函数
- 函数可以用来定义可重复代码,组织和简化
- 一般来说一个函数在实际开发中为一个小功能
- 一个类为一个大功能
- 同样函数的长度不要超过一屏
Python中的所有函数实际上都是有返回值(return None),
如果你没有设置return,那么Python将不显示None.
如果你设置return,那么将返回出return这个值.
In [29]:
def HJN():
print('Hello')
return 1000
In [30]:
b=HJN()
print(b)
In [3]:
HJN
Out[3]:
In [10]:
def panduan(number):
if number % 2 == 0:
print('O')
else:
print('J')
In [13]:
panduan(number=1)
In [12]:
panduan(2)
定义一个函数
def function_name(list of parameters):
do something


- 以前使用的random 或者range 或者print.. 其实都是函数或者类
函数的参数如果有默认值的情况,当你调用该函数的时候: 可以不给予参数值,那么就会走该参数的默认值 否则的话,就走你给予的参数值.
In [31]:
import random
In [ ]:
def hahah():
n = random.randint(0,5)
while 1:
N = eval(input('>>'))
if n == N:
print('smart')
break
elif n < N:
print('太小了')
elif n > N:
print('太大了')
调用一个函数
- functionName()
- "()" 就代表调用
In [1]:
def H():
print('hahaha')
In [2]:
def B():
H()
In [3]:
B()
In [4]:
def A(f):
f()
In [5]:
A(B)


带返回值和不带返回值的函数
- return 返回的内容
- return 返回多个值
- 一般情况下,在多个函数协同完成一个功能的时候,那么将会有返回值


- 当然也可以自定义返回None
EP:


In [8]:
def main():
print(min(min(5,6),(51,6)))
def min(n1,n2):
a = n1
if n2 < a:
a = n2
In [9]:
main()
类型和关键字参数
- 普通参数
- 多个参数
- 默认值参数
- 不定长参数
普通参数
多个参数
默认值参数
强制命名
In [60]:
def U(str_):
xiaoxie = 0
for i in str_:
ASCII = ord(i)
if 97<=ASCII<=122:
xiaoxie +=1
elif xxxx:
daxie += 1
elif xxxx:
shuzi += 1
return xiaoxie,daxie,shuzi
In [61]:
U('HJi12')
不定长参数
- *args
- 不定长,来多少装多少,不装也是可以的
- 返回的数据类型是元组
- args 名字是可以修改的,只是我们约定俗成的是args
- **kwargs
- 返回的字典
- 输入的一定要是表达式(键值对)
- name,*args,name2,**kwargs 使用参数名
In [ ]:
def TT(a,b)
In [51]:
def TT(*args,**kwargs):
print(kwargs)
print(args)
TT(1,2,3,4,6,a=100,b=1000)
In [13]:
{'key':'value'}
In [14]:
TT(1,2,4,5,7,8,9,)
In [38]:
def B(name1,nam3):
pass
In [39]:
B(name1=100,2)
In [43]:
def sum_(*args,A='sum'):
res = 0
count = 0
for i in args:
res +=i
count += 1
if A == "sum":
return res
elif A == "mean":
mean = res / count
return res,mean
else:
print(A,'还未开放')
In [46]:
sum_(-1,0,1,4,A='var')
In [ ]:
'aHbK134'.__iter__
In [48]:
b = 'asdkjfh'
for i in b :
print(i)
In [ ]:
2,5
2 + 22 + 222 + 2222 + 22222
变量的作用域
- 局部变量 local
- 全局变量 global
- globals 函数返回一个全局变量的字典,包括所有导入的变量
- locals() 函数会以字典类型返回当前位置的全部局部变量。
In [54]:
a = 1000
b = 10
def Y():
global a,b
a += 100
print(a)
Y()
In [55]:
def YY(a1):
a1 += 100
print(a1)
YY(a)
print(a)
注意:
- global :在进行赋值操作的时候需要声明
- 官方解释:This is because when you make an assignment to a variable in a scope, that variable becomes local to that scope and shadows any similarly named variable in the outer scope.


Homework
- 1


In [ ]:
import math
def getPentagonalNumber():
count = 0
for i in range(1, 101):
a = i * ( 3*i - 1) / 2
print(int(a),end = ' ')
count += 1
if count % 10 == 0:
print('
')
getPentagonalNumber()
- 2


In [1]:
def sumDigits(n):
a = n % 10
b = n // 100
c = (n // 10) - ((n // 100)*10)
d = a + b + c
print(d)
sumDigits(234)
- 3


In [2]:
def displaySortedNumbers(num1,num2,num3):
if num1 > num2 > num3:
print(num1,num2,num3)
elif num1 > num3 > num2:
print(num1,num3,num2)
elif num2 > num1 > num3:
print(num2,num1,num3)
elif num2 > num3 > num1:
print(num2,num3,num1)
elif num3 > num1 > num2:
print(num3,num1,num2)
elif num3 > num2 > num1:
print(num3,num2,num1)
displaySortedNumbers(3,8,1)
- 4


In [2]:
def futureInvestmentValue(principal,rate,years):
for i in range(years):
principal = principal * (1+rate)
print("{}年内总额{}: ".format(i+1,principal))
principal = eval(input("输入存款金额: "))
rate = eval(input("输入利率: "))
years = eval(input("输入年份:" ))
futureInvestmentValue(principal,rate,years)
- 5


In [1]:
li = [chr(i) for i in range(ord("A"),ord("Z")+1)]
count=0
for i in li:
print(i,end=' ')
count += 1
if(count%10==0):
print(end='
')
- 6


In [3]:
import math
def numberOfDaysInAYear():
for i in range(2010,2021):
if i % 4 == 0 and i % 100 != 0 or i % 400 == 0:
print(i,'是366天')
else:
print(i,'是365天')
numberOfDaysInAYear()
- 7


In [1]:
import numpy as np
import math
def xsj(x1,y1,x2,y2):
p1=np.array([x1,y1])
p2=np.array([x2,y2])
p3=p2-p1
p4=math.hypot(p3[0],p3[1])
print(p4)
x1,y1,x2,y2=map(int,input().split(','))
xsj(x1,y1,x2,y2)
- 8


In [ ]:
def a():
for i in range(2, 32):
p = (2 ** i) - 1
print(i,p)
a()
- 9



In [5]:
import time
localtime = time.asctime(time.localtime(time.time()))
print("本地时间为 :", localtime)
- 10

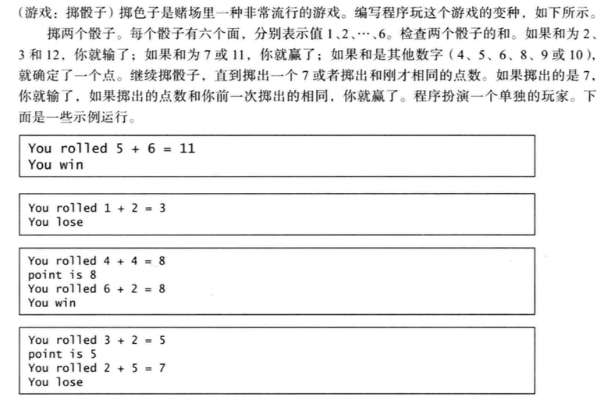
In [3]:
import random
random1 = random.randint(1,7)
random2 = random.randint(1,7)
random3 = random.randint(1,7)
total = random1 + random2
print('第一次摇到:{}'.format(random1))
print('第二次摇到:{}'.format(random2))
if total ==7 or total==11:
print('{}+{}={} you win!'.format(random1,random2,total))
elif total ==2 or total==3 or total ==12:
print('{}+{}={} you lose!'.format(random1,random2,total))
elif total==4 or total ==5 or total==6 or total==8 or total==9 or total==10:
total=total+random3
print('第三次摇到:{}'.format(random3))
print('diercihe{}'.format(total))
- 11
去网上寻找如何用Python代码发送邮件
In [4]:
import smtplib
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
def send_mail(username, passwd, recv, title, content, mail_host='smtp.163.com', port=25):
'''
发送邮件函数,默认使用163smtp
:param username: 邮箱账号 xx@163.com
:param passwd: 邮箱密码
:param recv: 邮箱接收人地址,多个账号以逗号隔开
:param title: 邮件标题
:param content: 邮件内容
:param mail_host: 邮箱服务器
:param port: 端口号
:return:
'''
msg = MIMEText(content) # 邮件内容
msg['Subject'] = title # 邮件主题
msg['From'] = username # 发送者账号
msg['To'] = recv # 接收者账号列表
smtp = smtplib.SMTP(mail_host, port=port) # 连接邮箱,传入邮箱地址,和端口号,smtp的端口号是25
smtp.login(username, passwd) # 发送者的邮箱账号,密码
smtp.sendmail(username, recv, msg.as_string())
# 参数分别是发送者,接收者,第三个是把上面的发送邮件的内容变成字符串
smtp.quit() # 发送完毕后退出smtp
print('email send success.')
email_user = 'xxxx@163.com' # 发送者账号
email_pwd = 'xxxxx' # 发送者密码
maillist = 'XXX@XXX.com'
title = '测试邮件标题'
content = '这里是邮件内容'
send_mail(email_user, email_pwd, maillist, title, content)