9.14 7.托普里茨矩阵
如果矩阵上每一条由左上到右下的对角线上的元素都相同,那么这个矩阵是 托普利茨矩阵 。
给定一个 M x N 的矩阵,当且仅当它是托普利茨矩阵时返回 True。
输入:
matrix = [
[1,2,3,4],
[5,1,2,3],
[9,5,1,2]
]
输出: True
解释:
在上述矩阵中, 其对角线为:
"[9]", "[5, 5]", "[1, 1, 1]", "[2, 2, 2]", "[3, 3]", "[4]"。
各条对角线上的所有元素均相同, 因此答案是True。
思路
满足条件是任一个坐标(x,y)的值都等于(x+1,y+1)的值,并且要做好条件限制
我的解:未解出来
最优解
class Solution:
def isToeplitzMatrix(self, matrix: list) -> bool:
res = matrix[0][:-1]
for line in matrix[1:]:
tmp = line[1:]
if res != tmp:
return False
res = line[:-1]
return True
总结
找到行与行之间的联系,逐行比较,而不是行内元素比较。行内元素符合的规律,那么行内元素组成的集合也符合这个规律,作为一个整体。
9.15 8. 重复叠加字符串匹配
给定两个字符串 A 和 B, 寻找重复叠加字符串A的最小次数,使得字符串B成为叠加后的字符串A的子串,如果不存在则返回 -1。
举个例子,A = "abcd",B = "cdabcdab"。
答案为 3, 因为 A 重复叠加三遍后为 “abcdabcdabcd”,此时 B 是其子串;A 重复叠加两遍后为"abcdabcd",B 并不是其子串。
注意:
A 与 B 字符串的长度在1和10000区间范围内。
思路
每次拼接a进行测试,是否能匹配到b
我的解法:
class Solution:
def repeatedStringMatch(self, a: str, b: str) -> int:
for i in range(1,10000//len(a)+1):
c = a * i
if c.find(b) != -1:
return i
return -1
9.16 9. 基本计算器
实现一个基本的计算器来计算一个简单的字符串表达式的值。
字符串表达式可以包含左括号 ( ,右括号 ),加号 + ,减号 -,非负整数和空格 。
示例 1:
输入: "1 + 1"
输出: 2
输入: "(1+(4+5+2)-3)+(6+8)"
输出: 23
思路:
无括号情况:如“1+3+22-33+2-6-7” 按加号分割,并且strip会得到单数字和含减号表达式,以及含减号表达式的[1,3,22-33,2-6-7],如果长度大于1则是含减号,用减号分割,求差,再总体求和
有括号情况:去掉所有空格,遍历,记录左括号出现的次数(key)和位置(value)和右括号对应的位置赞为none,如果出现了右括号,记录右括号出现的位置和上一个左括号的位置,并且填充之前为none的对应左括号记录的右括号的位置,每一组括号先求和,带入到上一组。
最优解
解决 - 结合律的问题的一个分厂简单的方法就是使将 - 运算符看作右侧操作数的大小。一旦我们将 - 看作操作数的大小,则表达式将只剩下一个操作符。就是 + 运算符,而 + 是遵循结合律的。
例如,A-B-CA−B−C 等于 A + (-B) + (-C)A+(−B)+(−C)。
重写以后的表达式将遵循结合律,所以我们从左或从右计算表达式都是正确的。
我们需要注意的是给定的表达式会很复杂,即会有嵌套在其他表达式的表达式。即 (A - (B - C)),我们需要 B-C 外面的 - 号与 B-C 关联起来,而不是仅仅与 B 关联起来。
/ 我们可以通过遵循前面的基本练习并将符号与其右侧的表达式关联来解决此问题。然而,我们将采用的方法有一个小的转折,因为我们将在运行中评估大多数表达式。这减少了推送和弹出操作的数量。
算法:
正序迭代字符串。
操作数可以由多个字符组成,字符串 "123" 表示数字 123,它可以被构造为:123 >> 120 + 3 >> 100 + 20 + 3。如果我们读取的字符是一个数字,则我们要将先前形成的操作数乘以 10 并于读取的数字相加,形成操作数。
每当我们遇到 + 或 - 运算符时,我们首先将表达式求值到左边,然后将正负符号保存到下一次求值。
如果字符是左括号 (,我们将迄今为止计算的结果和符号添加到栈上,然后重新开始进行计算,就像计算一个新的表达式一样。
如果字符是右括号 ),则首先计算左侧的表达式。则产生的结果就是刚刚结束的子表达式的结果。如果栈顶部有符号,则将此结果与符号相乘。
PythonJava
class Solution:
def calculate(self, s: str) -> int:
stack = []
operand = 0
res = 0 # For the on-going result
sign = 1 # 1 means positive, -1 means negative
for ch in s:
if ch.isdigit():
# Forming operand, since it could be more than one digit
operand = (operand * 10) + int(ch)
elif ch == '+':
# Evaluate the expression to the left,
# with result, sign, operand
res += sign * operand
# Save the recently encountered '+' sign
sign = 1
# Reset operand
operand = 0
elif ch == '-':
res += sign * operand
sign = -1
operand = 0
elif ch == '(':
# Push the result and sign on to the stack, for later
# We push the result first, then sign
stack.append(res)
stack.append(sign)
# Reset operand and result, as if new evaluation begins for the new sub-expression
sign = 1
res = 0
elif ch == ')':
# Evaluate the expression to the left
# with result, sign and operand
res += sign * operand
# ')' marks end of expression within a set of parenthesis
# Its result is multiplied with sign on top of stack
# as stack.pop() is the sign before the parenthesis
res *= stack.pop() # stack pop 1, sign
# Then add to the next operand on the top.
# as stack.pop() is the result calculated before this parenthesis
# (operand on stack) + (sign on stack * (result from parenthesis))
res += stack.pop() # stack pop 2, operand
# Reset the operand
operand = 0
return res + sign * operand
总结:
最优解遍历了字符串。
如果是数字接着遍历,*10 + 遍历的数,
如果是+就累加,-就改变符号为负一,继续累加后面的。
如果是(,先把之前的结果和符号,放进stack,还原符号和累加结果,重新算里面的。
如果是),先得出括号里的结果,在乘以pop出来的一个符号。
遇到括号就是要算出结果,放入stack中,连同符号push一起算出来。
9.17 10.表示数值的字符串
请实现一个函数用来判断字符串是否表示数值(包括整数和小数)。例如,字符串"+100"、"5e2"、"-123"、"3.1416"、"-1E-16"、"0123"都表示数值,但"12e"、"1a3.14"、"1.2.3"、"+-5"及"12e+5.4"都不是。
思路
总结是数字的几种情况
我的解
class Solution:
def isNumber(self, s: str) -> bool:
from collections import Counter
li = list(s.strip())
if len(li) == 0:
return False
# 长度为1的情况
if len(li) == 1:
if "0123456789".find(li[0]) == -1:
return False
# 如果以符号开头
if li[0] in ['+','-']:
# 判断后面有没有E
if 'e' in li:
index = li.index('e')
new_li = li[index:]
# 加减号之一出现1次,或数字
if new_li[1] not in ['+','-']:
return False
res = sum(not i.isdigit() for i in new_li[2:])
if res != 0:
return False
new_li_2 = li[1:index]
# e前多于两个小数点
if Counter(new_li_2).get('.') > 1:
return False
res2 =sum(not i.isdigit() for i in new_li_2)
if res2 != 0:
return False
elif 'E' in li:
index = li.index('E')
new_li = li[index:]
# 加减号之一出现1次,或数字
if new_li[1] not in ['+','-']:
return False
res = sum(i.isdigit() for i in new_li[2:])
if res != 0:
return False
new_li_2 = li[1:index]
# e前多于两个小数点
if Counter(new_li_2).get('.') > 1:
return False
res2 =sum(not i.isdigit() for i in new_li_2)
if res2 != 0:
return False
# 第一个不是数字且不是小数点
elif not li[0].isdigit() and li[0]!='.':
return False
# 没有符号
else:
if 'e' in li:
index = li.index('e')
new_li = li[index:]
# 加减号之一出现1次,或数字
if(len(new_li)==1):
return False
if new_li[1] not in ['+','-']:
return False
res = sum(not i.isdigit() for i in new_li[2:])
if res != 0:
return False
new_li_2 = li[1:index]
# e前多于两个小数点
if Counter(new_li_2).get('.') > 1:
return False
res2 =sum(not i.isdigit() for i in new_li_2)
if res2 != 0:
return False
elif 'E' in li:
index = li.index('E')
new_li = li[index:]
# 加减号之一出现1次,或数字
if new_li[1] not in ['+','-']:
return False
res = sum(i.isdigit() for i in new_li[2:])
if res != 0:
return False
new_li_2 = li[1:index]
# e前多于两个小数点
if Counter(new_li_2).get('.') > 1:
return False
res2 =sum(not i.isdigit() for i in new_li_2)
if res2 != 0:
return False
else:
if "." in Counter(li):
if Counter(li).get('.') > 1:
return False
elif Counter(li).get('.') == 1:
res2 =sum(not i.isdigit() for i in li)
if res2 > 1:
return False
else:
res3 =sum(not i.isdigit() for i in li)
if res3 > 0:
return False
return True
最优解:
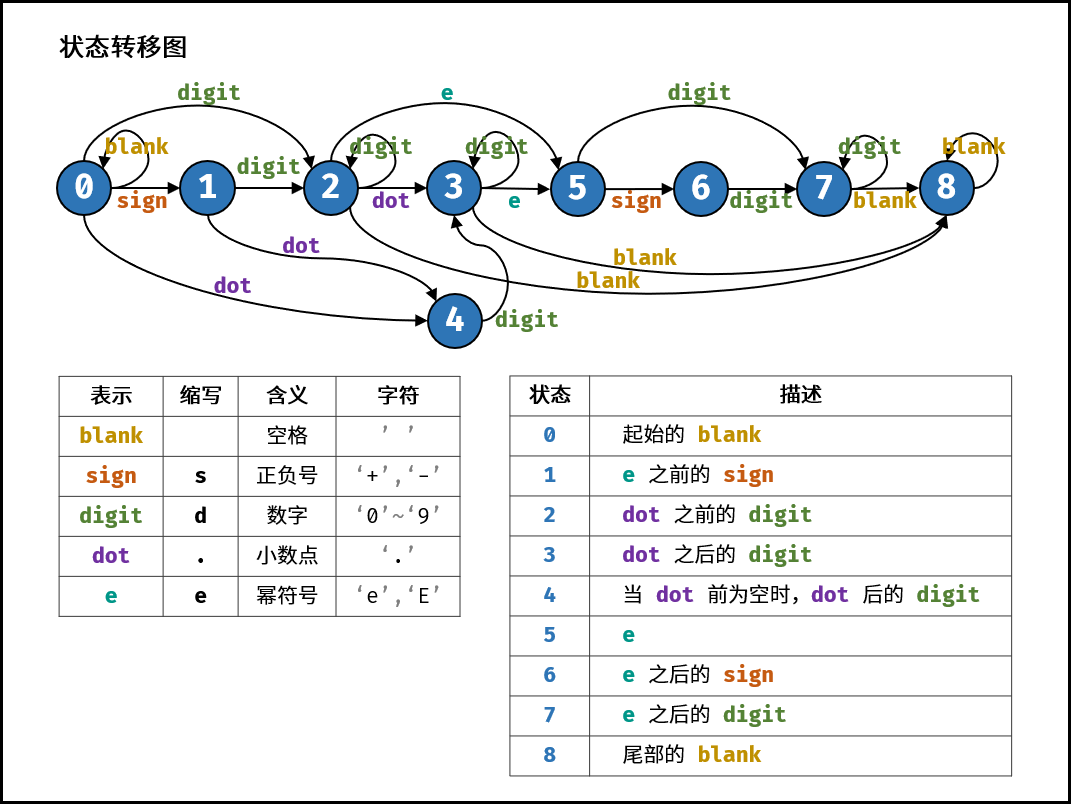
class Solution:
def isNumber(self, s: str) -> bool:
states = [
{ ' ': 0, 's': 1, 'd': 2, '.': 4 }, # 0. start with 'blank'
{ 'd': 2, '.': 4 } , # 1. 'sign' before 'e'
{ 'd': 2, '.': 3, 'e': 5, ' ': 8 }, # 2. 'digit' before 'dot'
{ 'd': 3, 'e': 5, ' ': 8 }, # 3. 'digit' after 'dot'
{ 'd': 3 }, # 4. 'digit' after 'dot' (‘blank’ before 'dot')
{ 's': 6, 'd': 7 }, # 5. 'e'
{ 'd': 7 }, # 6. 'sign' after 'e'
{ 'd': 7, ' ': 8 }, # 7. 'digit' after 'e'
{ ' ': 8 } # 8. end with 'blank'
]
p = 0 # start with state 0
for c in s:
if '0' <= c <= '9': t = 'd' # digit
elif c in "+-": t = 's' # sign
elif c in "eE": t = 'e' # e or E
elif c in ". ": t = c # dot, blank
else: t = '?' # unknown
if t not in states[p]: return False
p = states[p][t]
return p in (2, 3, 7, 8)
总结:
此题涉及到自动机,要复习一下自动机的算法原理是什么。做下标记,后期在看。
9.18 11. 把数组排成最小的数
输入一个非负整数数组,把数组里所有数字拼接起来排成一个数,打印能拼接出的所有数字中最小的一个。
输入: [10,2]
输出: "102"
思路
先求出数组中 位数最多是几位,所有元素补0,排序。最小的数往前排,大的数还原往后排
我的解
class Solution:
@classmethod
def minNumber(self, nums: list) -> str:
new_li = sorted(nums)
print(new_li)
max_len = len(str(new_li[-1]))
dic = dict()
index = 0
for i in new_li:
dic[index] = int(str(i).ljust(max_len,'0'))
print(dic)
index += 1
new_dic = sorted(dic.items(),key=lambda v:v[1])
print(new_dic)
res = ""
for item in new_dic:
res = res + str(new_li[item[0]])
return res
错误总结
没有考虑到 3,30这种形式的排序
最优解
- 快速排序
class Solution:
def minNumber(self, nums: List[int]) -> str:
def fast_sort(l , r):
if l >= r: return
i, j = l, r
while i < j:
while strs[j] + strs[l] >= strs[l] + strs[j] and i < j: j -= 1
while strs[i] + strs[l] <= strs[l] + strs[i] and i < j: i += 1
strs[i], strs[j] = strs[j], strs[i]
strs[i], strs[l] = strs[l], strs[i]
fast_sort(l, i - 1)
fast_sort(i + 1, r)
strs = [str(num) for num in nums]
fast_sort(0, len(strs) - 1)
return ''.join(strs)
- 内置函数
class Solution:
def minNumber(self, nums: List[int]) -> str:
def sort_rule(x, y):
a, b = x + y, y + x
if a > b: return 1
elif a < b: return -1
else: return 0
strs = [str(num) for num in nums]
strs.sort(key = functools.cmp_to_key(sort_rule))
return ''.join(strs)
总结
制定一个排序规则,比如3,30,如果3,30>303则3>30,按照这个规则快速排序成一个新的数组即可。
9.19 12. 统计作战单位数
n 名士兵站成一排。每个士兵都有一个 独一无二 的评分 rating 。
每 3 个士兵可以组成一个作战单位,分组规则如下:
从队伍中选出下标分别为 i、j、k 的 3 名士兵,他们的评分分别为 rating[i]、rating[j]、rating[k] 作战单位需满足: rating[i] < rating[j] < rating[k] 或者 rating[i] > rating[j] > rating[k] ,其中 0 <= i < j < k < n 请你返回按上述条件可以组建的作战单位数量。每个士兵都可以是多个作战单位的一部分。
示例 1:
输入:rating = [2,5,3,4,1]
输出:3
解释:我们可以组建三个作战单位 (2,3,4)、(5,4,1)、(5,3,1) 。
示例 2:
输入:rating = [2,1,3]
输出:0
解释:根据题目条件,我们无法组建作战单位。
示例 3:
输入:rating = [1,2,3,4]
输出:4
思路
列表长度至少大于等于3,3层遍历。
我的解
class Solution:
@classmethod
def numTeams(self, rating: list) -> int:
if len(rating) < 3:
return 0
res = 0
for i in range(len(rating)):
if i >= len(rating) -2: break
for j in range(i+1,len(rating)):
if j >= len(rating) -1: break
for k in range(j+1,len(rating)):
new_li = []
new_li.append(rating[i])
new_li.append(rating[j])
new_li.append(rating[k])
if all(x<y for x,y in zip(new_li,new_li[1:])) or all(x>y for x,y in zip(new_li,new_li[1:])):
res += 1
return res
最优解
class Solution:
def numTeams(self, rating: List[int]) -> int:
def func(nums):
dp = [0] * len_
res = 0
for i in range(1, len_):
idx = i - 1
while idx >= 0:
if nums[i] > nums[idx]:
dp[i] += 1
if dp[idx] > 0:
res += dp[idx]
idx -= 1
return res
len_ = len(rating)
return func(rating[::-1]) + func(rating)
总结
- 更新dp的同时,更新res;
- dp[i]记录的是第i个数之前比其值小的数的个数;
- 两层判断,如果nums[i] > nums[idx], 更新dp[i],其次,如果dp[idx]>0则再更新res。因为此时,num[i]已经大于nums[idx],再算上一个比nums[idx]小的数,就构成了一个3个数的升序,这样的组合有dp[idx];
- 另外的一种情况,将数组逆序即可。