采用面向对象的方法描述算法
面向对象的概念
面向对象程序程序设计的本质是把数据和处理数据的过程当成一个整体即对象。
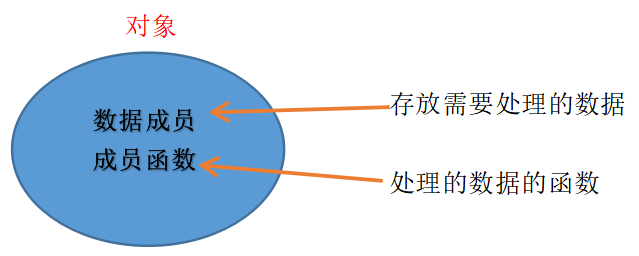
(1) 对象
- 对象是人们要进行研究的任何实际存在的事物。
- 具有属性(用数据来描述)和方法(用于处理数据的算法)。
定义对象:如
Box Box1; // 声明 Box1,类型为 Box Box Box2; // 声明 Box2,类型为 Box
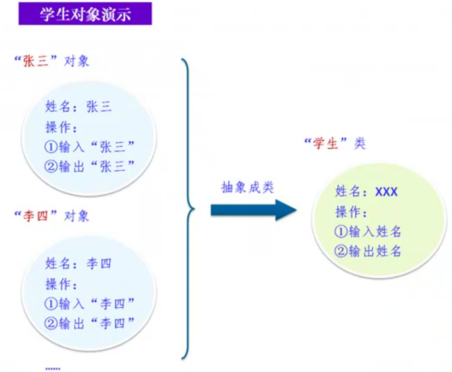
(2) 类
- 把众多事物归纳,划分成一些类。
- 把具有共性的事物划分为一类。得出一个抽象的概念。
- 是人们认识世界经常采用的思维方法。
|
概念 |
描述 |
|
类的成员函数是指那些把定义和原型写在类定义内部的函数,就像类定义中的其他变量一样。 |
|
|
类成员可以被定义为 public、private 或 protected。默认情况下是定义为 private。 |
|
|
类的构造函数是一种特殊的函数,在创建一个新的对象时调用。类的析构函数也是一种特殊的函数,在删除所创建的对象时调用。 |
|
|
拷贝构造函数,是一种特殊的构造函数,它在创建对象时,是使用同一类中之前创建的对象来初始化新创建的对象。 |
|
|
友元函数可以访问类的 private 和 protected 成员。 |
|
|
通过内联函数,编译器试图在调用函数的地方扩展函数体中的代码。 |
|
|
每个对象都有一个特殊的指针 this,它指向对象本身。 |
|
|
指向类的指针方式如同指向结构的指针。实际上,类可以看成是一个带有函数的结构。 |
|
|
类的数据成员和函数成员都可以被声明为静态的。 |
(3) 继承
- 类与类之间可以组成继承层次。
- 一个类的定义(称为子类)可以定义在另一个已定义类(称为父类)的基础上。
- 子类可以继承父类中的属性和操作。也可以定义自己的属性和操作,从而是内部表示上有差异的对象可以共享与它们结构有共同部分的有关操作,达到代码重用的目的。
class derived-class: access-specifier base-class
细节可以查看【菜鸟教程】。
(4) 消息
- 对象引用一个方法的过程称为向该对象发送一个消息,或者说一个对象接受到一个服务请求。
- 消息是对象之间交互的手酸。
面向对象=对象+类+继承+消息
面向对象的方法的主要优点
- 与人们习惯的思维方式一致
- 可重用性好
- 可维护性好
演示代码:
Animal类:
//Class Animal #include<iostream> using namespace std; class Animal { public: Animal(){} ~Animal(){} virtual int SetAge(){return -1;} /* private: dog(int age): itsAge(age){} ~dog(){} int SetAge(){return itsAge;} */ }; class dog: public Animal { public: dog(int age): itsAge(age){} ~dog(){} int SetAge(){return itsAge;} private: int itsAge; }; int main() { Animal * sp; sp = new dog(3); cout<< "The age of dog is " << sp->SetAge() <<endl; delete sp; return 0; }
BaseClass类
//BaseClass class. #include<iostream> using namespace std; class BaseClass { public: void fun0(){cout<< "Generating construct of BaseClass!" <<endl;} BaseClass(); ~BaseClass(){} void fun1(){cout<< "Generating construct of BaseClass!" <<endl;} virtual int SetNumber(){return -1;} }; BaseClass::BaseClass() { cout<< "Construct the base class object!" <<endl; } class DerivedClass: public BaseClass { public: void fun2(){cout<< "Generating construct of DerivedClass!" <<endl;} DerivedClass(int number): itsNumber(number){} ~DerivedClass(){} void fun3(){cout<< "Generating construct of DerivedClass!" <<endl;} int SetNumber(){return itsNumber;} private: int itsNumber; }; int main() { BaseClass * sp; sp = new DerivedClass(3); cout<< "The number of DerivedClass is " << sp->SetNumber() <<endl; delete sp; return 0; }
Vehicle类
//Vehicle class. #include<iostream> using namespace std; class vehicle { public: vehicle(){} ~vehicle(){} virtual int SetNum(){return -1;} }; class bicycle: public vehicle { public: bicycle(int Height): itsHeight(Height){} ~bicycle(){} int SetNum(){return itsHeight;} private: int itsHeight; }; // class motorcar: virtual public vehicle { public: motorcar(int SeatNum): itsSeatNum(SeatNum){} ~motorcar(){} int SetNum(){return itsSeatNum;} private: int itsSeatNum; }; int main() { vehicle * sp; sp = new bicycle(3); cout<< "The number of bicycle is " << sp->SetNum() <<endl; delete sp; sp = new motorcar(5); cout<< "The number of motorcar is " << sp->SetNum() <<endl; delete sp; return 0; }
People类
//Class people #include<iostream> #include<string> #include<cstring> #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> using namespace std; class Data { public: Data() {} Data(int yy, int mm, int dd); Data(Data &ap); ~Data(); int get_year(); int get_month(); int get_day(); void set_year(int y); void set_month(int m); void set_day(int d); private: int year; int month; int day; }; Data::Data(int yy, int mm, int dd) { year = yy; month = mm; day = dd; } Data::Data(Data &ap) { year = ap.year; month = ap.month; day = ap.day; } Data::~Data() { } int Data::get_day() { return day; } int Data::get_month() { return month; } int Data::get_year() { return year; } void Data::set_day(int d) { day = d; } void Data::set_month(int m) { month = m; } void Data::set_year(int y) { year = y; } class People { public: People(int num, string se, Data birthd, string iid); People(People &tp); People() {} People get_People(); ~People() { } void set_number(int num) { number = num; } void set_sex(string se) { sex = se; } void set_birthday(Data birth) { birthday = birth; } void set_id(string iidd) { id = iidd; } int get_number(); string get_sex(); Data get_birthday(); string get_id(); void details(); private: int number; string sex; Data birthday; string id; }; inline int People::get_number() { return number; } inline string People::get_sex() { return sex; } inline string People::get_id() { return id; } Data People::get_birthday() { return birthday; } void People::details() { cout << "Number:" << number << endl; cout << "Sex:" << sex << endl; cout << "Birhtday:" << birthday.get_year() << "/" << birthday.get_month() << "/" << birthday.get_day() << endl; cout << "ID:" << id << endl; } People::People(int num, string se, Data birth, string iid) :birthday(birth) { number = num; sex = se; id = iid; } People People::get_People() { int num, yy, mm, dd; string ID, se; cout << "Please enter the number of the people:"; cin >> num; cout << "Please enter the sex of the people:(male or female)"; cin >> se; cout << "Please enter the birthday of the people:" << endl << "(Warnning:The format is similar to 1998 8 3)" << endl; cin >> yy >> mm >> dd; cout << "Please enter the id of the people:"; cin >> ID; Data birth(yy, mm, dd); id = ID; number = num; sex = se; birthday = birth; return *this; } People::People(People &tp) { number = tp.get_number(); sex = tp.get_sex(); id = tp.get_id(); birthday = tp.get_birthday(); } class Student :virtual public People { public: char classNo[7]; Student(int num, string se, Data birthd, string iid, char a[7]) :People(num, se, birthd, iid) { strcpy(classNo, a); } ~Student() { }; void Show_Student() { cout << "This is student:" << endl; cout << "ClassNo :" << classNo << endl; } }; class Teacher :virtual public People { public: char principalship[11]; char department[21]; Teacher(int num, string se, Data birthd, string iid, char a[11],char b[21]) :People(num, se, birthd, iid) { strcpy(principalship, a); strcpy(department, b); } Teacher() { } void Show_Teacher() { cout << "This is teacher:" << endl; cout << "Principalship :" << principalship << endl; cout << "Department :" << department << endl; } }; class Graduate :virtual public Student { public: char subject[21]; Teacher adviser; Graduate(int num, string se, Data birthd, string iid, char a[7], char c[21],Teacher vt) :People(num, se, birthd, iid), Student(num, se, birthd, iid, a) { strcpy(subject, c); adviser = vt; } ~Graduate() { } void Show_Graduate() { cout << "This is Graduate:" << endl; cout << "The subject:" << subject << endl; cout << "The adviser teacher:" << endl; cout << "Principalship:" << adviser.principalship<< endl; cout << "Department:" << adviser.department << endl; cout << endl; } }; class TA :public Graduate, public Teacher { TA(int num, string se, Data birthd, string iid, char a[7], char c[21], Teacher vt) :People(num, se, birthd, iid), Student(num, se, birthd, iid, a), Graduate(num, se, birthd, iid, a, c, vt) { } ~TA() { } void Show_TA() { cout << "This is TA:" << endl; cout << "The classNo:" << classNo << endl; } }; int main() { People asp; asp.get_People(); asp.details(); Data a(1998, 8, 3); Student b(18,"male",a,"110","001"); b.Show_Student(); Data a1(1987, 8, 3); Teacher c(25, "female", a1,"1614","Advanced", "Promotion"); c.Show_Teacher(); Data a2(1990, 8, 3); Graduate d(22, "female", a2, "1013", "111", "CS", c); d.Show_Graduate(); return 0; }
参考
【1】 李春葆,数据结构教程,清华大学出版社。
【2】 菜鸟教程。