一、AIO简介
AIO是java中IO模型的一种,作为NIO的改进和增强随JDK1.7版本更新被集成在JDK的nio包中,因此AIO也被称作是NIO2.0。区别于传统的BIO(Blocking IO,同步阻塞式模型,JDK1.4之前就存在于JDK中,NIO于JDK1.4版本发布更新)的阻塞式读写,AIO提供了从建立连接到读、写的全异步操作。AIO可用于异步的文件读写和网络通信。
二、同步/异步、阻塞/非阻塞
我们先来了解下什么是同步/异步,以及什么是阻塞/非阻塞。在IO操作中,IO分两阶段(一旦拿到数据后就变成了数据操作,不再是IO):
- 数据准备阶段
- 内核空间复制数据到用户进程缓冲区(用户空间)阶段 在操作系统中,程序运行的空间分为内核空间和用户空间。 应用程序都是运行在用户空间的,所以它们能操作的数据也都在用户空间。
- 同步和异步IO的概念:同步是用户线程发起I/O请求后需要等待或者轮询内核I/O操作完成后才能继续执行 异步是用户线程发起I/O请求后仍需要继续执行,当内核I/O操作完成后会通知用户线程,或者调用用户线程注册的回调函数。
- 阻塞和非阻塞IO的概念: 阻塞是指I/O操作需要彻底完成后才能返回用户空间 非阻塞是指I/O操作被调用后立即返回一个状态值,无需等I/O操作彻底完成。
一般来讲: 阻塞IO模型、非阻塞IO模型、IO复用模型(select/poll/epoll)、信号驱动IO模型都属于同步IO,因为阶段2是阻塞的(尽管时间很短)。同步IO和异步IO的区别就在于第二个步骤是否阻塞: 如果不阻塞,而是操作系统帮你做完IO操作再将结果返回给你,那么就是异步IO。
三、异步IO模型
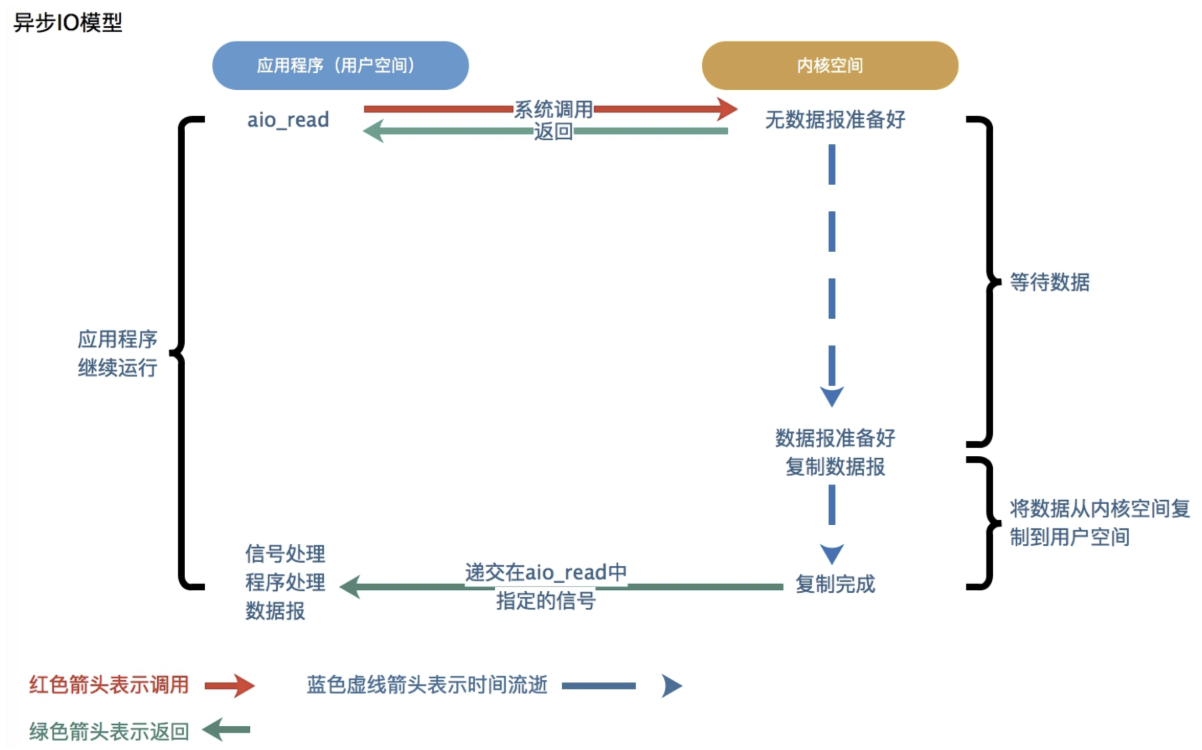
异步IO则采用“订阅-通知”模式:即应用程序向操作系统注册IO监听,然后继续做自己的事情。当操作系统发生IO事件,并且准备好数据后,在主动通知应用程序,触发相应的函数。也可以如下图理解:

和同步IO一样,异步IO也是由操作系统进行支持的。微软的windows系统提供了一种异步IO技术:IOCP(I/O CompletionPort,I/O完成端口);Linux下由于没有这种异步IO技术,所以使用的是epoll对异步IO进行模拟。
四、JAVA AIO框架简析
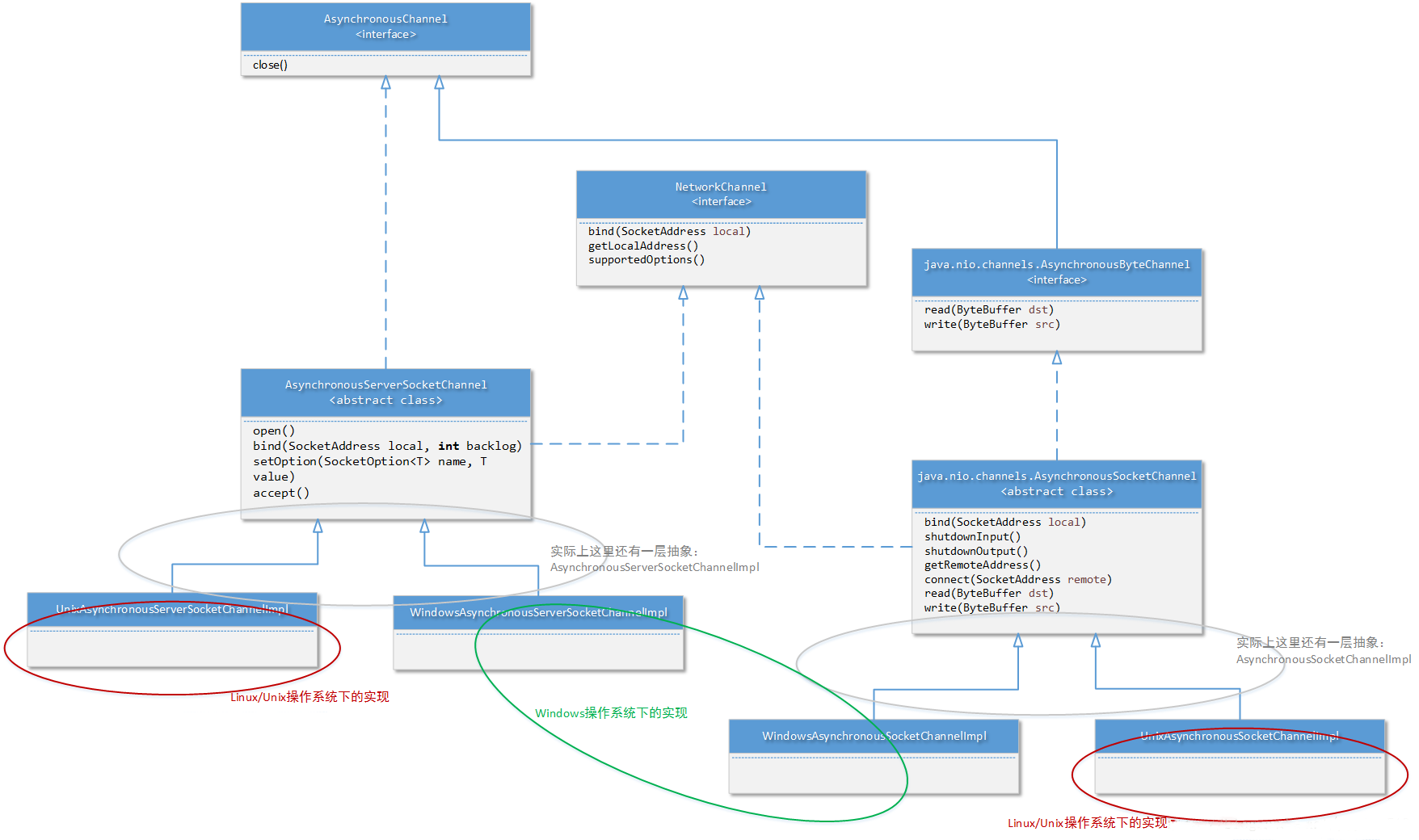
JAVA AIO框架在windows下使用windows IOCP技术,在Linux下使用epoll多路复用IO技术模拟异步IO,这个从JAVA AIO框架的部分类设计上就可以看出来。例如框架中,在Windows下负责实现套接字通道的具体类是“sun.nio.ch.WindowsAsynchronousSocketChannelImpl”,在Linux下负责实现套接字通道的具体类是“sun.nio.ch.UnixAsynchronousServerSocketChannelImpl”,如下图在Mac上安装的JDK可以看到:
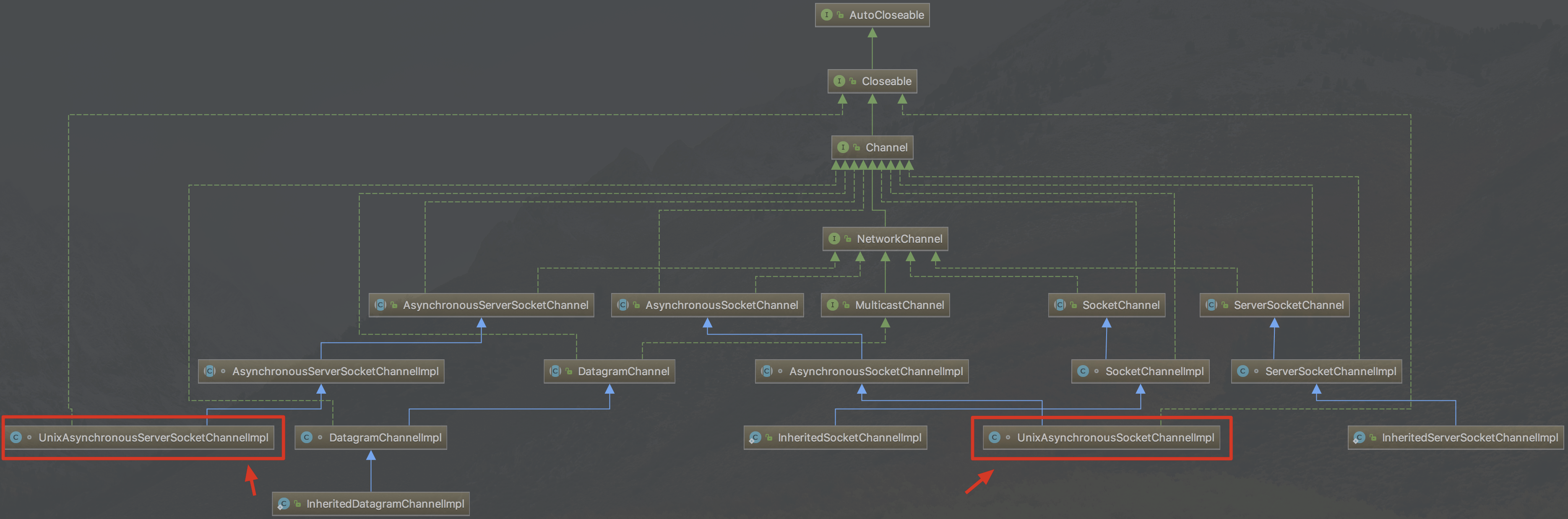
另外特别说明一下,请注意在上图中的“java.nio.channels.NetworkChannel”接口,这个接口同样被JAVA NIO框架实现了,如上图所示:SocketChannel以及ServerSocketChannel就是NetworkChannel的实现。
在java中,支持异步模型的方式有两个类:
- Future类
- Callable接口
五、AIO重要类
实现一个最简单的AIO socket通信server、client,主要需要这些相关的类和接口:
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel服务端Socket通道类,负责服务端Socket的创建和监听;
AsynchronousSocketChannel客户端Socket通道类,负责客户端消息读写;
CompletionHandler<A,V>消息处理回调接口,是一个负责消费异步IO操作结果的消息处理器;
ByteBuffer负责承载通信过程中需要读、写的消息。
此外,还有可选的用于异步通道资源共享的AsynchronousChannelGroup类,接下来将一一介绍这些类的主要接口及使用。
1、AsynchronousServerSocketChannel
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel是一个流式监听套接字的异步通道,是ServerSocketChannel的异步版本的通道,支持异步处理。AsynchronousServerSocketChannel的使用和ServerSocketChannel一样需要经过三个步骤:创建/打开通道、绑定地址和端口和监听客户端连接请求。
1.1 创建/打开通道
try { AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
当打开通道失败时,会抛出一个IOException异常。
1.2 绑定地址和端口
通过调用AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.bind(SocketAddress)方法来绑定监听地址和端口:
// 构建一个InetSocketAddress实例以指定监听的地址和端口,如果需要指定ip,则调用InetSocketAddress(ip,port)构造方法创建即可 serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
1.3 监听和接收客户端连接请求
监听客户端连接请求,主要通过调用AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.accept()方法完成。accept()有两个重载方法:
public abstract <A> void accept(A,CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel,? super A>); public abstract Future<AsynchronousSocketChannel> accept();
这两个重载方法的行为方式完全相同一种基于Future,一种基于回调,事实上,AIO的很多异步API都封装了诸如此类的重载方法:提供CompletionHandle回调参数或者返回一个Future<T>类型变量。用过Feture接口的都知道,可以调用Feture.get()方法阻塞等待调用结果。无论是哪种方式来获取连接,最终的处理对象都是Socket,和ServerSocketChannel不同的是,这里的socket是封装在AsynchronousSocketChannel中的。
基于Future实现:
public void AsynchronousServerSocketChannel() { try { AsynchronousServerSocketChannel channel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open(); channel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8888)); while (true) { Future<AsynchronousSocketChannel> conn = channel.accept(); // 阻塞等待直到future有结果 AsynchronousSocketChannel asyncSocketChannel = conn.get(); // 异步处理连接 asyncHandle(asyncSocketChannel); } } catch (IOException | InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
基于回调:
public void AsynchronousServerSocketChannelCallback() { try { AsynchronousServerSocketChannel channel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open(); channel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8888)); channel.accept(null, new CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, Void>() { @Override public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel result, Void attachment) {
// 接收到新的客户端连接时调用,result就是和客户端的连接对话,此时可以通过result和客户端进行通信 System.out.println("accept completed"); // 异步处理连接 asyncHandle(result); // 继续监听accept channel.accept(null, this); } @Override public void failed(Throwable exc, Void attachment) {
// accept失败时回调 System.out.println("accept failed"); } }); // 让主线程保持存活 while (true) { System.in.read(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
需要注意的是,AsynchronousServerSocketChannel是线程安全的,但在任何时候同一时间内只能允许有一个accept操作。因此,必须得等待前一个accept操作完成之后才能启动下一个accept:
serverSocketChannel .accept(serverSocketChannel, new CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, AsynchronousServerSocketChannel>() { @Override public void completed(final AsynchronousSocketChannel result, final AsynchronousServerSocketChannel attachment) { // 接收到新的客户端连接,此时本次accept已经完成 // 继续监听下一个客户端连接到来 serverSocketChannel.accept(serverSocketChannel,this); // result即和该客户端的连接会话 // 此时可以通过result与客户端进行交互 } ... });
此外,还可以通过以下方法获取和设置AsynchronousServerSocketChannel的socket选项:
// 设置socket选项 serverSocketChannel.setOption(StandardSocketOptions.SO_KEEPALIVE,true); // 获取socket选项设置 boolean keepAlive = serverSocketChannel.getOption(StandardSocketOptions.SO_KEEPALIVE);
其中StandardSocketOptions类封装了常用的socket设置选项。
获取本地地址:
InetSocketAddress address = (InetSocketAddress) serverSocketChannel.getLocalAddress();
1.4 AsynchronousChannelGroup异步通道组
try { ExecutorService pool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); AsynchronousChannelGroup group = AsynchronousChannelGroup.withCachedThreadPool(pool, 10); AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open(group); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel提供了设置通道分组(AsynchronousChannelGroup)的功能,以实现组内通道资源共享。可以调用open(AsynchronousChannelGroup)重载方法创建指定分组的通道,默认情况下,具有 open() 方法的通道属于一个全局通道组,可利用如下系统变量对其进行配置:
java.nio.channels.DefaultThreadPoolthreadFactory,其不采用默认设置,而是定义一个 java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactoryjava.nio.channels.DefaultThreadPool.initialSize,指定线程池的初始规模
java.nio.channels.AsynchronousChannelGroup 中的三个实用方法提供了创建新通道组的方法:
withCachedThreadPool()
withFixedThreadPool()
withThreadPool()
这些方法或者对线程池进行定义,如 java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService,或者是 java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory。例如,以下调用创建了具有线程池的新的通道组,该线程池包含 10 个线程,其中每个都构造为来自 Executors 类的线程工厂:
AsynchronousChannelGroup tenThreadGroup =
AsynchronousChannelGroup.withFixedThreadPool(10, Executors.defaultThreadFactory());
三个异步网络通道都具有 open() 方法的替代版本,它们采用给出的通道组而不是默认通道组。例如,当有异步操作请求时,此调用告诉 channel 使用 tenThreadGroup 而不是默认通道组来获取线程:
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel channel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open(tenThreadGroup);
定义自己的通道组可更好地控制服务于操作的线程,并能提供关闭线程或者等待终止的机制。
AsynchronousChannelGroup封装了处理由绑定到组的异步通道所触发的I/O操作完成所需的机制。每个AsynchronousChannelGroup关联了一个被用于提交处理I/O事件和分发消费在组内通道上执行的异步操作结果的completion-handlers的线程池。除了处理I/O事件,该线程池还有可能处理其他一些用于支持完成异步I/O操作的任务。从上面例子可以看到,通过指定AsynchronousChannelGroup的方式打开AsynchronousServerSocketChannel,可以定制server channel执行的线程池。如果不指定AsynchronousChannelGroup,则AsynchronousServerSocketChannel会归类到一个默认的分组中。
2、AsynchronousSocketChannel
AsynchronousSocketChannel和NIO通道是SocketChannel功能相似。是一个流式连接套接字的异步通道。
AsynchronousSocketChannel表示服务端与客户端之间的连接通道。客户端可以通过调用AsynchronousSocketChannel静态方法open()创建,而服务端则通过调用AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.accept()方法后由AIO内部在合适的时候创建。下面以客户端实现为例,介绍AsynchronousSocketChannel。
2.1 创建AsynchronousSocketChannel
需要通过open()创建和打开一个AsynchronousSocketChannel实例,再调用其connect()方法连接到服务端,接着才可以与服务端交互:
// 打开一个socket通道 AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel = AsynchronousSocketChannel.open(); // 阻塞等待连接成功 socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(ip,port)).get(); // 连接成功,接下来可以进行read、write操作
同AsynchronousServerSocketChannel,AsynchronousSocketChannel也提供了open(AsynchronousChannelGroup)方法用于指定通道分组和定制线程池。
2.2 connect
socketChannel.connect()也提供了CompletionHandler回调和Future返回值两个重载方法,上面例子使用带Future返回值的重载,并调用get()方法阻塞等待连接建立完成。
// 基于回调 public abstract <A> void connect(SocketAddress remote, A attachment, CompletionHandler<Void,? super A> handler); // 基于Future 调用get()方法阻塞等待连接建立完成 public abstract Future<Void> connect(SocketAddress remote);
2.3 发送消息
可以构建一个ByteBuffer对象并调用socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer)方法异步发送消息,并通过CompletionHandler回调接收处理发送结果:
ByteBuffer writeBuf = ByteBuffer.wrap("From socketChannel:Hello i am socketChannel".getBytes());
socketChannel.write(writeBuf, null, new CompletionHandler<Integer, Object>() {
@Override
public void completed(final Integer result, final Object attachment) {
// 发送完成,result:总共写入的字节数
}
@Override
public void failed(final Throwable exc, final Object attachment) {
// 发送失败
}
});
2.4 读取消息
构建一个指定接收长度的ByteBuffer用于接收数据,调用socketChannel.read()方法读取消息并通过CompletionHandler处理读取结果:
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(128); socketChannel.read(readBuffer, null, new CompletionHandler<Integer, Object>() { @Override public void completed(final Integer result, final Object attachment) { // 读取完成,result:实际读取的字节数。如果通道中没有数据可读则result=-1。 } @Override public void failed(final Throwable exc, final Object attachment) { // 读取失败 } });
此外,AsynchronousSocketChannel也封装了设置/获取socket选项的方法:
// 设置socket选项 socketChannel.setOption(StandardSocketOptions.SO_KEEPALIVE,true); // 获取socket选项设置 boolean keepAlive = socketChannel.getOption(StandardSocketOptions.SO_KEEPALIVE);
注意:读写操作,有多个重载的Future和回调式的read和write方法:
public abstract <A> void read(ByteBuffer dst, long timeout, TimeUnit unit, A attachment, CompletionHandler<Integer,? super A> handler); public final <A> void read(ByteBuffer dst, A attachment, CompletionHandler<Integer,? super A> handler) public abstract Future<Integer> read(ByteBuffer dst); public abstract <A> void read(ByteBuffer[] dsts, int offset, int length, long timeout, TimeUnit unit, A attachment, CompletionHandler<Long,? super A> handler); // write public abstract <A> void write(ByteBuffer src, long timeout, TimeUnit unit, A attachment, CompletionHandler<Integer,? super A> handler); public final <A> void write(ByteBuffer src, A attachment, CompletionHandler<Integer,? super A> handler); public abstract Future<Integer> write(ByteBuffer src); public abstract <A> void write(ByteBuffer[] srcs, int offset, int length, long timeout, TimeUnit unit, A attachment, CompletionHandler<Long,? super A> handler);
如下服务器端示例,使用的是accept返回的channel:
// 基于future 实际上是同步的读取方式 private void asyncHandle(AsynchronousSocketChannel asyncSocketChannel) { ByteBuffer dst = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); // based on Future, // 实际上是同步处理的方式,为了不将处理变成阻塞式单连接的socket形式,使用子线程来获取输入流 new Thread(() -> { while (asyncSocketChannel.isOpen()) { Future<Integer> readFuture = asyncSocketChannel.read(dst); try { // 阻塞等待读取结果 Integer readResult = readFuture.get(); if (readResult > 0) { System.out.println(new String(dst.array(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); dst.clear(); } else { // doOtherthing } } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }).start(); } // 基于回调 private void asyncHandle(AsynchronousSocketChannel asyncSocketChannel) { asyncSocketChannel.read(dst, null, new CompletionHandler<Integer, Void>() { @Override public void completed(Integer result, Void attachment) { if (result > 0) { System.out.println(new String(dst.array(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); dst.clear(); } // 注册回调,继续读取输入 asyncSocketChannel.read(dst, null, this); } @Override public void failed(Throwable exc, Void attachment) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } }); }
3、CompletionHandler
CompletionHandler是一个用于消费异步I/O操作结果的处理器。
AIO中定义的异步通道允许指定一个CompletionHandler处理器消费一个异步操作的结果。从上文中也可以看到,AIO中大部分的异步I/O操作接口都封装了一个带CompletionHandler类型参数的重载方法,使用CompletionHandler可以很方便地处理AIO中的异步I/O操作结果。CompletionHandler是一个具有两个泛型类型参数的接口,声明了两个接口方法:
public interface CompletionHandler<V,A> { void completed(V result, A attachment); void failed(Throwable exc, A attachment); }
其中,泛型V表示I/O操作的结果类型,通过该类型参数消费I/O操作的结果;泛型A为附加到I/O操作中的对象类型,可以通过该类型参数将需要的变量传入到CompletionHandler实现中使用。因此,AIO中大部分的异步I/O操作都有一个类似这样的重载方法:
<V,A> void ioOperate(params,A attachment,CompletionHandler<V,A> handler);
例如,AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.accept()方法:
public abstract <A> void accept(A attachment,CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel,? super A> handler);
AsynchronousSocketChannel.write()方法等:
public final <A> void write(ByteBuffer src,A attachment,CompletionHandler<Integer,? super A> handler)
当I/O操作成功完成时,会回调到completed方法,failed方法则在I/O操作失败时被回调。需要注意的是:在CompletionHandler的实现中应当即使处理操作结果,以避免一直占用调用线程而不能分发其他的CompletionHandler处理器。
六、AIO代码实现
1、服务端
public class Server { private static int DEFAULT_PORT = 8888; private static AsyncServerHandler serverHandle; public volatile static long clientCount = 0; public static void start(){ start(DEFAULT_PORT); } public static synchronized void start(int port){ if(serverHandle!=null) return; serverHandle = new AsyncServerHandler(port); new Thread(serverHandle,"Server").start(); } public static void main(String[] args){ Server.start(); } }
public class AsyncServerHandler implements Runnable { public CountDownLatch latch; public AsynchronousServerSocketChannel channel; public AsyncServerHandler(int port) { try { //创建服务端通道 channel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open(); //绑定端口 channel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port)); System.out.println("服务器已启动,端口号:" + port); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public void run() { //CountDownLatch初始化 //它的作用:在完成一组正在执行的操作之前,允许当前的现场一直阻塞 //此处,让现场在此阻塞,防止服务端执行完成后退出 //也可以使用while(true)+sleep //生成环境就不需要担心这个问题,以为服务端是不会退出的 latch = new CountDownLatch(1); //用于接收客户端的连接 channel.accept(this,new AcceptHandler()); try { latch.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
//作为handler接收客户端连接 public class AcceptHandler implements CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, AsyncServerHandler> { @Override public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel channel,AsyncServerHandler serverHandler) { //继续接受其他客户端的请求 Server.clientCount++; System.out.println("连接的客户端数:" + Server.clientCount); serverHandler.channel.accept(serverHandler, this); //创建新的Buffer ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //异步读 第三个参数为接收消息回调的业务Handler channel.read(buffer, buffer, new ReadHandler(channel)); } @Override public void failed(Throwable exc, AsyncServerHandler serverHandler) { exc.printStackTrace(); serverHandler.latch.countDown(); } }
public class ReadHandler implements CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer> { //用于读取半包消息和发送应答 private AsynchronousSocketChannel channel; public ReadHandler(AsynchronousSocketChannel channel) { this.channel = channel; } //读取到消息后的处理 @Override public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) { //flip操作 attachment.flip(); //根据 byte[] message = new byte[attachment.remaining()]; attachment.get(message); try { String expression = new String(message, "UTF-8"); System.out.println("服务器收到消息: " + expression); String calrResult = null; try{ calrResult = Caculator.cal(expression).toString(); }catch(Exception e){ calrResult = "计算错误:" + e.getMessage(); } //向客户端发送消息 doWrite(calrResult); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //发送消息 private void doWrite(String result) { byte[] bytes = result.getBytes(); ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(bytes.length); writeBuffer.put(bytes); writeBuffer.flip(); //异步写数据 参数与前面的read一样 channel.write(writeBuffer, writeBuffer,new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() { @Override public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer buffer) { //如果没有发送完,就继续发送直到完成 if (buffer.hasRemaining()) channel.write(buffer, buffer, this); else{ //创建新的Buffer ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //异步读 第三个参数为接收消息回调的业务Handler channel.read(readBuffer, readBuffer, new ReadHandler(channel)); } } @Override public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) { try { channel.close(); } catch (IOException e) { } } }); } @Override public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) { try { this.channel.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
2、客户端
public class Client { private static String DEFAULT_HOST = "localhost"; private static int DEFAULT_PORT = 8888; private static AsyncClientHandler clientHandle; public static void start(){ start(DEFAULT_HOST,DEFAULT_PORT); } public static synchronized void start(String ip,int port){ if(clientHandle!=null) return; clientHandle = new AsyncClientHandler(ip,port); new Thread(clientHandle,"Client").start(); } //向服务器发送消息 public static boolean sendMsg(String msg) throws Exception{ if(msg.equals("q")) return false; clientHandle.sendMsg(msg); return true; } @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ Client.start(); System.out.println("请输入请求消息:"); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); while(Client.sendMsg(scanner.nextLine())); } }
public class AsyncClientHandler implements CompletionHandler<Void, AsyncClientHandler>, Runnable { private AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel; private String host; private int port; private CountDownLatch latch; public AsyncClientHandler(String host, int port) { this.host = host; this.port = port; try { //创建异步的客户端通道 clientChannel = AsynchronousSocketChannel.open(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public void run() { //创建CountDownLatch等待 latch = new CountDownLatch(1); //发起异步连接操作,回调参数就是这个类本身,如果连接成功会回调completed方法 clientChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(host, port), this, this); try { latch.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } try { clientChannel.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //连接服务器成功 //意味着TCP三次握手完成 @Override public void completed(Void result, AsyncClientHandler attachment) { System.out.println("客户端成功连接到服务器..."); } //连接服务器失败 @Override public void failed(Throwable exc, AsyncClientHandler attachment) { System.err.println("连接服务器失败..."); exc.printStackTrace(); try { clientChannel.close(); latch.countDown(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //向服务器发送消息 public void sendMsg(String msg){ byte[] req = msg.getBytes(); ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(req.length); writeBuffer.put(req); writeBuffer.flip(); //异步写 clientChannel.write(writeBuffer, writeBuffer,new WriteHandler(clientChannel, latch)); } }
public class WriteHandler implements CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer> { private AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel; private CountDownLatch latch; public WriteHandler(AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel, CountDownLatch latch) { this.clientChannel = clientChannel; this.latch = latch; } @Override public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer buffer) { //完成全部数据的写入 if (buffer.hasRemaining()) { clientChannel.write(buffer, buffer, this); } else { //读取数据 ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); clientChannel.read(readBuffer, readBuffer, new ReadHandler(clientChannel, latch)); } } @Override public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) { System.err.println("数据发送失败..."); try { clientChannel.close(); latch.countDown(); } catch (IOException e) { } } }
public class ReadHandler implements CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer> { private AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel; private CountDownLatch latch; public ReadHandler(AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel,CountDownLatch latch) { this.clientChannel = clientChannel; this.latch = latch; } @Override public void completed(Integer result,ByteBuffer buffer) { buffer.flip(); byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.remaining()]; buffer.get(bytes); String body; try { body = new String(bytes,"UTF-8"); System.out.println("客户端收到结果:"+ body); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public void failed(Throwable exc,ByteBuffer attachment) { System.err.println("数据读取失败..."); try { clientChannel.close(); latch.countDown(); } catch (IOException e) { } } }
3、测试类
public class Test { //测试主方法 @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //运行服务器 Server.start(); //避免客户端先于服务器启动前执行代码 Thread.sleep(100); //运行客户端 Client.start(); System.out.println("请输入请求消息:"); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); while (Client.sendMsg(scanner.nextLine())) ; } }
public final class Caculator { private final static ScriptEngine jse = new ScriptEngineManager().getEngineByName("JavaScript"); public static Object cal(String expression) throws ScriptException { return jse.eval(expression); } }