要求:地球的平均半径为6371千米,已知地球上两个城市A、B的经度和纬度,编程序求出这两个城市之间的地面距离。
首先,固定两点,a(x1,y1,z1),b(x2,y2,z2)。
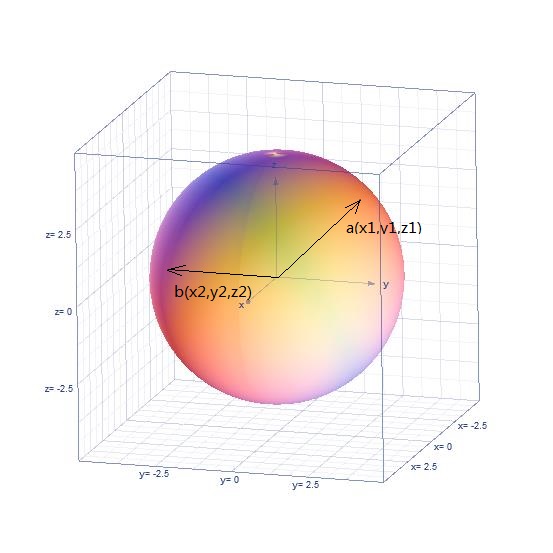
由空间解析几何及向量知识知:
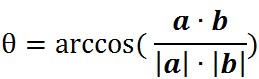
其中,theta是两向量夹角,球面距离d:
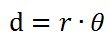
对于A点来说(图中a应改为A,画图的时候写错了),
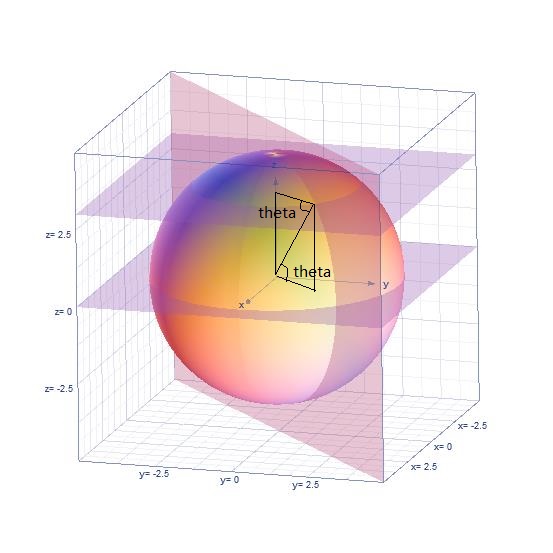
theta就是A点的纬度值,即:
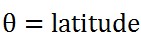
也即:
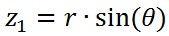
而对于A点的x,y坐标,首先:
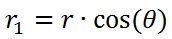
r1是小圆的半径,也就是下图中的蓝色圆:
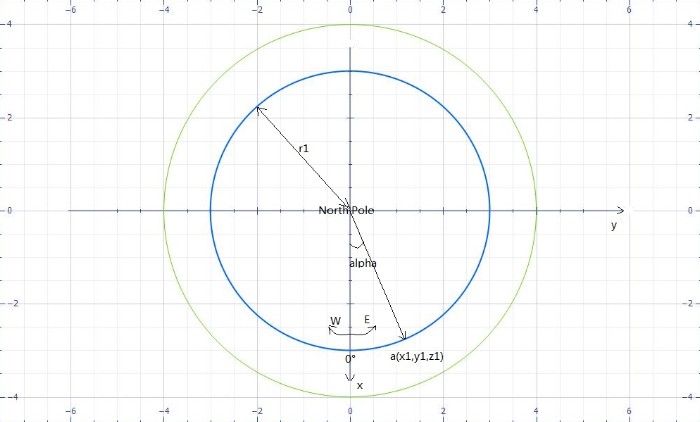
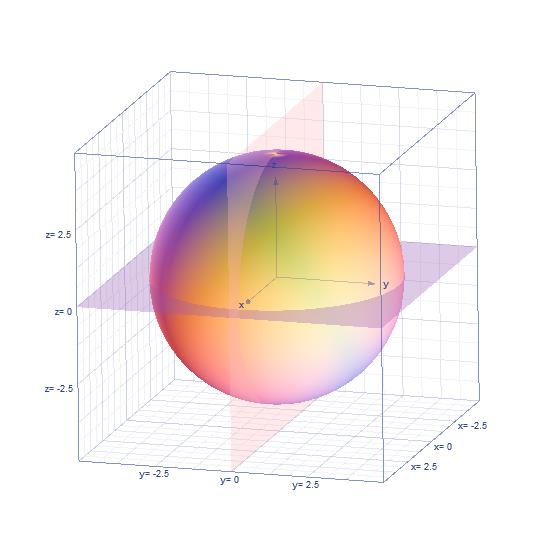
请注意平面图与立体图中坐标的对应,我已一一对应好,注意观察。
图中的alpha即:
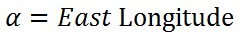
所以,坐标与经度之间有如下关系:
实际的北极点是这样的:
还有一点,东西经南北纬转化问题。
关于东西经和南北纬,在上面的阐述中,东经的点的y值都是正值,西经的点的y值都是负值,北纬的点的z值都是正值,南纬的点的z值都是负值。因为如下图,地球被分为了东北半球,东南半球,西北半球,西南半球:
如上分析,不难写出如下代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
#define pi 3.1415926535
#define radio 6378137.0
//defining a new struct for the convenience of calculating
typedef struct
{
long double Longitude;
long double Lantitude;
string East_or_West;
string North_or_South;
} dot;
//function for calculating
int Distance(float lat1, float lon1, float lat2, float lon2)
{
double latitude1,longitude1,latitude2,longitude2;
double dlat,dlon;
latitude1=lat1;
longitude1=lon1;
latitude2=lat2;
longitude2=lon2;
//computing procedure
double a,c,distance;
dlon =fabs((longitude2 - longitude1))*pi/180;
dlat =fabs((latitude2 - latitude1))*pi/180;
a = (sin(dlat/2)*sin(dlat/2)) + cos(latitude1*pi/180) * cos(latitude2*pi/180) * (sin(dlon/2)*sin(dlon/2));
if(a==1.0)
c=pi;
else
c = 2 * atan(sqrt(a)/sqrt(1-a));
distance= radio*c;
return distance;
}
int main()
{
long double r = 6371.004;
dot a, b;
//freopen("D:\example.txt","r",stdin);
while(1)
{
cout<<"Please input the two dots' coordinates like the following format: "<<endl;
cout<<"East 30 North 20"<<"West 40 North 10"<<endl;
//data input procedure
cin>>a.East_or_West>>a.Longitude>>a.North_or_South>>a.Lantitude;
cin>>b.East_or_West>>b.Longitude>>b.North_or_South>>b.Lantitude;
//transfer
{
if(a.East_or_West == "East")
{
a.Longitude = a.Longitude;
}
else if(a.East_or_West == "West")
{
a.Longitude = - a.Longitude;
}
}
{
if(a.North_or_South == "North")
{
a.Lantitude = pi / 2 - a.Lantitude;
}
else if (a.North_or_South == "South")
{
a.Lantitude = pi / 2 + a.Lantitude;
}
}
{
if(b.East_or_West == "East")
{
b.Longitude = b.Longitude;
}
else if(a.East_or_West == "West")
{
b.Longitude = - b.Longitude;
}
}
{
if(a.North_or_South == "North")
{
b.Lantitude = pi / 2 - b.Lantitude;
}
else if (a.North_or_South == "South")
{
b.Lantitude = pi / 2 + b.Lantitude;
}
}
//data output procedure
float result = Distance(a.Lantitude, a.Longitude, b.Lantitude, b.Longitude);
cout<<"The distance is: "<<result<<endl<<endl;
}
}
可能有所纰漏,因为第一遍写代码的时候没这么仔细分析。
想要更深层次了解此问题,请参看微分几何中关于测地线及测地线曲率的相关问题。
欲证明该思想的正确性,可以采取如下反证法:
假设通过二点存在一个小圆对应的劣弧长比球面距离小,那条曲线未必是平面曲线,所以未必是圆弧。