Java 演示多线程死锁
当业务比较复杂,多线程应用里有可能会发生死锁
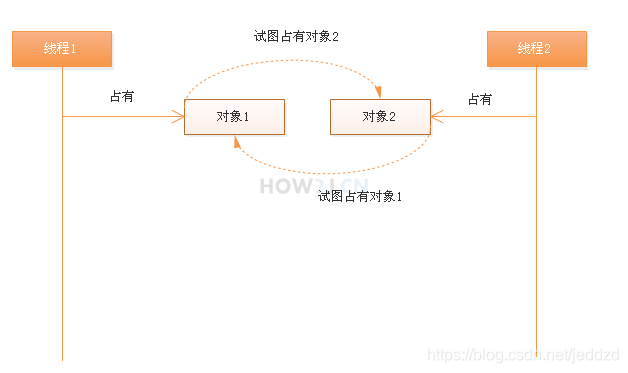
步骤 1 : 演示死锁
- 线程1 首先占有对象1,接着试图占有对象2
- 线程2 首先占有对象2,接着试图占有对象1
- 线程1 等待线程2释放对象2
- 与此同时,线程2等待线程1释放对象1
这样就会。。。一直等待下去
package multiplethread;
import charactor.Hero;
public class TestThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Hero ahri = new Hero();
ahri.name = "九尾妖狐";
final Hero annie = new Hero();
annie.name = "安妮";
Thread t1 = new Thread(){
public void run(){
//占有九尾妖狐
synchronized (ahri) {
System.out.println("t1 已占有九尾妖狐");
try {
//停顿1000毫秒,另一个线程有足够的时间占有安妮
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("t1 试图占有安妮");
System.out.println("t1 等待中 。。。。");
synchronized (annie) {
System.out.println("do something");
}
}
}
};
t1.start();
Thread t2 = new Thread(){
public void run(){
//占有安妮
synchronized (annie) {
System.out.println("t2 已占有安妮");
try {
//停顿1000毫秒,另一个线程有足够的时间占有暂用九尾妖狐
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("t2 试图占有九尾妖狐");
System.out.println("t2 等待中 。。。。");
synchronized (ahri) {
System.out.println("do something");
}
}
}
};
t2.start();
}
}
练习: 死锁
3个同步对象a, b, c
3个线程 t1,t2,t3
故意设计场景,使这3个线程彼此死锁
答案:
package multiplethread;
public class TestThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object a = new Object();
Object b = new Object();
Object c = new Object();
Thread t1 =new Thread(){
public void run(){
synchronized (a) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (b) {
synchronized (c) {
}
}
}
}
};
Thread t2 =new Thread(){
public void run(){
synchronized (c) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (a) {
synchronized (b) {
}
}
}
}
};
Thread t3 =new Thread(){
public void run(){
synchronized (b) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (c) {
synchronized (a) {
}
}
}
}
};
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}