India and China Origins
Time Limit: 2000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)
Problem Description
A long time ago there are no himalayas between India and China, the both cultures are frequently exchanged and are kept in sync at that time, but eventually himalayas rise up. With that at first the communation started to reduce and eventually died.
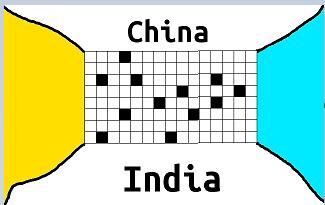
Let's assume from my crude drawing that the only way to reaching from India to China or viceversa is through that grid, blue portion is the ocean and people haven't yet invented the ship. and the yellow portion is desert and has ghosts roaming around so people can't travel that way. and the black portions are the location which have mountains and white portions are plateau which are suitable for travelling. moutains are very big to get to the top, height of these mountains is infinite. So if there is mountain between two white portions you can't travel by climbing the mountain.
And at each step people can go to 4 adjacent positions.
Our archeologists have taken sample of each mountain and estimated at which point they rise up at that place. So given the times at which each mountains rised up you have to tell at which time the communication between India and China got completely cut off.

Let's assume from my crude drawing that the only way to reaching from India to China or viceversa is through that grid, blue portion is the ocean and people haven't yet invented the ship. and the yellow portion is desert and has ghosts roaming around so people can't travel that way. and the black portions are the location which have mountains and white portions are plateau which are suitable for travelling. moutains are very big to get to the top, height of these mountains is infinite. So if there is mountain between two white portions you can't travel by climbing the mountain.
And at each step people can go to 4 adjacent positions.
Our archeologists have taken sample of each mountain and estimated at which point they rise up at that place. So given the times at which each mountains rised up you have to tell at which time the communication between India and China got completely cut off.
Input
There are multi test cases. the first line is a sinle integer T which represents the number of test cases.
For each test case, the first line contains two space seperated integers N,M. next N lines consists of strings composed of 0,1 characters. 1 denoting that there's already a mountain at that place, 0 denoting the plateau. on N+2 line there will be an integer Q denoting the number of mountains that rised up in the order of times. Next Q lines contain 2 space seperated integers X,Y denoting that at ith year a mountain rised up at location X,Y.
T≤10
1≤N≤500
1≤M≤500
1≤Q≤N∗M
0≤X<N
0≤Y<M
For each test case, the first line contains two space seperated integers N,M. next N lines consists of strings composed of 0,1 characters. 1 denoting that there's already a mountain at that place, 0 denoting the plateau. on N+2 line there will be an integer Q denoting the number of mountains that rised up in the order of times. Next Q lines contain 2 space seperated integers X,Y denoting that at ith year a mountain rised up at location X,Y.
T≤10
1≤N≤500
1≤M≤500
1≤Q≤N∗M
0≤X<N
0≤Y<M
Output
Single line at which year the communication got cut off.
print -1 if these two countries still connected in the end.
Hint:
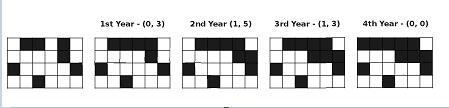
From the picture above, we can see that China and India have no communication since 4th year.
print -1 if these two countries still connected in the end.
Hint:

From the picture above, we can see that China and India have no communication since 4th year.
Sample Input
1
4 6
011010
000010
100001
001000
7
0 3
1 5
1 3
0 0
1 2
2 4
2 1
Sample Output
4
Source
思路:这是一个连通性的问题。你会发现如果将所有操作逆序来看的话就很容易用并查集来处理了。 首先把所有的山峰都加到图中,然后逆序处理每个操作: 对某次操作,在图中删除该位置的山峰,然后判断两个点是否联通,一旦联通就得到了结果。 这里需要对China和India分别新建一个对应的节点。(然而数据好像没有-1的情况~~~)

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cmath> #include<string> #include<queue> #include<algorithm> #include<stack> #include<cstring> #include<vector> #include<list> #include<set> #include<map> using namespace std; #define ll __int64 #define mod 1000000007 int scan() { int res = 0 , ch ; while( !( ( ch = getchar() ) >= '0' && ch <= '9' ) ) { if( ch == EOF ) return 1 << 30 ; } res = ch - '0' ; while( ( ch = getchar() ) >= '0' && ch <= '9' ) res = res * 10 + ( ch - '0' ) ; return res ; } int l,k; char a[510][510]; struct is { int l,r; }ch[250010]; int father[500010]; int vis[510][510]; int xz[4]={1,0,-1,0}; int yz[4]={0,1,0,-1}; int find_father(int x) { return x==father[x]? x:father[x]=find_father(father[x]); } void hebing(int x,int y) { int xx=find_father(x); int yy=find_father(y); if(xx!=yy) father[xx]=yy; } int number(int x,int y) { return (x-1)*k+y; } int check(int ff) { memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); for(int i=0;i<=l*k;i++) father[i]=i; father[399999]=399999; father[400000]=400000; for(int i=1;i<=l;i++) for(int t=1;t<=k;t++) if(a[i][t]=='1') vis[i][t]=1; else vis[i][t]=0; for(int i=1;i<=ff;i++) vis[ch[i].l+1][ch[i].r+1]=1; for(int i=1;i<=l;i++) for(int t=1;t<=k;t++) { if(vis[i][t])continue; for(int j=0;j<4;j++) { int xx=i+xz[j]; int yy=t+yz[j]; if(yy<=0||yy>k||vis[xx][yy])continue; if(xx==0)hebing(number(i,t),399999); else if(xx==l+1)hebing(number(i,t),400000); else hebing(number(i,t),number(xx,yy)); } } int ans1=find_father(399999); int ans2=find_father(400000); if(ans1==ans2) return 1; return 0; } int main() { int x,y,i,t; scanf("%d",&x); while(x--) { scanf("%d%d",&l,&k); for(i=1;i<=l;i++) scanf("%s",a[i]+1); scanf("%d",&y); for(t=1;t<=y;t++) scanf("%d%d",&ch[t].l,&ch[t].r); if(!check(0)) { printf("-1 "); continue; } int st=1,en=y,mid; while(st<en) { mid=(st+en)>>1; if(check(mid)) st=mid+1; else en=mid; } printf("%d ",st); } return 0; }
