一种是工厂bean(FactoryBean),FactoryBean可以生产某一个类型的Bean实例,也就是说我们可以借助它自定义Bean的创建过程。
@Component("user")
public class UserFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<User> {
@Override
public User getObject() throws Exception {
User user=new User();
Account account=new Account();
account.setName("mmc");
user.setAccount(account);
List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add("a");
user.setList(list);
user.setId(2);
return user;
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return User.class;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
运行测试代码,取出beanname为user的对象。
@Test
public void testAno(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
Object user = applicationContext.getBean("user");
System.out.println(user);
}
运行结果如下:

可以看出虽然是UserFactoryBean放入了容器,但是取出来的却是User对象。这就是FactoryBean的作用。
Spring扩展接口和方法
- BeanNameAware
- BeanFactoryAware
- ApplicationContextAware
- InitializingBean
- DisposableBean
- @PostConstruct
- @PreDestroy
- init-method
- destroy-method
- BeanPostProcessor
- BeanFactoryPostProcessor
从获取Spring里的东西来分有:
- BeanNameAware
- BeanFactoryAware
- ApplicationContextAware
初始化:
- @PostConstruct
- InitializingBean
- init-method
销毁:
- @PreDestroy
- DisposableBean
- destroy-method
初始化和销毁的执行先后顺序都是注解->接口->xml
使用示例:
<bean id="account" class="com.mmc.ioc.bean.Account" init-method="initMethod" destroy-method="destroyMethod"></bean>
public class Account implements BeanNameAware,BeanFactoryAware,ApplicationContextAware,InitializingBean,DisposableBean {
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanFactoryAware:"+beanFactory);
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("BeanNameAware:"+name);
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("DisposableBean");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("InitializingBean");
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("ApplicationContextAware:"+applicationContext);
}
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct(){
System.out.println("postConstruct");
}
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroy(){
System.out.println("preDestroy");
}
public void initMethod(){
System.out.println("init-method");
}
public void destroyMethod(){
System.out.println("destroy-method");
}
}
全局的:
BeanFactoryPostProcessor是在BeanFactory初始化之后可以处理一些事情,是针对Bean的工厂进行处理,典型应用:PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer
BeanPostProcessor是针对所有的bean进行拦截进行处理,使用如下:
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(beanName.equals("account")){
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor before"+bean);
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(beanName.equals("account")){
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor after"+bean);
}
return bean;
}
}
全部配置好后,打印查看执行先后顺序:

可以得到下面的执行流程图:
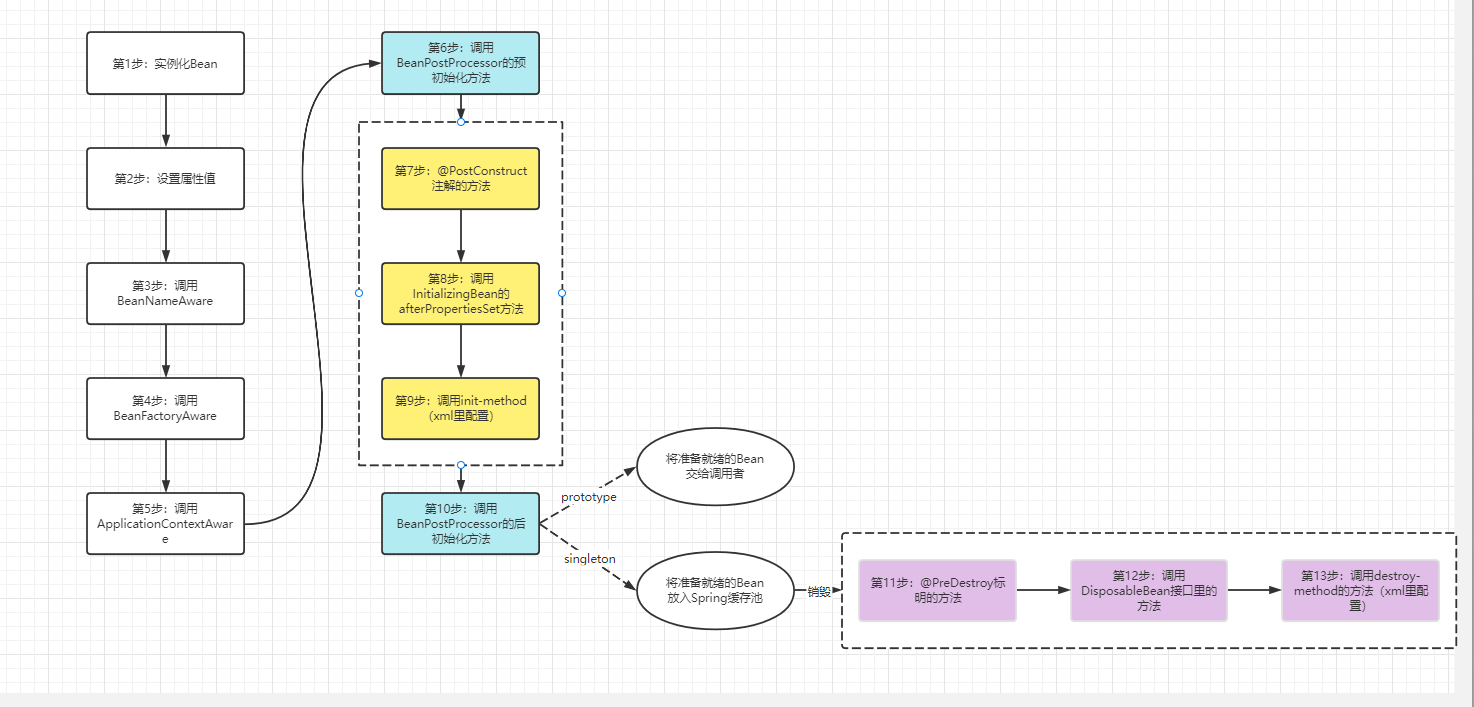
高频面试题:
BeanFactory、FactoryBean、ApplicationContext的区别
- BeanFactory是Spring框架中IOC容器的顶层接口,它只是用来定义一些基础功能
- ApplicationContext是它的一个子接口,它拥有更多的功能,如国际化支持和资源访问等等。
- FactoryBean:一般情况下,Spring通过反射机制实例化Bean,在某些情况下,实例化bean过程比较复杂,这时配置起来就比较麻烦。如果采用编码的方式会简单一些。于是Spring给我们提供了FactoryBean的接口,用户就可以通过实现这个接口来自定义实例化Bean的逻辑。
总结:BeanFactory是负责生产和管理Bean的一个工厂接口,提供一个Spring Ioc容器规范。FactoryBean是一种Bean创建的方法,对Bean的一种扩展。
类图如下:
