1.ceilometer负责什么事情?
2.ceilometer 有哪些概念?
3.ceilometer 怎样採集hardware?
附上openstack 官网API http://docs.openstack.org/developer/python-ceilometerclient/
ceilometer主要负责监控数据的採集。採集的项目包含虚拟机的性能数据,neutron-l3-router使用的网络带宽,glance&cinder&swift等租户使用信息,甚至是通过snmp採集物理机的信息,以及採集支持opendaylight的网络设备信息。
基本概念
ceilometer 主要有以下几个概念:
- meter 是ceilometer定义的监控项,诸如内存占用,网络IO,磁盘IO等等
- sample 是每一个採集时间点上meter相应的值
- statistics 通常是统计学上某个周期内,meter相应的值(平均值之类)
- resource 是被监控的资源对象,这个能够是一台虚拟机,一台物理机或者一块云硬盘
- alarm 是ceilometer的告警机制,你能够通过阈值或者组合条件告警。并设置告警时触发的action
採集机制
ceilometer的各个服务中,与採集相关的服务是ceilometer-collector、ceilometer-agent-central、ceilometer-agent-compute、ceilometer-agent-notification。
我们能够通过下图了解一下他们之间的关系:
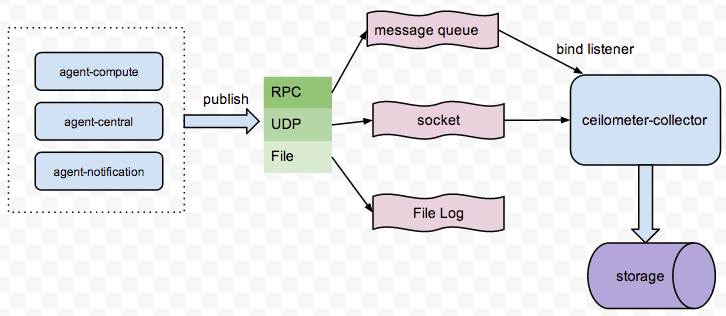
agent-*服务负责採集信息,採集的信息能够通过三种方式publish出来,包含RPC、UDP、File。RPC是将採集的信息以payload方式公布到消息队列,collector服务通过监听相应的queue来收集这些信息。并保存到存储介质中;UDP通过socket创建一个UDP数据通道。然后collector通过bind这个socket来接收数据。并保存到存储介质中;File方式比較直接,就是将採集的数据以filelog的方式写入log文件里。
至于使用哪种方式publish,那么就要看你的pipline文件是怎样配置的了。详细能够查看/etc/ceilometer/pipline.yaml中的publishers配置。
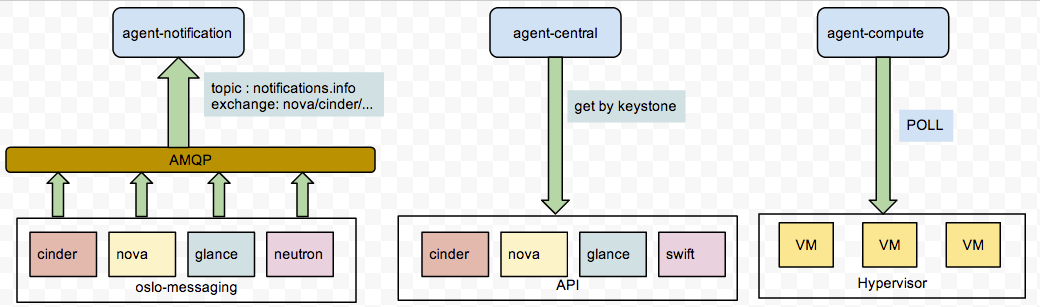
agent-*三个採集组件分别负责採集不同类型的信息。agent-notification负责收集各个组件推送到oslo-messaging的消息,oslo-messaging是openstack总体的消息队列框架,全部组件的消息队列都使用这个组件。agent-compute仅仅负责收集虚拟机的CPU内存IO等信息。所以他须要安装在Hypervisor机器上;agent-central是通过各个组件API方式收集实用的信息;agent-notification仅仅需监听AMQP中的queue就可以收到信息。而agent-compute和agent-central都须要定期Poll轮询收集信息。看下图来了解一下:
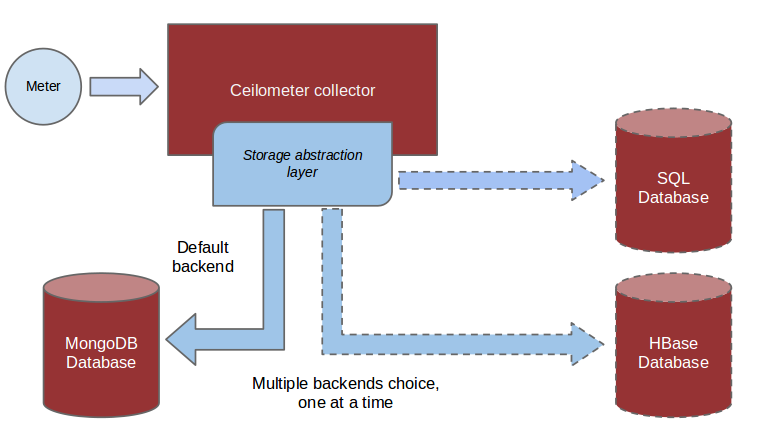
信息通过agent-*採集并由collector汇总处理,终于须要持久化到存储介质中,ceilometer眼下支持的存储包含mysql、DB2、HBase、mongoDB,从支持的数据库来看。监控数据持久化的压力还是相当大的。
採集项
agent-*组件在启动时候。通过stevedore的插件机制来载入採集项,包含每一个採集项相应的运行程序。
stevedore的插件配置是利用了setuptools的entry_points。所以我们能够通过查看entry_points的配置信息。来确定有哪些採集项。假设你的程序打包完成并公布到了python的搜索路径中。那么你须要查看ceilometer的egg文件来查看。或者你能够下载源代码查看setup.cf文件,相关信息例如以下:
- [entry_points]
- ceilometer.notification =
- instance = ceilometer.compute.notifications.instance:Instance
- instance_flavor = ceilometer.compute.notifications.instance:InstanceFlavor
- memory = ceilometer.compute.notifications.instance:Memory
- ...
- ...
- ceilometer.poll.compute =
- disk.read.requests = ceilometer.compute.pollsters.disk:ReadRequestsPollster
- cpu = ceilometer.compute.pollsters.cpu:CPUPollster
- ...
- ...
- ceilometer.poll.central =
- image = ceilometer.image.glance:ImagePollster
- storage.containers.objects = ceilometer.objectstore.swift:ContainersObjectsPollster
- ...
- ...
ceilometer.notification 相应的是agent-notification组件。ceilometer.poll.compute相应的是agent-compute组件。ceilometer.poll.central相应的是agent-central组件。
採集neutron l3 router 的bandwidth
与ceilometer其它採集方式不同的是。bandwidth的採集是通过neutron-meter-agent收集,然后push到oslo-messaging,ceilometer-agent-notification通过监听消息队列来收取bandwidth信息,能够看一些官方的wiki(https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/Neutron/Metering/Bandwidth)。
依照wiki上的描写叙述,设置好rule,ceilometer就能够收集bandwidth信息了。router上的流量计算是利用了iptables的特性,iptables本身能够用于做流量统计。这里不清楚的去Google一下就可以。
比方我们使用neutron-meter 设定了这样一组规则:
- $ neutron meter-label-rule-list
- +--------------------------------------+----------+-----------+------------------+
- | id | excluded | direction | remote_ip_prefix |
- +--------------------------------------+----------+-----------+------------------+
- | d2f28556-7369-42a7-9a92-9f2a12e929ce | False | egress | 66.66.66.0/24 |
- | e6a3542d-596b-415a-ab96-90df211c027b | False | ingress | 66.66.66.0/24 |
- +--------------------------------------+----------+-----------+------------------+
那么相应此规则建立的iptables规则例如以下:
- -A neutron-meter-r-d49bfb44-546 -d 66.66.66.0/24 -o qg-874a8e9b-4d -j neutron-meter-l-d49bfb44-546
- -A neutron-meter-r-d49bfb44-546 -d 66.66.66.0/24 -i qg-874a8e9b-4d -j neutron-meter-l-d49bfb44-546
neutron-meter-agent 会在设定的间隔时间内去通过iptables统计流量,然后push到oslo-messaging:
- $ ip netns exec qrouter-94cca346-ea17-48fe-94fd-30004078e339 iptables -t filter -L neutron-meter-l-d49bfb44-546 -n -v -x -Z
- Chain neutron-meter-l-d49bfb44-546 (2 references)
- pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
- 0 0 all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
採集hardware
ceilometer除了能够收集openstack组件的相关信息。也能够收集诸如kwapi、hardware、opendaylight信息。kwapi是採集物理机能耗信息的项目,agent-central组件通过kwapi暴露的api来收集物理机的能耗信息;agent-central也能够通过snmp协议直接收集hardware的CPU、MEM、IO等信息。opendaylight是SDN解决方式的开源项目,opendaylight规范中包含暴露一个API接口来提供SDN内部的一些信息,agent-central正是通过这个API能够收集opendaylight组件的信息。
假设我们想扩展这些监控信息。须要对ceilometer添加一些额外的配置。可是这些配置原理都是一样的,我们这里以採集hardware信息为例。
首先须要在被监控的hardw上开启SNMP协议。比方我们要监控一台物理机host为icehouse-ncloud-compute-a1。系统为ubuntu,先安装snmp和snmpd包,然后改动配置文件:
- #开启监听port和相应的ip
- agentAddress udp:161,udp6:[::1]:161
- #开启全部SNMP訪问项
- view systemonly included .1 80
重新启动snmp服务,在ceilometer的pipline.yaml文件里增加例如以下(以採集hardware.memory为例),interval是poll的轮询间隔时间,能够按自家需求配置:
- - name: hardware_memory_source
- interval: 1800
- meters:
- - "hardware.memory.*"
- resources:
- - snmp://icehouse-ncloud-compute-a1
- sinks:
- - meter_sink
通过 ceilometer meter-list | grep hardware ,能够看到新增的监控项。假设要查看监控数据能够这样:
- $ ceilometer sample-list -m hardware.memory.total
- +----------------------------+-----------------------+-------+-------------+------+---------------------+
- | Resource ID | Name | Type | Volume | Unit | Timestamp |
- +----------------------------+-----------------------+-------+-------------+------+---------------------+
- | icehouse-ncloud-compute-a1 | hardware.memory.total | gauge | 131996840.0 | B | 2014-05-21T03:07:40 |
- | icehouse-ncloud-compute-a1 | hardware.memory.total | gauge | 131996840.0 | B | 2014-05-21T02:37:40 |