| 这个作业属于哪个班级 | 数据结构--网络2011/2012 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业的地址 | DS博客作业03--树 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 学习树结构设计及运算操作 |
| 黄帅 |
0.PTA得分截图

1.本周学习总结(5分)
1.1 二叉树结构
1.1.1 二叉树的2种存储结构
树的顺序存储结构
采用一组地址连续的存储单元来存放二叉树的数据元素(数组元素的下标关系反应完全二叉树中结点之间的逻辑关系)
把二叉树的所有结点安排成为一个恰当的序列,结点在这个序列中的相互位置能反映出结点之间的逻辑关系,用编号的方法从树根起,自上层至下层,每层自左至右地给所有结点编号
例:
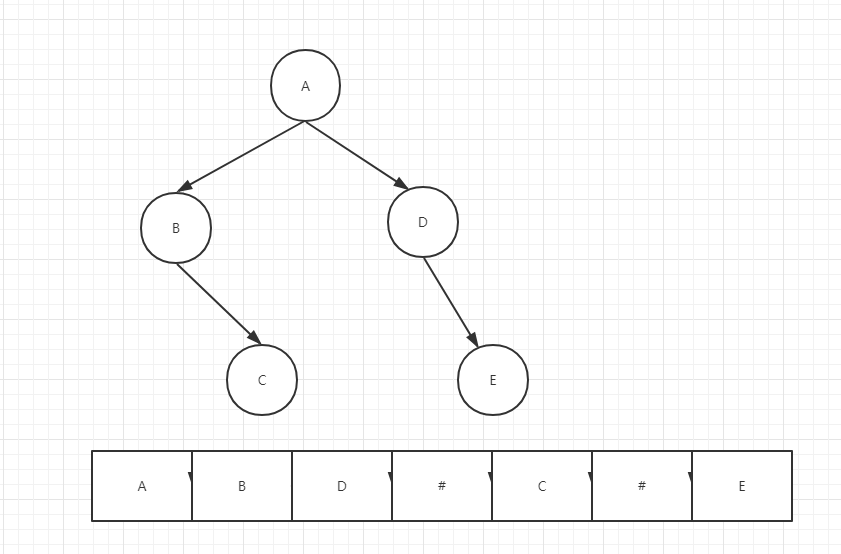
优点:对于完全二叉树而言,采用顺序存储结构可以节省存储空间
缺点:对于一般二叉树而言,容易造成空间上的浪费
树的链式存储结构
typedef struct BTNode
{
ElementType data;//结点数据
BTree lchild;//指向左孩子
BTree rchild;//指向右孩子
}BTNode,*BTree;
用链表来表示一棵二叉树,即用链来指示元素的逻辑关系。通常的方法是链表中每个结点由三个域组成,数据域和左右指针域,左右指针分别用来给出该结点左孩子和右孩子所在的链结点的存储地址。
例:
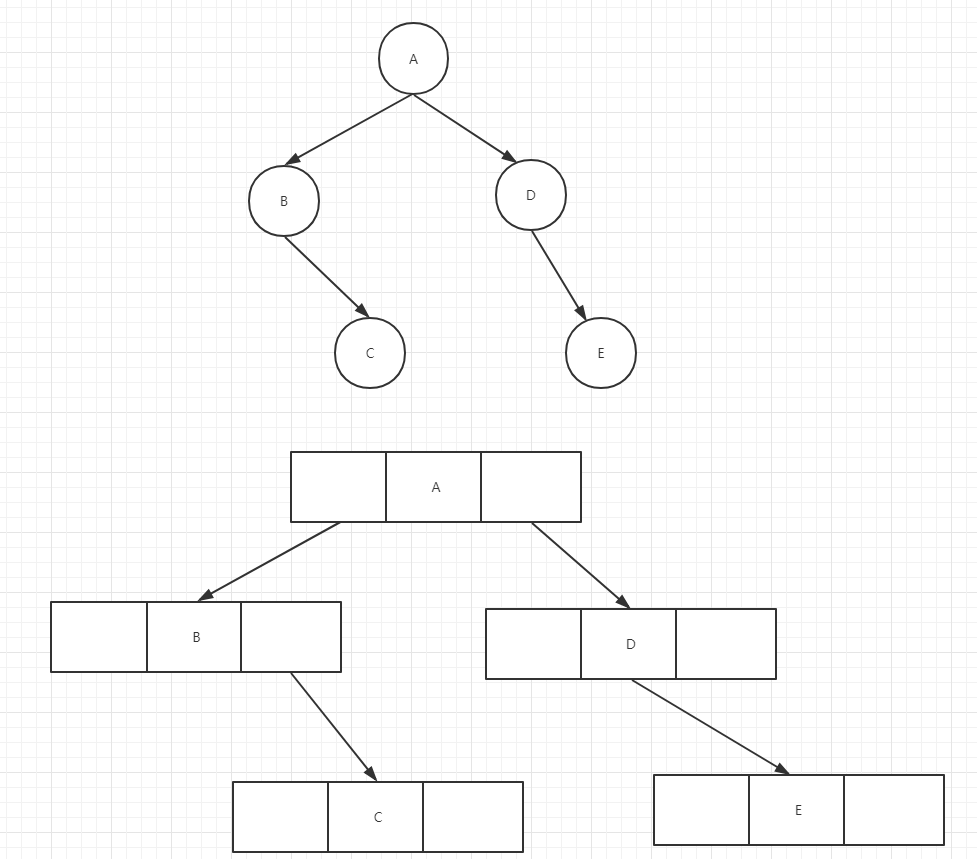
优点:访问结点的孩子较方便
缺点:访问指定的结点较困难
1.1.2 二叉树的构造
构造二叉树,就是根据两个遍历序列推算出二叉树的结构。
这两个遍历序列必须有一个是中序遍历序列,另一个可以是前序/后序/层次遍历序列。
务必介绍如何通过先序遍历序列和中序遍历序列、后序遍历序列和中序遍历序列构造二叉树。
已知一棵二叉树的先序遍历和中序遍历
利用先序遍历判断首结点后,带入到中序遍历中,将其分为左中序和右中序,并对照字母顺序将先序遍历分为左先序和右先序,后先判断一边,利用先序遍历找到根结点,带入中序遍历中,观察该结点在该序列中位于上一结点的左侧还是右侧,对应其为左孩子还是右孩子,依次进行后再判断另一侧。
例:
先序遍历:abdgcef
中序遍历:dgbacef

左先序:bdg 右先序:cef
左中序:dgb 右中序:ecf
已知一棵二叉树的后序遍历和中序遍历
利用后序遍历找到首结点,带入到中序遍历中,将其分为左中序和右中序,并对照字母顺序将先序遍历分为左后序和右后序,后先判断一边,利用后序遍历找到根结点,带入中序遍历中,观察该结点在该序列中位于上一结点的左侧还是右侧,对应其为左孩子还是右孩子,依次进行后再判断另一侧。
例:
先序遍历:abdgcef
中序遍历:gdbefca

左先序:bdg 右先序:cef
左中序:gdb 右中序:efc
1.1.3 二叉树的遍历
总结二叉树的4种遍历方式,如何实现。
先序遍历
若二叉树为空,则空操作返回,否则先访问根结点,然后前序遍历左子树,再前序遍历右子树
void PreOrder(BTNode *b)
{
if (b != NULL)
{
cout << b->data;
PreOrder(b->lchild);
PreOrder(b->rchild);
}
}
中序遍历
若二叉树为空,则空操作返回,否则从根结点开始(注意并不是先访问根结点),中序遍历根结点的左子树,然后访问根结点,最后中序遍历右子树
void PreOrder(BTNode *b)
{
if (b != NULL)
{
PreOrder(b->lchild);
cout << b->data;
PreOrder(b->rchild);
}
}
后序遍历
若二叉树为空,则空操作返回,否则从左到右先叶子结点后结点的方式遍历访问左右子树,最后访问根结点
void PreOrder(BTNode *b)
{
if (b != NULL)
{
PreOrder(b->lchild);
PreOrder(b->rchild);
cout << b->data;
}
}
层序遍历
若二叉树为空,则空返回,否则从树的第一层,即根结点开始访问,从上而下逐层遍历,在同一层中,按从左到右的顺序对结点逐个访问
void LevelTravesal(BiTree T)
{
queue<BiTree>qu;
BiTree BT;
int flag = 0;
if (T == NULL)
{
cout << "NULL";
return;
}
qu.push(T);
while (!qu.empty())
{
BT = qu.front();
if (flag == 0)
{
cout << BT->data;
flag = 1;
}
else
{
cout << " " << BT->data;
}
qu.pop();
if (BT->lchild != NULL)
{
qu.push(BT->lchild);
}
if (BT->rchild != NULL)
{
qu.push(BT->rchild);
}
}
}
1.1.4 线索二叉树
线索二叉树设计
规定当某个结点的左指针为空时,该指针指向这个序列中该结点的前驱结点,当右指针为空时,指向该序列中该结点的后继结点。指向前驱和后继结点的指针为线索。
需要定义标志域进行判断是否指向孩子还是前驱和后继结点
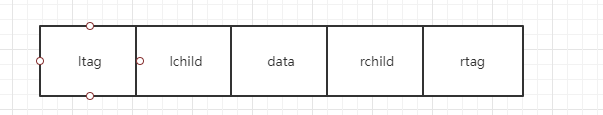
在每个结点再增设两个标志域ltag和rtag,决定lchild是指向左孩子还是前驱,rchild是指向右孩子还是后继
ltag=0表示有左孩子,指向左孩子
ltag=1表示无左孩子,指向上一-结点
rtag=0表示有右孩子,指向右孩子
rtag=1表示无右孩子,指向下一结点
中序线索二叉树特点
中序线索二叉树的遍历二叉树不需要递归,所有结点只需遍历一次,时间和空间的利用效率高。
在中序线索二叉树查找前驱和后继
先找到最左边的节点,然后判断其右子树是否为线索,如果是线索,那么就遍历后继结点,如果右子树是右孩子,那么就进入到右孩子的最左边的节点,进行同样的判断,直到遍历完了整棵树为止。
void InThreading(BiThrTree p)
{
if (p)
{
InThreading(p->lchild);
if (!p->lchild)
{
p->ltag = 1;
p->lchild = pre;
}
if (!pre->rchild)
{
pre->rtag = 1;
pre->rchild = p;
}
pre = p;
InThreading(p->rchild);
}
}
1.1.5 二叉树的应用--表达式树
表达式树构造
void InitExpTree(BTree& T, string str) //建二叉表达式树
{
stack<char>op;
stack<BTree>t;
int i = 0;
BTree p = NULL, a, b;//结点
while (str[i])
{
if (!In(str[i]))
{
p = new BTNode;
p->data = str[i];
p->lchild = NULL;
p->rchild = NULL;
t.push(p);
}
else
{
if (op.empty())
{
op.push(str[i]);
}
else
{
switch (Precede(op.top(), str[i]))
{
case'<':
op.push(str[i]); break;
case'=':
op.pop(); break;
case'>':
a = t.top();
t.pop();
b = t.top();
t.pop();
CreateExpTree(p, b, a, op.top());
op.pop();
t.push(p);
i--;
break;
}
}
}
i++;
}
while (!t.empty() && !op.empty())
{
b = t.top();
t.pop();
a = t.top();
t.pop();
CreateExpTree(p, a, b, op.top());
op.pop();
t.push(p);
}
T = p;
}
计算表达式树
double EvaluateExTree(BTree T)//计算表达式树
{
double sum = 0;
double a, b;
if (T->lchild == NULL && T->rchild == NULL)
{
return T->data - '0';
}
a = EvaluateExTree(T->lchild);
b = EvaluateExTree(T->rchild);
switch (T->data)
{
case'+':
return a + b;
break;
case'-':
return a - b;
break;
case'*':
return a * b;
break;
case'/':
if (b==0)
{
cout << "divide 0 error!";
exit(0);
}
return a / b;
break;
}
}
1.2 多叉树结构
1.2.1 多叉树结构
(1)双亲存储结构:
typedef struct
{
ElemType data;
int parent;//存放双亲
};
利用该性质可以准确有效的找到父亲母亲,但不易找到孩子
(2)孩子链存储结构:
typedef struct node
{
ElemType data;
struct node *son;//孩子结点
};
找到某结点的孩子容易,但找双亲费劲,且树的度较大时存在较多的空指针域
(3)孩子兄弟链存储结构
typedef struct node
{
ElemType data;
struct node *son;//孩子结点
struct node *brother;//兄弟结点
};
结构相似于二叉树,其优点为可方便实现树和二叉树的转换,缺点是查找指定双亲结点较难,利用该结构可解决目录树问题。
1.2.2 多叉树遍历
先序遍历
若树不空,则先访问根结点,然后依次先根遍历各子树
1.3 哈夫曼树
1.3.1 哈夫曼树定义
哈夫曼树的定义:
给定N个权值作为N个叶子结点,构造一棵二叉树,若该树的带权路径长度达到最小,称这样的二叉树为最优二叉树,也称为哈夫曼树(Huffman Tree)。哈夫曼树是带权路径长度最短的树,权值较大的结点离根较近。
哈夫曼树解决什么问题?
哈夫曼树可解决数据通信中的文字转二进制数字,此时二进制数字越少越好,故哈夫曼树起到很大的作用。同时也可解决程序判断的时间效率问题,利用哈夫曼树减少程序查找的次数以及时间,实现更好的优化。
1.3.2 哈夫曼树的结构体
(1)顺序存储结构
typedef struct
{
char data;
double weight;//权重
int parent;
int lchild;
int rchild;
};
(2)链式存储结构
typedef struct node
{
char data;
double weight;//权重
struct node *parent;
struct node *lchild;
struct node *rchild;
};
1.3.2 哈夫曼树构建及哈夫曼编码
如何构造哈夫曼树及哈夫曼编码:
每次找到最小的两个结点组成树后再放入序列中重复比较操作,构建完树后,给每条边标上记号,左子树的边为0,右子树的边为1,后每个叶子结点的哈夫曼编码对应走过的边所做记号的序列。
1.4 并查集
并查集定义:
支持查找一个元素所属的集合以及2个元素各自专属的集合等运算,当给出(a,b)时,快速合并a和b所在的集合。在这种数据中,n个不同的元素被分为若干组,每组是一个集合,称之为并查集。
(3)结构体:
并查集解决的问题
可实现多个不同的集合或者树的合并,找到其中元素间的对应关系,例如等价问题和朋友圈问题。
并查集优势
并查集可以大大提高查找效率
*并查集的结构体
typedef struct node
{
int data;
int rank;//对应的秩,进行高度合并
int parent;//双亲下标
}UFSTree;
查找
int Find(USFTree t[], int x)//在x所在的子树查找集合编号
{
if (x != t[x].parent)//双亲不是自己
{
return Find(t, t[x].parent);//递归父母直至找到
}
else
{
return x;//找到自己
}
}
合并
int Find(USFTree t[], int x)//在x所在的子树查找集合编号
{
if (x != t[x].parent)//双亲不是自己
{
return Find(t, t[x].parent);//递归父母直至找到
}
else
{
return x;//找到自己
}
}
1.5.谈谈你对树的认识及学习体会。
感觉树的这章比较容易懂,但是有的操作还是需要灵活的思路,以致于做pta里较难的题的时候花了很多时间,上了习题课以后学到了很多写代码应该有的习惯,自我反思以后确实是自己写代码的习惯不太好,以后要多养成先进行思路的构想,经常检查等好习惯
2.PTA实验作业(4分)
此处请放置下面2题代码所在码云地址(markdown插入代码所在的链接)。如何上传VS代码到码云
2.1 二叉树
二叉树叶子结点带权路径长度和
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
typedef struct node {
char data;
struct node* lchild; struct node* rchild;
}BTNode, * BTree;
BTree CreatTree(string str, int i);
void GetWPL(BTree bt, int h, int& wpl);
int len;
int main()
{
BTree bt;
string str;
cin >> str;
int h = 0;
int wpl = 0;
len = str.size();
bt = CreatTree(str, 1);
GetWPL(bt, h, wpl);
cout << wpl;
return 0;
}
BTree CreatTree(string str, int i)
{
BTree bt;
if (i > len - 1)
{
return NULL;
}
if (str[i] == '#')
{
return NULL;
}
bt = new BTNode;
bt->data = str[i];
bt->lchild = CreatTree(str, 2 * i);
bt->rchild = CreatTree(str, 2 * i + 1);
return bt;
}
void GetWPL(BTree bt, int h, int& wpl)
{
if (bt == NULL)
{
return;
}
if (bt->lchild == NULL && bt->rchild == NULL)
{
wpl = wpl + (bt->data - '0') * h;
}
GetWPL(bt->lchild, h + 1, wpl);
GetWPL(bt->rchild, h + 1, wpl);
}
2.1.1 解题思路及伪代码
解题思路:
建树
定义wpl存放树的权
定义h存放树的高
利用递归来计算带权路径长度和
伪代码:
main
{
BTree bt
int h,wpl
建树
GetWPL
输出wpl
}
wpl
{
if 孩子节点不空
wpl = wpl + (bt->data - '0') * h
endif
GetWPL(bt->lchild, h + 1, wpl)
GetWPL(bt->rchild, h + 1, wpl)
}
2.1.2 总结解题所用的知识点
树结构体的定义
建树的方法
递归的使用
2.2 目录树
2.2.1 解题思路及伪代码
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
typedef struct node {
string data;
bool isDir;
struct node* firstchild;
struct node* brother;
}DirTNode, * DirTree;
void CreateTree(DirTree& tr);
void InitDirTree(DirTree& tr);
void PrintDirTree(DirTree tr,int h);
void InsertTreeNode(DirTree& tr, DirTree node);
int main()
{
DirTree tr;
CreateTree(tr);
int h = 0;
PrintDirTree(tr, h);
return 0;
}
void CreateTree(DirTree& tr)
{
DirTree trnode;
DirTree rootNode;
int num;
int i;
string nodestr;
string datastr;
InitDirTree(tr);
rootNode = tr;
cin >> num;
int begin;
int index=-1;
//字符串分离,生成树结点
for (i = 1; i <= num; i++)
{
tr = rootNode;
cin >> nodestr;
begin = 0;
while ((index = nodestr.find('\', begin)) != -1)
{
datastr = nodestr.substr(begin, index - begin);
//cout << datastr;
begin = index + 1;
trnode = new DirTNode;
trnode->data = datastr;
trnode->isDir = true;
trnode->firstchild = NULL;
trnode->brother = NULL;
InsertTreeNode(tr, trnode);
}
if (begin < nodestr.length())
{
datastr = nodestr.substr(begin, nodestr.length()-begin);
trnode = new DirTNode;
trnode->data = datastr;
trnode->isDir = false;
trnode->firstchild = NULL;
trnode->brother = NULL;
InsertTreeNode(tr, trnode);
}
}
tr = rootNode;
}
void InitDirTree(DirTree& tr)
{
tr = new DirTNode;
tr->data = "root";
tr->isDir = true;//true表示是目录
tr->firstchild = NULL;
tr->brother = NULL;
}
void InsertTreeNode(DirTree& tr, DirTree node)
{
DirTree head;
head = tr->firstchild;
//树节点 插入目录树
//没有第一个孩子,直接生成第一个孩子结点
if (tr->firstchild == NULL)
{
tr->firstchild = node;
tr = node;
return;
}
//更改孩子
if ((tr->firstchild->isDir == false && node->isDir == true) ||
(node->isDir == tr->firstchild->isDir && node->data < tr->firstchild->data))
{
node->brother = tr->firstchild;
tr->firstchild = node;
tr = node;
return;
}
//结点存在,即数据相等且目录文件熟悉相等,则不新建孩子结点
if (head->isDir == node->isDir)
{
if (head->data == node->data)
{
tr = tr->firstchild;
return;
}
}
//插入作为兄弟
if ((head->brother == NULL))
{
while (head)
{
if (head->brother == NULL)
{
head->brother = node;
tr = node;
return;
}
head = head->brother;
}
}
else
{
DirTree ftr;
ftr = head;
if (node->isDir == true)
{
while (head != NULL && node->data > head->data && head->isDir == true)
{
if (head->data == node->data)
{
tr = tr->firstchild;
return;
}
ftr = head;
head = head->brother;
if (head!=NULL)
{
if (head->data == node->data)
{
tr = head;
return;
}
}
}
if (head != NULL)
{
if (head->isDir != true)
{
node->brother = head;
ftr->brother = node;
tr = node;
return;
}
node->brother = head;
ftr->brother = node;
tr = node;
return;
}
else
{
ftr->brother = node;
tr = node;
return;
}
}
else
{
while (head != NULL && head->isDir == true)
{
ftr = head;
head = head->brother;
}
if (head != NULL)
{
while (head != NULL&& node->data > head->data)
{
ftr = head;
head = head->brother;
}
if (head != NULL)
{
node->brother = head;
ftr->brother = node;
tr = node;
return;
}
else
{
ftr->brother = node;
tr = node;
return;
}
}
else
{
ftr->brother = node;
tr = node;
return;
}
}
}
}
void PrintDirTree(DirTree tr, int h)
{
if (tr == NULL)
{
return;
}
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= h; i++)
{
cout << " ";
}
cout << tr->data << endl;
PrintDirTree(tr->firstchild, h + 1);
PrintDirTree(tr->brother, h);
}
解题思路:
设计目录树结构体
进行初始化树,建根结点
对输入的字符串进行切割,分离文件名和目录名:
判断何时更改孩子
判断何时新建孩子结点
判断何时更改插入作为兄弟
对应产生树结点,插入建立目录树。
定义变量h来控制输出时空格的个数
伪代码:
typedef struct node {
string data
bool isDir
struct node* firstchild
struct node* brother
}DirTNode, * DirTree
int main()
{
DirTree tr
CreateTree(tr)
int h = 0;
PrintDirTree(tr, h)
return 0
}
void CreateTree(DirTree& tr)
{
DirTree trnode
DirTree rootNode 存放头结点
int num 行数
int i
string nodestr
string datastr
InitDirTree(tr)
rootNode = tr
cin >> num
int begin
int index=-1
//字符串分离,生成树结点
for i=1 to num
tr = rootNode
cin >> nodestr
begin = 0
while ((index = nodestr.find('\', begin)) != -1)
datastr = nodestr.substr(begin, index - begin)
begin = index + 1
trnode = new DirTNode
新建trnode,赋data值,置孩子兄弟为空,插入链中
end while
if (begin < nodestr.length())
新建trnode,赋data值,置孩子兄弟为空,插入链中
end if
end for
tr = rootNode;
}
void InitDirTree(DirTree& tr)
{
初始化
tr = new DirTNode
tr->data = "root"
tr->isDir = true true表示是目录
tr->firstchild = NULL
tr->brother = NULL
}
void InsertTreeNode(DirTree& tr, DirTree node)
{
DirTree head
head = tr->firstchild
//没有第一个孩子,直接生成第一个孩子结点
if 没有第一个孩子
直接生成第一个孩子结点
return;
end if
//更改孩子
if (要插入的是目录文件夹,而firstchild是文件) ||(文件属性相同 && 要插入的文件排序在前))
node->brother = tr->firstchild
tr->firstchild = node
tr = node
return
end if
//结点存在,即数据相等且目录文件熟悉相等,则不新建孩子结点
if (属性相同且数据相等)
不新建孩子结点
tr = tr->firstchild
return
end if
//插入作为兄弟
if ((head->brother == NULL))
while (head)
if (head->brother == NULL)
head->brother = node
tr = node
return
end if
head = head->brother
end while
else
DirTree ftr;
ftr = head;
if (要插入的文件属性为目录)
while (head != NULL && node->data > head->data && head->isDir == true)
if (head->data == node->data)
tr = tr->firstchild
return
end if
ftr = head
head = head->brother
if (head!=NULL)
if (head->data == node->data)
tr = head
return
end if
end if
end while
if (head != NULL)
if (head->isDir != true)
node->brother = head
ftr->brother = node
tr = node
return
end if
node->brother = head
ftr->brother = node
tr = node
return
else
ftr->brother = node
tr = node
return
end if
else
while (head != NULL && head->isDir == true)
ftr = head
head = head->brother
end while
if (head != NULL)
while (head != NULL&& node->data > head->data)
ftr = head
head = head->brother
end while
if (head != NULL)
node->brother = head
ftr->brother = node
tr = node
return
else
ftr->brother = node
tr = node
return
end if
else
ftr->brother = node
tr = node
return
end if
end if
end if
}
void PrintDirTree(DirTree tr, int h)
{
if (tr == NULL)
{
return
}
int i
for i=1 to h
{
cout << " "
}
cout << tr->data << endl
PrintDirTree(tr->firstchild, h + 1)
PrintDirTree(tr->brother, h)
}
2.2.2 总结解题所用的知识点
孩子兄弟链结构的定义
孩子兄弟链结构的创建
截取字符串中用''分割的函数:nodestr.substr(begin, index - begin) 其中begin=0,index=-1
3.阅读代码(0--1分)
3.1 题目及解题代码
二叉树的最大宽度
已知一个二叉树,写一个函数得到已知二叉树的最大宽度。一个树的宽度指的是所有层的宽度的最大值。
int LevelWidth(BT root,int level)//find the width of a level(amounts of nodes in the level).
{
if(!root)return 0;
else
{
if(level==1)return 1;
level=LevelWidth(root->lchild,level-1)+LevelWidth(root->rchild,level-1);
}
return level;
}
int Width(BT root)//find the maximum width of the btree.
{
int width,i;
int w[20];
for(i=0;i<20;i++)w[i]=0;
if(!root)width=0;
else
{
for(i=0;i<=Depth(root);i++)w[i]=LevelWidth(root,i+1);
}
i=0;
while(w[i])
{
if(w[i]>width)width=w[i];
i++;
}
return width;
}
3.2 该题的设计思路及伪代码
本题使用了递归的思想
并非是指整个函数递归,而是说其中一个子函数使用了递归
循环求取每一层的宽度,存入一个数组,然后在这个数组里求最大值,数组下标即层数(或高度)。
用一个子函数求某一层的宽度,参数考虑起始结点以及对应的层数,举例:对于根节点来说,其第三层的宽度,就是其左孩子的第二层的宽度与其右孩子的第二层的宽度之和。

int LevelWidth(BT root,int level)//find the width of a level(amounts of nodes in the level).
{
if(!root)
return 0
else
if(level==1)
return 1
end if
level=LevelWidth(root->lchild,level-1)+LevelWidth(root->rchild,level-1)
end if
return level
}
int Width(BT root)//find the maximum width of the btree.
{
int width,i
int w[20]
fori=0 to 20
w[i]=0
if(!root)
width=0
else
for i=0 to Depth(root)
w[i]=LevelWidth(root,i+1)
end for
end if
i=0
while(w[i])
if(w[i]>width)width=w[i]
i++
end while
return width
}
3.3 分析该题目解题优势及难点。
本题的难度中等,有多种解题方法,有益于学生思维发散,本题采用了递归的方法解题,也可以采用非递归的方法,即队列
难点有如何求每一层的宽度以及在此基础上的如何找出最大值