一、引言
工作了好几年,一直在网上查找资料和学习,得到了博客园很多园友的帮助,在积累了一些东西之后,一直也没有系统的总结下来,现在终于下决心来博客园记录这些年的一些知识体系,希望可以坚持下来。
那么第一篇博文就从.net角度来理解一下http请求从浏览器到达服务器响应的一个过程吧。
二、正文
当用户在浏览器上输入url地址按下回车键后究竟发生了什么呢?浏览器会像浏览器发送一次请求Request,请求经过的过程可以看下面的这张图。
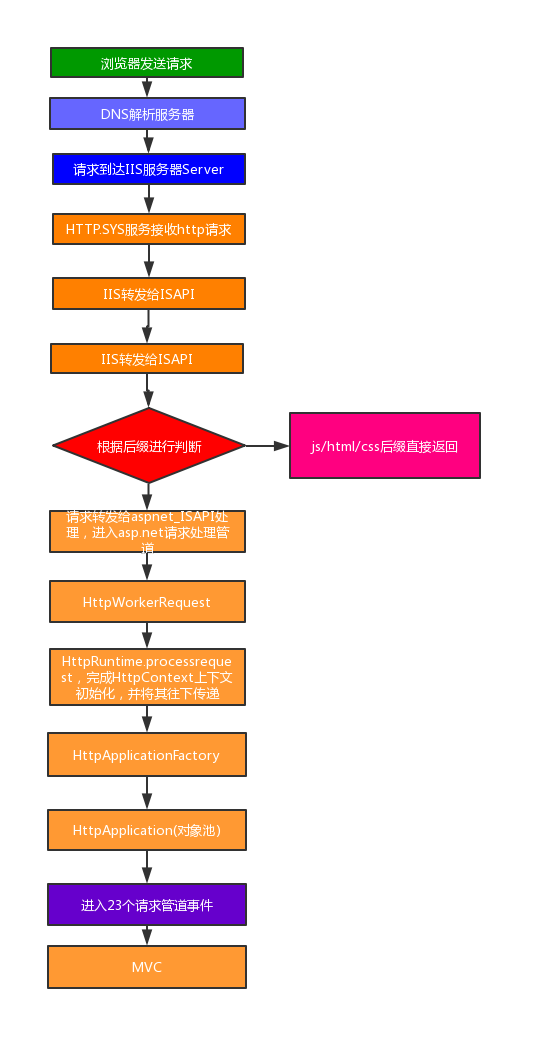
可以看到,请求到达域名供应商的DNS服务器,通过DNS解析获取到真实服务器的IP和Port,DNS将请求转发到真正的服务器上,服务器中的Http.sys组件接收到http请求,将其转给IIS处理,IIS根据请求找到对应的w3wp进程(w3wp.exe是在IIS与应用程序池相关联的一个进程,如果你有多个应用程序池,就会有对应的多个w3wp.exe的进程实例运行)。
IIS根据请求的后缀来决定如何处理请求,当请求的文件为静态文件如以 js/html/htm/css结尾会直接返回。而会将其他后缀的请求转发给 Aspnet_ISAPI 进行处理,当然,如果我们采用MVC的模式请求是不带有后缀的,这个时候IIS6.0会为没有后缀的请求加上一个axd的后缀,而IIS7.0以上的就不需要,因为IIS7.0以上的使用的是UrlRoutingModules扩展来处理MVC请求(IIS7.0以上会看到应用程序池有两种模式:集成模式和经典模式,其中经典模式代表的是旧模式,即兼容IIS 6)。
当IIS将请求转发给AspNet_ISAPI后,这时候请求就进入了Asp.Net请求处理管道,将由.net来处理该请求并做出响应。aspnet_isapi会将请求封装成HttpWorkerRequest的一个对象传递给HttpRuntime的ProcessRequest方法。这点我们可以从Asp.Net的源码中看到,它们存在于System.Web当中。
// System.Web.HttpRuntime /// <summary> /// Drives all ASP.NET Web processing execution. /// </summary> /// <param name="wr"> /// An <see cref="T:System.Web.HttpWorkerRequest" /> for the current application. /// </param> /// <exception cref="T:System.ArgumentNullException"> /// The <paramref name="wr" /> parameter is null. /// </exception> [AspNetHostingPermission(SecurityAction.Demand, Level = AspNetHostingPermissionLevel.Medium)] public static void ProcessRequest(HttpWorkerRequest wr) { if (wr == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("wr"); } if (HttpRuntime.UseIntegratedPipeline) { throw new PlatformNotSupportedException(SR.GetString("Method_Not_Supported_By_Iis_Integrated_Mode", new object[] { "HttpRuntime.ProcessRequest" })); } HttpRuntime.ProcessRequestNoDemand(wr); }
// System.Web.HttpRuntime private void ProcessRequestInternal(HttpWorkerRequest wr) { HttpContext httpContext; try { httpContext = new HttpContext(wr, false); } catch { wr.SendStatus(400, "Bad Request"); wr.SendKnownResponseHeader(12, "text/html; charset=utf-8"); byte[] bytes = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("<html><body>Bad Request</body></html>"); wr.SendResponseFromMemory(bytes, bytes.Length); wr.FlushResponse(true); wr.EndOfRequest(); return; } wr.SetEndOfSendNotification(this._asyncEndOfSendCallback, httpContext); Interlocked.Increment(ref this._activeRequestCount); HostingEnvironment.IncrementBusyCount(); try { try { this.EnsureFirstRequestInit(httpContext); } catch { if (!httpContext.Request.IsDebuggingRequest) { throw; } } httpContext.Response.InitResponseWriter(); IHttpHandler applicationInstance = HttpApplicationFactory.GetApplicationInstance(httpContext); if (applicationInstance == null) { throw new HttpException(SR.GetString("Unable_create_app_object")); } if (EtwTrace.IsTraceEnabled(5, 1)) { EtwTrace.Trace(EtwTraceType.ETW_TYPE_START_HANDLER, httpContext.WorkerRequest, applicationInstance.GetType().FullName, "Start"); } if (applicationInstance is IHttpAsyncHandler) { IHttpAsyncHandler httpAsyncHandler = (IHttpAsyncHandler)applicationInstance; httpContext.AsyncAppHandler = httpAsyncHandler; httpAsyncHandler.BeginProcessRequest(httpContext, this._handlerCompletionCallback, httpContext); } else { applicationInstance.ProcessRequest(httpContext); this.FinishRequest(httpContext.WorkerRequest, httpContext, null); } } catch (Exception e) { httpContext.Response.InitResponseWriter(); this.FinishRequest(wr, httpContext, e); } }
从源码可以看到,HttpRuntime会完成HttpContext的初始化,然后将其作为参数传递给HttpApplicationFactory创建HttpApplication对象池,HttpApplication处理各种各样的请求。
到这,请求就进入了asp.net的请求管道中的管道事件,其中最重要的是IhttpHandler和IHttpModule两个对象,我们可以对其做很多扩展。

至此,我们大概清楚了浏览器发送一条请求后是如何达到我们的服务器了,那么下一篇就来讲一下请求管道里面的各种事件。