Mybatis的基础使用以及与Spring的相关集成在官方文档都写的非常详细,但无论我们采用xml还是注解方式在使用的过程中经常会出现各种奇怪的问题,需要花费大量的时间解决。
抽空了解一下Mybatis的相关源码还是很有必要。
先来看一个简单的Demo:
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
MethodInfo info = (MethodInfo) session.selectOne("com.ycdhz.mybatis.dao.MethodInfoMapper.selectById", 1);
System.out.println(info.toString());
}
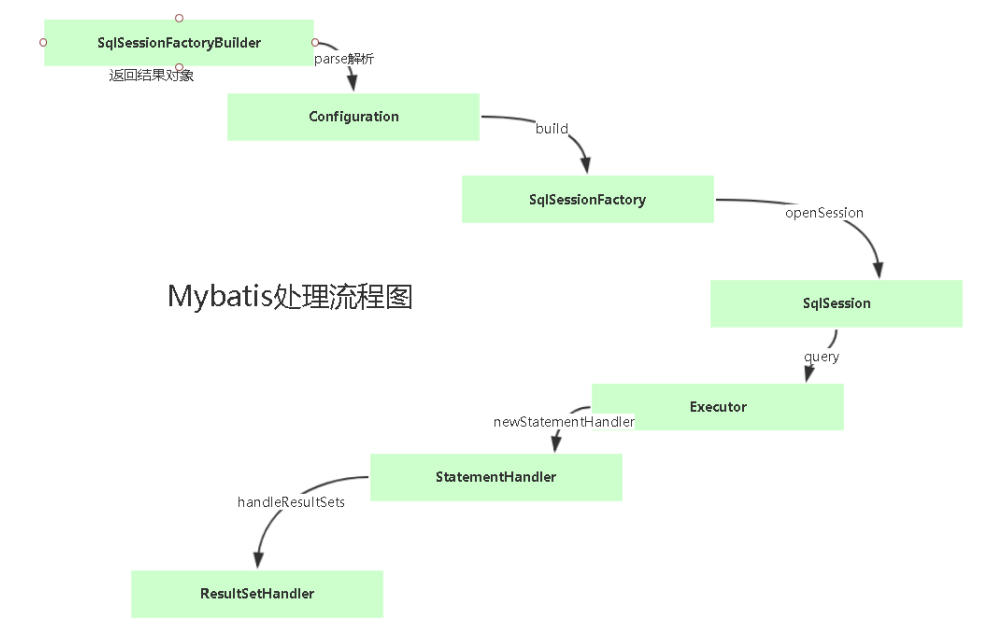
这个是官网中入门的一段代码,我根据自己的情况做了一些参数上的改动。这段代码很容易理解,解析一个xml文件,通过SqlSessionFactoryBuilder构建一个SqlSessionFactory实例。
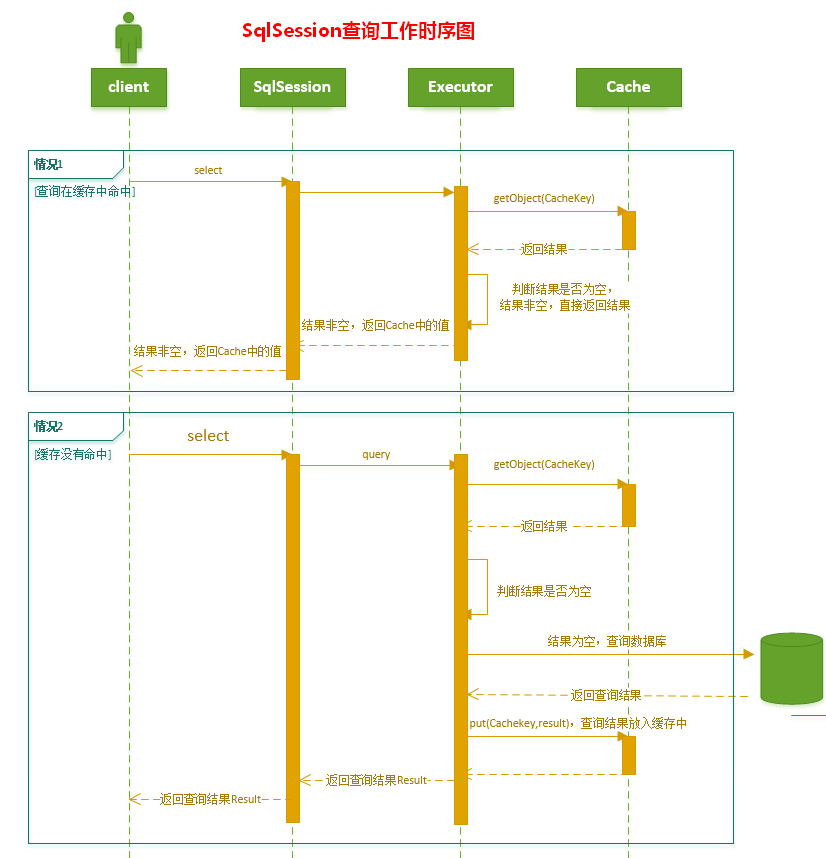
拿到了SqlSessionFactory我们就可以获取SqlSession。SqlSession 包含了面向数据库执行 SQL 命令所需的所有方法,所以我们可以通过 SqlSession 实例来直接执行已映射的 SQL 语句。
代码很简单的展示了Mybatis到底是什么,有什么作用。
Mybatis主线流程:解析Configuration返回SqlSessionFactory;拿到SqlSession对执行器进行初始化 SimpleExecutor;操作数据库;
<!ELEMENT configuration (properties?, settings?, typeAliases?, typeHandlers?, objectFactory?, objectWrapperFactory?, reflectorFactory?, plugins?, environments?, databaseIdProvider?, mappers?)>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mytest"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mybatis/MethodInfoMapper.xml"/>
<!--<mapper class="com.ycdhz.mybatis.dao.MethodInfoMapper" />-->
<!--<package name="com.ycdhz.mybatis.dao" />-->
</mappers>
</configuration>
test()前两行主要是通过流来读取配置文件,我们直接从new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream)这段代码开始:
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) {
return build(inputStream, null, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
// SqlSessionFactoryBuilde拿到输入流后,构建了一个XmlConfigBuilder的实例。通过parse()进行解析
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
//XmlConfigBuilder.parse()解析完后将数据传给DefaultSqlSessionFactory
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
}
public class XMLConfigBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private boolean parsed;
private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) {
super(new Configuration());
ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration");
this.parsed = false;
}
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
//这个方法主要就是解析xml文件了
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
mybatis-config.xml 文件中的mapper属性支持四种配置方式,但是只有package,class这两种发式支持通过注解来配置和映射原生信息(原因在于configuration.addMappers()这个方法)。
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
addMappers()调用了MapperAnnotationBuilder.parse()这样一段代码。我们发现当resource不为空的时候,代码首先会调用loadXmlResource()去Resource文件夹下查找(com/ycdhz/mybatis/dao/MethodInfoMapper.xml),
如果发现当前文件就加载。但实际这个时候type信息来自注解,MethodInfoMapper.xml在容器中被加载两次。所以Configruation下的静态类StrictMap.put()时会抛出一个 Mapped Statements collection already contains value for com.ycdhz.mybatis.dao.MethodInfoMapper.selectById 的异常
public class MapperAnnotationBuilder {
public void parse() {
String resource = type.toString();
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
loadXmlResource();
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
parseCache();
parseCacheRef();
Method[] methods = type.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
try {
// issue #237
if (!method.isBridge()) {
parseStatement(method);
}
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
parsePendingMethods();
}
private void loadXmlResource() {
// Spring may not know the real resource name so we check a flag
// to prevent loading again a resource twice
// this flag is set at XMLMapperBuilder#bindMapperForNamespace
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded("namespace:" + type.getName())) {
String xmlResource = type.getName().replace('.', '/') + ".xml";
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(type.getClassLoader(), xmlResource);
} catch (IOException e) {
// ignore, resource is not required
}
if (inputStream != null) {
XMLMapperBuilder xmlParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, assistant.getConfiguration(), xmlResource, configuration.getSqlFragments(), type.getName());
xmlParser.parse();
}
}
}
}
这个时候我们已经完成了xml文件的解析过程,拿到了DefaultSqlSessionFactory。下面我们再来看一下sqlSessionFactory.openSession()的过程:
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory{
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}
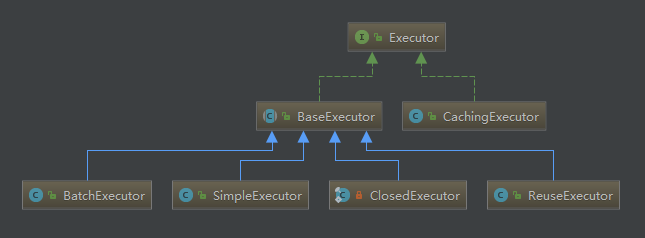
public class Configuration {
protected boolean cacheEnabled = true;
protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE;
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain();
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
}
openSession()方法会调用DefaultSqlSessionFactory.openSessionFromDataSource()方法,在这个方法中会开启事务、创建了执行器Executor:
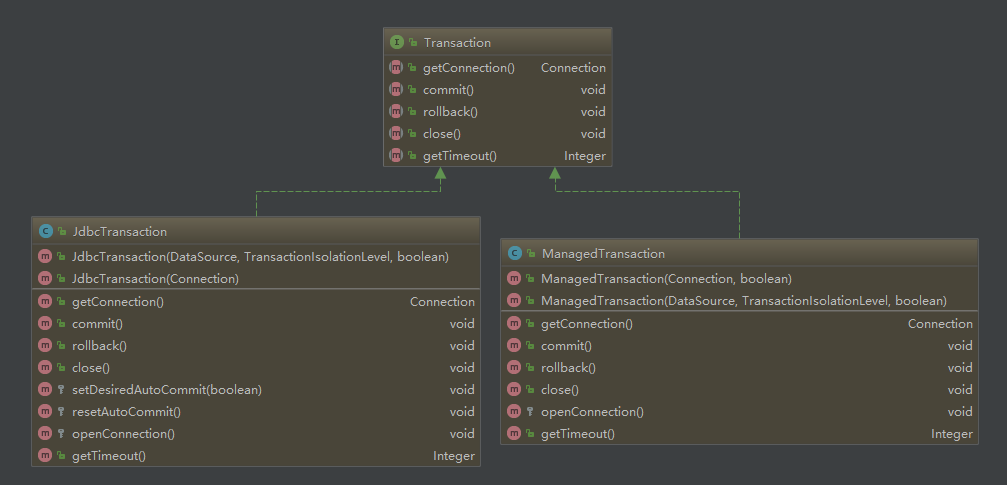
MyBatis的事务管理分为两种形式(配置mybatis-config.xml文件的transactionManager属性):
1)使用JDBC的事务管理机制:即利用java.sql.Connection对象完成对事务的提交(commit())、回滚(rollback())、关闭(close())等
2)使用MANAGED的事务管理机制:这种机制MyBatis自身不会去实现事务管理,而是让程序的容器如(JBOSS,Weblogic)来实现对事务的管理
执行器ExecutorType分为三类(默认使用的是ExecutorType.SIMPLE):
1)ExecutorType.SIMPLE: 这个执行器类型不做特殊的事情。它为每个语句的执行创建一个新的预处理语句。
2)ExecutorType.REUSE: 这个执行器类型会复用预处理语句。
3)ExecutorType.BATCH: 这个执行器会批量执行所有更新语句,如果 SELECT 在它们中间执行还会标定它们是 必须的,来保证一个简单并易于理解的行为。
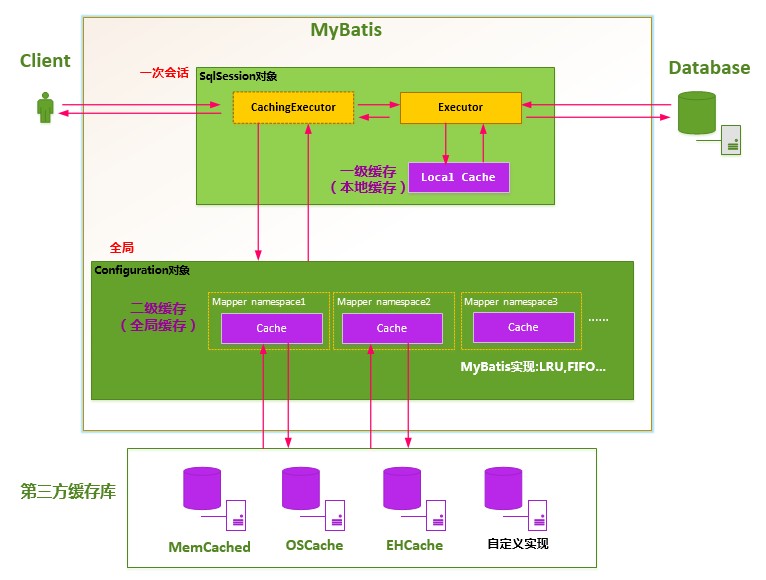
因为Mybatis的一级缓存是默认开启的,查看newExecutor()不难发现,最后通过CachingExecutor对SimpleExecutor进行了装饰(详细代码可以查看https://www.cnblogs.com/jiangyaxiong1990/p/9236764.html)
Mybatis缓存设计成两级结构,分为一级缓存、二级缓存:(参考 https://blog.csdn.net/luanlouis/article/details/41280959 )
1)一级缓存是Session会话级别的缓存,位于表示一次数据库会话的SqlSession对象之中,又被称之为本地缓存。默认情况下自动开启,用户没有定制它的权利(不过这也不是绝对的,可以通过开发插件对它进行修改);
实际上MyBatis的一级缓存是使用PerpetualCache来维护的,PerpetualCache实现原理其实很简单,其内部就是通过一个简单的HashMap<k,v> 来实现的,没有其他的任何限制。
2)二级缓存是Application应用级别的缓存,它的是生命周期很长,跟Application的声明周期一样,也就是说它的作用范围是整个Application应用。
MyBatis的二级缓存设计得比较灵活,你可以使用MyBatis自己定义的二级缓存实现;你也可以通过实现org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache接口自定义缓存;也可以使用第三方内存缓存库,如Redis等