At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at him. A lot of important things were lost, in particular the favorite sequence of Picks.
Fortunately, Picks remembers how to repair the sequence. Initially he should create an integer array a[1], a[2], ..., a[n]. Then he should perform a sequence of m operations. An operation can be one of the following:
- Print operation l, r. Picks should write down the value of
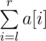 .
. - Modulo operation l, r, x. Picks should perform assignment a[i] = a[i] mod x for each i (l ≤ i ≤ r).
- Set operation k, x. Picks should set the value of a[k] to x (in other words perform an assignment a[k] = x).
Can you help Picks to perform the whole sequence of operations?
The first line of input contains two integer: n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105). The second line contains n integers, separated by space:a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] (1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109) — initial value of array elements.
Each of the next m lines begins with a number type 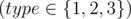 .
.
- If type = 1, there will be two integers more in the line: l, r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n), which correspond the operation 1.
- If type = 2, there will be three integers more in the line: l, r, x (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109), which correspond the operation 2.
- If type = 3, there will be two integers more in the line: k, x (1 ≤ k ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109), which correspond the operation 3.
For each operation 1, please print a line containing the answer. Notice that the answer may exceed the 32-bit integer.
5 5
1 2 3 4 5
2 3 5 4
3 3 5
1 2 5
2 1 3 3
1 1 3
8
5
10 10
6 9 6 7 6 1 10 10 9 5
1 3 9
2 7 10 9
2 5 10 8
1 4 7
3 3 7
2 7 9 9
1 2 4
1 6 6
1 5 9
3 1 10
49
15
23
1
9
Consider the first testcase:
- At first, a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}.
- After operation 1, a = {1, 2, 3, 0, 1}.
- After operation 2, a = {1, 2, 5, 0, 1}.
- At operation 3, 2 + 5 + 0 + 1 = 8.
- After operation 4, a = {1, 2, 2, 0, 1}.
- At operation 5, 1 + 2 + 2 = 5.
题意:给你一个序列;
操作1,给你一个区间[l,r]求区间和;
操作2,给你区间每个点取模;
操作3,单点修改;
思路:开始写了个延迟标记,发现那个每个点取模和并不等于区间和取模,例如: 1 2 模3 ,等于3,并不等于0;
更新到每个点显然超时,所以需要一点优化,记录一个最大值,判断最大值是否大于模,不大于则不用更新;
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ll long long #define pi (4*atan(1.0)) const int N=1e5+10,M=4e6+10,inf=1e9+10; ll sum[N<<2]; ll maxx[N<<2]; void pushup(int pos) { sum[pos]=sum[pos<<1|1]+sum[pos<<1]; maxx[pos]=max(maxx[pos<<1|1],maxx[pos<<1]); } void buildtree(int l,int r,int pos) { if(l==r) { scanf("%lld",&sum[pos]); maxx[pos]=sum[pos]; return; } int mid=(l+r)>>1; buildtree(l,mid,pos<<1); buildtree(mid+1,r,pos<<1|1); pushup(pos); } void update3(int point,ll change,int l,int r,int pos) { if(l==r&&l==point) { sum[pos]=change; maxx[pos]=change; return; } int mid=(l+r)>>1; if(point<=mid) update3(point,change,l,mid,pos<<1); else update3(point,change,mid+1,r,pos<<1|1); pushup(pos); } void update2(int L,int R,int m,int l,int r,int pos) { if(l==r) { sum[pos]%=m; maxx[pos]=sum[pos]; return; } int mid=(l+r)>>1; if(L<=mid&&maxx[pos<<1]>=m) update2(L,R,m,l,mid,pos<<1); if(R>mid&&maxx[pos<<1|1]>=m) update2(L,R,m,mid+1,r,pos<<1|1); pushup(pos); } ll query(int L,int R,int l,int r,int pos) { if(L<=l&&r<=R) return sum[pos]; int mid=(l+r)>>1; ll ans=0; if(L<=mid) ans+=query(L,R,l,mid,pos<<1); if(R>mid) ans+=query(L,R,mid+1,r,pos<<1|1); return ans; } int main() { int n,m; scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); buildtree(1,n,1); while(m--) { int flag,l,r,mo; ll x; scanf("%d",&flag); if(flag==1) { scanf("%d%d",&l,&r); printf("%lld ",query(l,r,1,n,1)); } else if(flag==2) { scanf("%d%d%d",&l,&r,&mo); update2(l,r,mo,1,n,1); } else { scanf("%d%lld",&mo,&x); update3(mo,x,1,n,1); } } return 0; }