1. 选择开发工具
我们小组集中讨论后,决定以Eclipse做为我们的开发工具 。我从前已经安装并使用过Eclipse开发工具,开发工具截图如下图1.

2. 练习自动单元测试技术
2.1 编写被测试类
由于我曾经使用过Junit进行单元测试,所以这里直接使用Junit工具生成测试方法的方法进行7大常见排序算法的测试,排序算法如下。
public class Sort {
// 冒泡排序
public static int[] bubbleSort(int[] arr){
int len = arr.length;
for(int i=0;i<len-1 ;i++){
for(int j=i;j < len-1 ;j++){
if(arr[j] > arr[j+1]){
int temp ;
temp = arr[j];
arr[j]=arr[j+1];
arr[j+1]=temp;
}
}
}
return arr;
}
// 选择排序
public static int[] selectSort(int[] arr){
int len = arr.length;
for(int i=0;i<len-1;i++){
int k=i;
for(int j=k+1;j<len;j++){
if(arr[k]>arr[j]){
k=j;
}
}
if(i!=k){
int temp ;
temp = arr[k];
arr[k]=arr[i];
arr[i]=temp;
}
}
return arr;
}
// 快速排序
public static void quickSort(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
if (low >= high)
return;
int left = low;
int right = high;
int key = arr[left];
while (left < right) {
while (left < right && arr[right] >= key)
right--;
if (left < right) {
arr[left] = arr[right];
left++;
}
while (left < right && arr[left] <= key)
left++;
if (left < right) {
arr[right] = arr[left];
right--;
}
}
arr[left] = key;
quickSort(arr, low, left - 1);
quickSort(arr, right + 1, high);
}
// 插入排序
public static void insertSort(int[] arr) {
int temp;
int len = arr.length;
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
if (arr[i] < arr[i - 1]) {
temp = arr[i];
int j;
for (j = i - 1; arr[j] > arr[i] && j >= 0; j--)
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
// 堆排序
public static void heapSort(int[] arr) {
for (int i = (arr.length - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--) {// 建立小顶堆
heapAdjust(arr, i, arr.length - 1);
}
for (int i = arr.length - 1; i >= 1; i--) {//
int t = arr[0];// 堆顶元素与堆最后一个元素交换,并重新调整为小顶堆
arr[0] = arr[i];
arr[i] = t;
heapAdjust(arr, 0, i - 1);
// System.out.println(arr[0]);
}
}
public static void heapAdjust(int[] arr, int s, int m) {//调整堆为小顶堆
int rc = arr[s];
int j;
for (j = s * 2; j <= m; j *= 2) {
if (j < m && arr[j] > arr[j + 1])
j++;
if (rc <= arr[j])
break;
arr[s] = arr[j];
s = j;
}
arr[s] = rc;
}
// 归并排序
public static int[] arr1 = new int[100];
public static void mergeSort(int[] arr, int s, int m) {
if (s == m) {
arr1[s] = arr[s];
} else {
int mid = (s + m) / 2;
mergeSort(arr, s, mid);
mergeSort(arr, mid + 1, m);
merge(arr, s, mid, m);
}
}
public static void merge(int[] arr, int s, int mid, int m) {
int k, j;
for (k = s, j = mid + 1; s <= mid && j <= m; k++) {
if (arr[s] <= arr[j]) {
arr1[k] = arr[s++];
} else {
arr1[k] = arr[j++];
}
}
if (s <= mid) {
for (; s <= mid; s++) {
arr1[k++] = arr[s];
}
}
if (j <= m) {
for (; j <= m; j++) {
arr1[k++] = arr[j];
}
}
}
// 希尔排序
public static void shellSort(int[] arr) {
int gap;// 增量
for (gap = arr.length / 2; gap > 0; gap = gap / 2) {
for (int j = gap; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[j - gap]) {
int temp = arr[j];
int i;
for (i = j - gap; i >= 0 && arr[i] > temp; i -= gap) {
arr[i + gap] = arr[i];
}
arr[i + gap] = temp;
}
}
}
}
2.2 测试类
Junit工具生成测试方法具体过程如下:
Junit工具生成的测试方法:
import org.junit.Test;
import Coding.Sort;
public class SortTest {
@Test
public void testBubbleSort() {// 测试冒泡排序
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 34, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 123, 124 };
int[] res = { 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 34, 123, 124 };
assertArrayEquals("实际结果与预期结果不一致", res, Sort.bubbleSort(arr));
}
@Test
public void testSelectSort() {// 测试选择排序
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 34, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 123, 124 };
int[] res = { 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 34, 123, 124 };
assertArrayEquals("实际结果与预期结果不一致", res, Sort.selectSort(arr));
}
@Test
public void testQuickSort() {// 测试快速排序
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 34, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 123, 124 };
int[] res = { 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 34, 123, 124 };
Sort.quickSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
assertArrayEquals("实际结果与预期结果不一致", res, arr);
}
@Test
public void testInsertSort() {// 测试插入排序
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 34, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 123, 124 };
int[] res = { 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 34, 123, 124 };
Sort.insertSort(arr);
assertArrayEquals("实际结果与预期结果不一致", res, arr);
}
@Test
public void testHeapSort() {// 测试堆排序
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 34, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 123, 124 };
int[] res = { 124, 123, 34, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 2, 1 };
Sort.heapSort(arr);
assertArrayEquals("实际结果与预期结果不一致", res, arr);
}
@Test
public void testMergeSort() {// 测试归并排序
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 34, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 123, 124 };
Sort.mergeSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
@Test
public void testShellSort() {// 测试希尔排序
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 34, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 123, 124 };
int[] res = { 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 34, 123, 124 };
Sort.shellSort(arr);
assertArrayEquals("实际结果与预期结果不一致", res, arr);
}
}
## 2.3 运行测试类
<font face="微软雅黑" size=3 >  右键点击Run as ->JunitTest 运行测试类,结果如下:</font>
<center>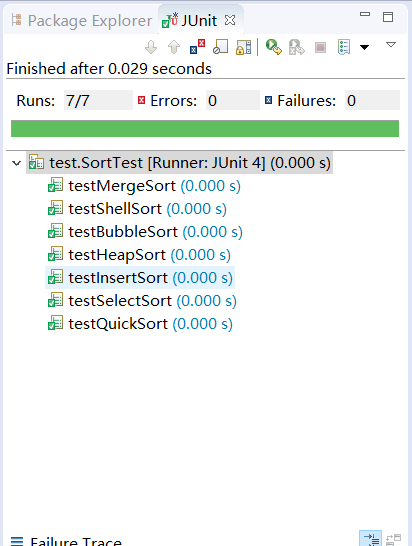</center>
<font face="宋体" size=3 ><center>**图5**</center></font>