1. IoU(区域交并比)
计算IoU的公式如下图,可以看到IoU是一个比值,即交并比。
在分子中,我们计算预测框和ground-truth之间的重叠区域;
分母是并集区域,或者更简单地说,是预测框和ground-truth所包含的总区域。
重叠区域和并集区域的比值,就是IoU。

1.1 为什么使用IoU来评估目标检测器
与分类任务不同,我们预测的bounding box的坐标需要去匹配ground-truth的坐标,而坐标完全匹配基本是不现实的。因此,我们需要定义一个评估指标,奖励那些与ground-truth匹配较好(重叠较大)的预测框。
1.2 IoU的python实现
1 def bb_intersection_over_union(boxA, boxB): 2 # determine the (x, y)-coordinates of the intersection rectangle 3 # 画个图会很明显,x左、y上取大的,x右、y下取小的,刚好对应交集 4 xA = max(boxA[0], boxB[0]) 5 yA = max(boxA[1], boxB[1]) 6 xB = min(boxA[2], boxB[2]) 7 yB = min(boxA[3], boxB[3]) 8 9 # compute the area of intersection rectangle 10 # 计算交集部分面积 11 interArea = max(0, xB - xA + 1) * max(0, yB - yA + 1) 12 13 # compute the area of both the prediction and ground-truth rectangles 14 # 计算预测值和真实值的面积 15 boxAArea = (boxA[2] - boxA[0] + 1) * (boxA[3] - boxA[1] + 1) 16 boxBArea = (boxB[2] - boxB[0] + 1) * (boxB[3] - boxB[1] + 1) 17 18 # compute the intersection over union by taking the intersection 19 # area and dividing it by the sum of prediction + ground-truth 20 # areas - the interesection area 21 # 计算IoU,即 交/(A+B-交) 22 iou = interArea / float(boxAArea + boxBArea - interArea) 23 24 # return the intersection over union value 25 return iou
2. 非极大化抑制(NMS)
2.1 算法思想
所谓非极大值抑制:先假设有6个输出的矩形框(即proposal_clip_box),根据分类器类别分类概率做排序,从小到大分别属于车辆的概率(scores)分别为A、B、C、D、E、F。
(1)从最大概率矩形框F开始,分别判断A~E与F的重叠度IOU是否大于某个设定的阈值;
(2)假设B、D与F的重叠度超过阈值,那么就扔掉B、D;并标记第一个矩形框F,是我们保留下来的。
(3)从剩下的矩形框A、C、E中,选择概率最大的E,然后判断E与A、C的重叠度,重叠度大于一定的阈值,那么就扔掉;并标记E是我们保留下来的第二个矩形框。
就这样一直重复,找到所有被保留下来的矩形框。
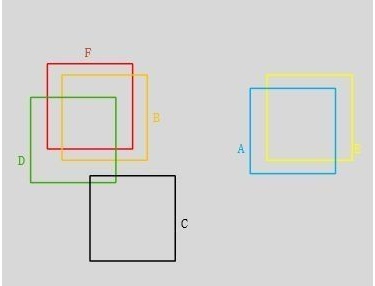
如上图F与BD重合度较大,可以去除BD。AE重合度较大,我们删除A,保留scores较大的E。C和其他重叠都小保留C。最终留下了C、E、F三个。
2.2 python实现
1.无条件保留置信度最高的框;
2.删除与保留框IOU大于阈值的候选框;
1 # -------------------------------------------------------- 2 # Fast R-CNN 3 # Copyright (c) 2015 Microsoft 4 # Licensed under The MIT License [see LICENSE for details] 5 # Written by Ross Girshick 6 # -------------------------------------------------------- 7 8 import numpy as np 9 10 def py_cpu_nms(dets, thresh): 11 """Pure Python NMS baseline.""" 12 x1 = dets[:, 0] 13 y1 = dets[:, 1] 14 x2 = dets[:, 2] 15 y2 = dets[:, 3] 16 scores = dets[:, 4] 17 18 areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1) 19 order = scores.argsort()[::-1] 20 21 keep = [] 22 while order.size > 0: 23 i = order[0] 24 keep.append(i) 25 xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]]) 26 yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]]) 27 xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]]) 28 yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]]) 29 30 w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1) 31 h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1) 32 inter = w * h 33 ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter) 34 35 inds = np.where(ovr <= thresh)[0] 36 order = order[inds + 1] 37 38 return keep
3. soft-NMS
soft NMS提出尤其对密集物体检测的检测效果有一定的提升作用
绝大部分目标检测方法,最后都要用到 NMS-非极大值抑制进行后处理。 通常的做法是将检测框按得分排序,然后保留得分最高的框,同时删除与该框重叠面积大于一定比例的其它框。
这种贪心式方法存在如下图所示的问题: 红色框和绿色框是当前的检测结果,二者的得分分别是0.95和0.80。如果按照传统的NMS进行处理,首先选中得分最高的红色框,然后绿色框就会因为与之重叠面积过大而被删掉。
另一方面,NMS的阈值也不太容易确定,设小了会出现下图的情况(绿色框因为和红色框重叠面积较大而被删掉),设置过高又容易增大误检。

soft NMS算法的大致思路为:M为当前得分最高框,bi 为待处理框,bi 和M的IOU越大,bi 的得分si 就下降的越厉害。
算法结构如图所示:
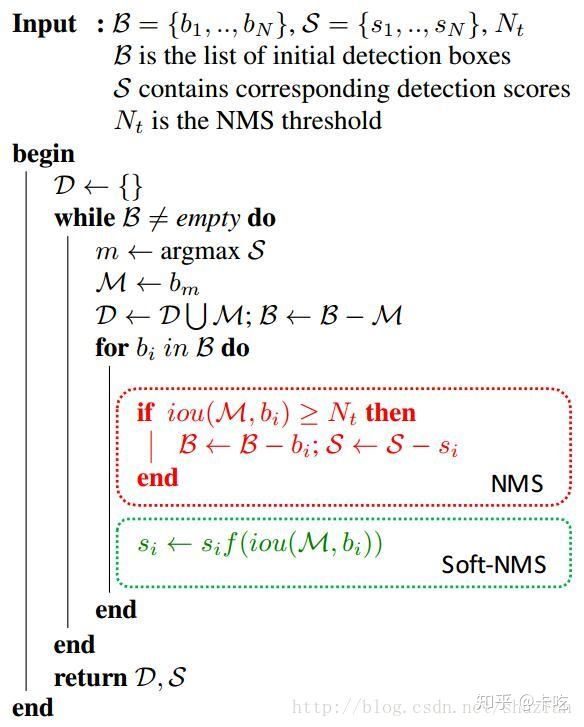
NMS中:
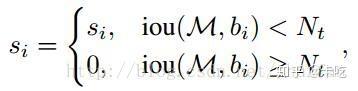
soft NMS中:
(1)线性加权:
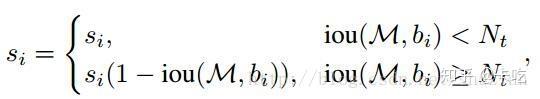
(2)高斯加权:
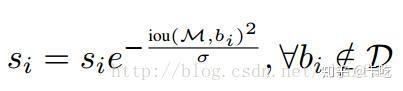
soft NMS仍然有问题:其阈值仍然需要手工设定
soft nms 代码实现:
# coding:utf-8 import numpy as np def soft_nms(boxes, sigma=0.5, Nt=0.1, threshold=0.001, method=1): N = boxes.shape[0] pos = 0 maxscore = 0 maxpos = 0 for i in range(N): maxscore = boxes[i, 4] maxpos = i tx1 = boxes[i,0] ty1 = boxes[i,1] tx2 = boxes[i,2] ty2 = boxes[i,3] ts = boxes[i,4] pos = i + 1 # get max box while pos < N: if maxscore < boxes[pos, 4]: maxscore = boxes[pos, 4] maxpos = pos pos = pos + 1 # add max box as a detection boxes[i,0] = boxes[maxpos,0] boxes[i,1] = boxes[maxpos,1] boxes[i,2] = boxes[maxpos,2] boxes[i,3] = boxes[maxpos,3] boxes[i,4] = boxes[maxpos,4] # swap ith box with position of max box boxes[maxpos,0] = tx1 boxes[maxpos,1] = ty1 boxes[maxpos,2] = tx2 boxes[maxpos,3] = ty2 boxes[maxpos,4] = ts tx1 = boxes[i,0] ty1 = boxes[i,1] tx2 = boxes[i,2] ty2 = boxes[i,3] ts = boxes[i,4] pos = i + 1 # NMS iterations, note that N changes if detection boxes fall below threshold while pos < N: x1 = boxes[pos, 0] y1 = boxes[pos, 1] x2 = boxes[pos, 2] y2 = boxes[pos, 3] s = boxes[pos, 4] area = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1) iw = (min(tx2, x2) - max(tx1, x1) + 1) if iw > 0: ih = (min(ty2, y2) - max(ty1, y1) + 1) if ih > 0: ua = float((tx2 - tx1 + 1) * (ty2 - ty1 + 1) + area - iw * ih) ov = iw * ih / ua #iou between max box and detection box if method == 1: # linear if ov > Nt: weight = 1 - ov else: weight = 1 elif method == 2: # gaussian weight = np.exp(-(ov * ov)/sigma) else: # original NMS if ov > Nt: weight = 0 else: weight = 1 boxes[pos, 4] = weight*boxes[pos, 4] print(boxes[:, 4]) # if box score falls below threshold, discard the box by swapping with last box # update N if boxes[pos, 4] < threshold: boxes[pos,0] = boxes[N-1, 0] boxes[pos,1] = boxes[N-1, 1] boxes[pos,2] = boxes[N-1, 2] boxes[pos,3] = boxes[N-1, 3] boxes[pos,4] = boxes[N-1, 4] N = N - 1 pos = pos - 1 pos = pos + 1 keep = [i for i in range(N)] return keep boxes = np.array([[100, 100, 150, 168, 0.63],[166, 70, 312, 190, 0.55],[221, 250, 389, 500, 0.79],[12, 190, 300, 399, 0.9],[28, 130, 134, 302, 0.3]]) keep = soft_nms(boxes) print(keep)
参考链接:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/47189358
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/70768666
https://blog.csdn.net/leviopku/article/details/80886386