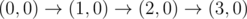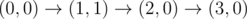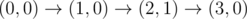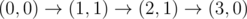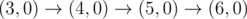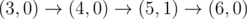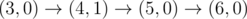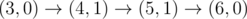Okabe likes to take walks but knows that spies from the Organization could be anywhere; that's why he wants to know how many different walks he can take in his city safely. Okabe's city can be represented as all points (x, y) such that x and y are non-negative. Okabe starts at the origin (point (0, 0)), and needs to reach the point (k, 0). If Okabe is currently at the point (x, y), in one step he can go to (x + 1, y + 1), (x + 1, y), or (x + 1, y - 1).
Additionally, there are n horizontal line segments, the i-th of which goes from x = ai to x = bi inclusive, and is at y = ci. It is guaranteed that a1 = 0, an ≤ k ≤ bn, and ai = bi - 1 for 2 ≤ i ≤ n. The i-th line segment forces Okabe to walk with y-value in the range 0 ≤ y ≤ ci when his x value satisfies ai ≤ x ≤ bi, or else he might be spied on. This also means he is required to be under two line segments when one segment ends and another begins.
Okabe now wants to know how many walks there are from the origin to the point (k, 0) satisfying these conditions, modulo 109 + 7.
The first line of input contains the integers n and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 100, 1 ≤ k ≤ 1018) — the number of segments and the destination x coordinate.
The next n lines contain three space-separated integers ai, bi, and ci (0 ≤ ai < bi ≤ 1018, 0 ≤ ci ≤ 15) — the left and right ends of a segment, and its y coordinate.
It is guaranteed that a1 = 0, an ≤ k ≤ bn, and ai = bi - 1 for 2 ≤ i ≤ n.
Print the number of walks satisfying the conditions, modulo 1000000007 (109 + 7).
1 3
0 3 3
4
2 6
0 3 0
3 10 2
4
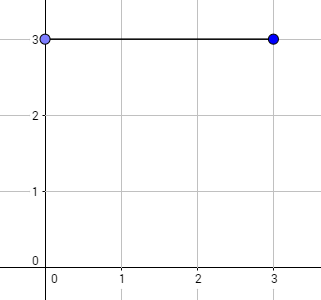
The graph above corresponds to sample 1. The possible walks are:
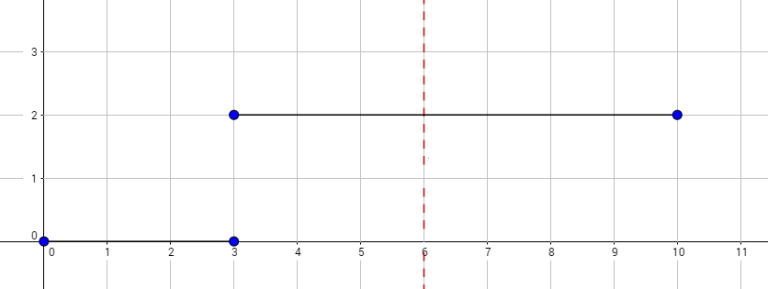
The graph above corresponds to sample 2. There is only one walk for Okabe to reach (3, 0). After this, the possible walks are:
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000") #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cmath> #include<string> #include<queue> #include<algorithm> #include<stack> #include<cstring> #include<vector> #include<list> #include<set> #include<map> #include<bitset> #include<time.h> using namespace std; #define LL long long #define pi (4*atan(1.0)) #define eps 1e-4 #define bug(x) cout<<"bug"<<x<<endl; const int N=3e5+10,M=4e6+10,inf=2147483647,mod=1e9+7; const LL INF=1e18+10,MOD=1e9+7; struct Matrix { LL a[20][20]; Matrix() { memset(a,0,sizeof(a)); } void init() { for(int i=0;i<18;i++) for(int j=0;j<18;j++) a[i][j]=(i==j); } Matrix operator + (const Matrix &B)const { Matrix C; for(int i=0;i<18;i++) for(int j=0;j<18;j++) C.a[i][j]=(a[i][j]+B.a[i][j])%MOD; return C; } Matrix operator * (const Matrix &B)const { Matrix C; for(int i=0;i<18;i++) for(int k=0;k<18;k++) for(int j=0;j<18;j++) C.a[i][j]=(C.a[i][j]+1LL*a[i][k]*B.a[k][j])%MOD; return C; } Matrix operator ^ (const LL &t)const { Matrix A=(*this),res; res.init(); LL p=t; while(p) { if(p&1)res=res*A; A=A*A; p>>=1; } return res; } }; map<pair<LL,int> ,LL >dp; LL a[N],b[N];int c[N]; Matrix Gbase(int n) { Matrix a; a.init(); for(int i=0;i<=n;i++) { if(i-1>=0)a.a[i-1][i]=1; a.a[i][i]=1; if(i+1<=n)a.a[i+1][i]=1; } return a; } Matrix Gpre(LL x,int n) { Matrix a; a.init(); for(int i=0;i<=n;i++) a.a[0][i]=dp[make_pair(x,i)]; return a; } int main() { int n; LL k; scanf("%d%lld",&n,&k); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%lld%lld%d",&a[i],&b[i],&c[i]); dp[make_pair(0,0)]=1; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { Matrix base=Gbase(c[i]); Matrix pre=Gpre(a[i],c[i]); LL l=a[i],r=min(b[i],k); base=base^(r-l); Matrix ans=pre*base; for(int j=0;j<=c[i];j++) dp[make_pair(r,j)]=ans.a[0][j]; if(b[i]>=k)break; } printf("%lld ",dp[make_pair(k,0)]); return 0; }