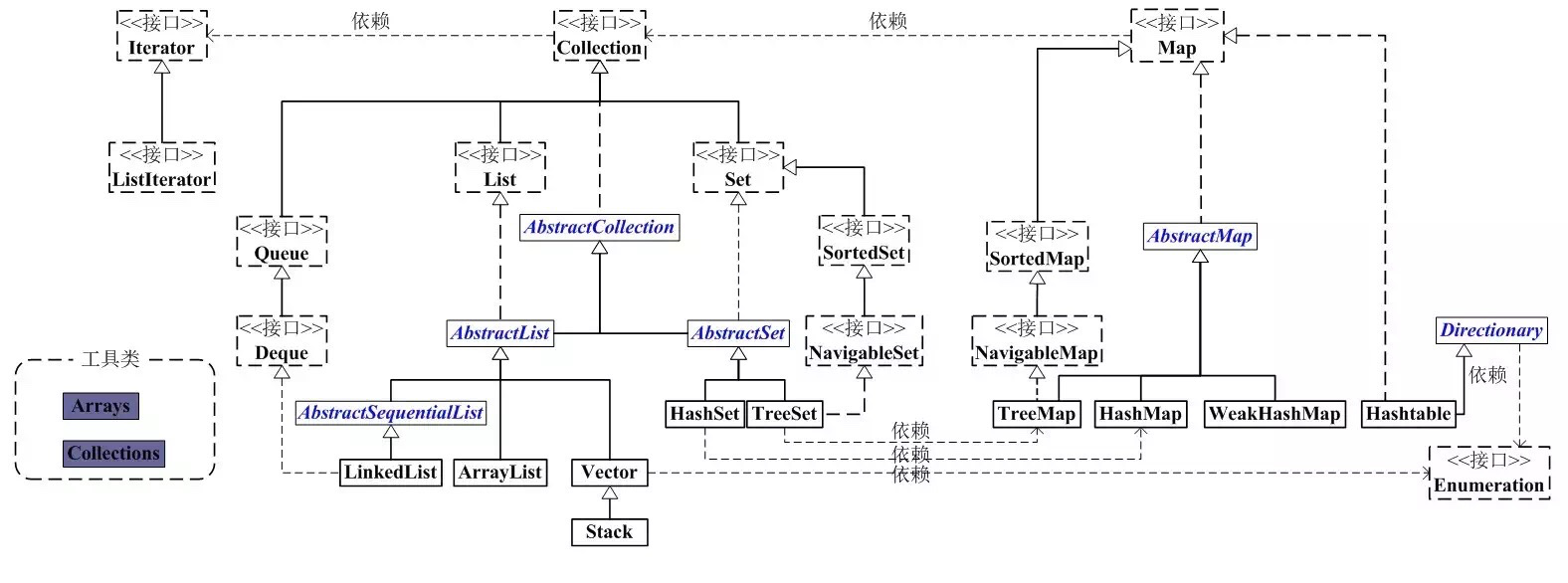
扩容的容器: ArrayList 、HashSet、TreeSet、HashMap、WeakHashMap 、Hashtable 再加一个常用的StringBuilder
LinkedList它的底层是用双向链表实现的,没有初始化大小,也没有扩容的机制;
TreeMap由红黑树实现,容量方面没有限制;
1.ArrayList
底层实现为数组存储在内存中,线程不同步;新增元素时
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) { if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } return minCapacity; }
/*计算长度,如果为空,则取默认长度10与参数的最大值*/
判断如果容器装不下,则调用grow方法扩容。
private void grow(int minCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);//原长度+原长度右移一位(可以看成1.5倍) if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);//太长了就调hugeCapacity方法 // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
2.HashSet
我看这个是直接调用的HashMap的put方法
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
3.TreeSet
调用的是map类的:put(K key, V value);方法
public boolean add(E e) {
return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
4.HashMap
/**
* Initializes or doubles table size. If null, allocates in
* accord with initial capacity target held in field threshold.
* Otherwise, because we are using power-of-two expansion, the
* elements from each bin must either stay at same index, or move
* with a power of two offset in the new table.
*
* @return the table
*/
初始化或加倍表大小。如果为空,则在符合场阈值内的初始容量目标。否则,因为我们使用的是二次展开的能力每个bin中的元素必须保持在同一索引中,或者移动在新表中有两个偏移量的幂。
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
https://www.iteye.com/topic/539465
当hashmap中的元素越来越多的时候,碰撞的几率也就越来越高(因为数组的长度是固定的),所以为了提高查询的效率,就要对hashmap的数组进行扩容,数组扩容这个操作也会出现在ArrayList中,所以这是一个通用的操作,很多人对它的性能表示过怀疑,不过想想我们的“均摊”原理,就释然了,而在hashmap数组扩容之后,最消耗性能的点就出现了:原数组中的数据必须重新计算其在新数组中的位置,并放进去,这就是resize。
那么hashmap什么时候进行扩容呢?当hashmap中的元素个数超过数组大小*loadFactor时,就会进行数组扩容,loadFactor的默认值为0.75,也就是说,默认情况下,数组大小为16,那么当hashmap中元素个数超过16*0.75=12的时候,就把数组的大小扩展为2*16=32,即扩大一倍,然后重新计算每个元素在数组中的位置,而这是一个非常消耗性能的操作,所以如果我们已经预知hashmap中元素的个数,那么预设元素的个数能够有效的提高hashmap的性能。比如说,我们有1000个元素new HashMap(1000), 但是理论上来讲new HashMap(1024)更合适,不过上面annegu已经说过,即使是1000,hashmap也自动会将其设置为1024。 但是new HashMap(1024)还不是更合适的,因为0.75*1000 < 1000, 也就是说为了让0.75 * size > 1000, 我们必须这样new HashMap(2048)才最合适,既考虑了&的问题,也避免了resize的问题。
5.WeakHashMap
public V put(K key, V value) {
Object k = maskNull(key);
int h = hash(k);
Entry<K,V>[] tab = getTable();
int i = indexFor(h, tab.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (h == e.hash && eq(k, e.get())) {
V oldValue = e.value;
if (value != oldValue)
e.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
Entry<K,V> e = tab[i];
tab[i] = new Entry<>(k, value, queue, h, e);
if (++size >= threshold)
resize(tab.length * 2);
return null;
}
调用了他自己的resize方法,入参是当前table长度的二倍
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry<K,V>[] oldTable = getTable();
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry<K,V>[] newTable = newTable(newCapacity);
transfer(oldTable, newTable);
table = newTable;
/*
* If ignoring null elements and processing ref queue caused massive
* shrinkage, then restore old table. This should be rare, but avoids
* unbounded expansion of garbage-filled tables.
*/
if (size >= threshold / 2) {
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
} else {
expungeStaleEntries();
transfer(newTable, oldTable);
table = oldTable;
}
}
6.Hashtable
value不能为空,有synchronized
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
}
7.StringBuilder
左移一位+2
private int newCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int newCapacity = (value.length << 1) + 2;
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) {
newCapacity = minCapacity;
}
return (newCapacity <= 0 || MAX_ARRAY_SIZE - newCapacity < 0)
? hugeCapacity(minCapacity)
: newCapacity;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minimumCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minimumCapacity - value.length > 0) {
value = Arrays.copyOf(value,
newCapacity(minimumCapacity));
}
}
@Override
public AbstractStringBuilder append(CharSequence s, int start, int end) {
if (s == null)
s = "null";
if ((start < 0) || (start > end) || (end > s.length()))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
"start " + start + ", end " + end + ", s.length() "
+ s.length());
int len = end - start;
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
for (int i = start, j = count; i < end; i++, j++)
value[j] = s.charAt(i);
count += len;
return this;
}