Super fast color transfer between images
About a month ago, I spent a morning down at the beach, walking along the sand, letting the crisp, cold water lap against my feet. It was tranquil, relaxing. I then took out my iPhone and snapped a few photos of the ocean and clouds passing by. You know, something to remember the moment by. Because I knew that as soon as I got back to the office, that my nose was going back on the grindstone.
Back at home, I imported my photos to my laptop and thought, hey, there must be a way to take this picture of the beach that I took during the mid-morning and make it look like it was taken at dusk.
And since I’m a computer vision scientist, I certainly wasn’t going to resort to Photoshop.
No, this had to be a hand engineered algorithm that could take two arbitrary images, a source and a target, and then transfer the color space from the source image to the target image.
A couple weeks ago I was browsing reddit and I came across a post on how to transfer colors between two images. The authors’ implementation used a histogram based method, which aimed to balance between three “types” of bins: equal, excess, and deficit.
The approach obtained good results — but at the expense of speed. Using this algorithm would require you to perform a lookup for each and every pixel in the source image, which will become extremely expensive as the image grows in size. And while you can certainly speed the process up using a little NumPy magic you can do better.
Much, much better in fact.
What if I told you that you could create a color transfer algorithm that uses nothing but the mean and standard deviation of the image channels.
That’s it. No complicated code. No computing histograms. Just simple statistics.
And by the way…this method can handle even gigantic images with ease.
Interested?
Read on.
You can also download the code via GitHub or install via PyPI (assuming that you already have OpenCV installed).
The Color Transfer Algorithm
My implementation of color transfer is (loosely) based on Color Transfer between Images by Reinhard et al, 2001.
In this paper, Reinhard and colleagues demonstrate that by utilizing the L*a*b* color space and the mean and standard deviation of each L*, a*, and b* channel, respectively, that the color can be transferred between two images.
The algorithm goes like this:
- Step 1: Input a
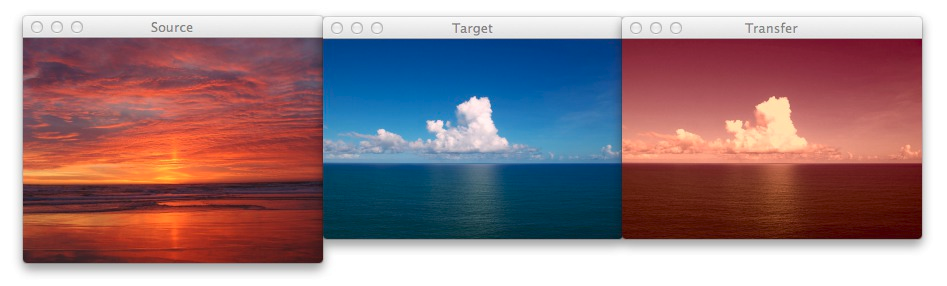
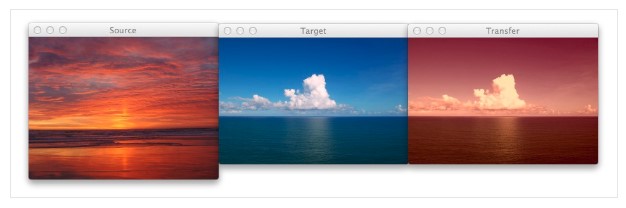
sourceand atargetimage. The source image contains the color space that you want yourtargetimage to mimic. In the figure at the top of this page, the sunset image on the left is mysource, the middle image is mytarget, and the image on the right is the color space of thesourceapplied to thetarget. - Step 2: Convert both the
sourceand thetargetimage to the L*a*b* color space. The L*a*b* color space models perceptual uniformity, where a small change in an amount of color value should also produce a relatively equal change in color importance. The L*a*b* color space does a substantially better job mimicking how humans interpret color than the standard RGB color space, and as you’ll see, works very well for color transfer. - Step 3: Split the channels for both the
sourceandtarget. - Step 4: Compute the mean and standard deviation of each of the L*a*b* channels for the
sourceandtargetimages. - Step 5: Subtract the mean of the L*a*b* channels of the
targetimage fromtargetchannels. - Step 6: Scale the
targetchannels by the ratio of the standard deviation of thetargetdivided by the standard deviation of thesource, multiplied by thetargetchannels. - Step 7: Add in the means of the L*a*b* channels for the
source. - Step 8: Clip any values that fall outside the range [0, 255]. (Note: This step is not part of the original paper. I have added it due to how OpenCV handles color space conversions. If you were to implement this algorithm in a different language/library, you would either have to perform the color space conversion yourself, or understand how the library doing the conversion is working).
- Step 9: Merge the channels back together.
- Step 10: Convert back to the RGB color space from the L*a*b* space.
I know that seems like a lot of steps, but it’s really not, especially given how simple this algorithm is to implement when using Python, NumPy, and OpenCV.
If it seems a bit complex right now, don’t worry. Keep reading and I’ll explain the code that powers the algorithm.
Requirements
I’ll assume that you have Python, OpenCV (with Python bindings), and NumPy installed on your system.
If anyone wants to help me out by creating a requirements.txt file in the GitHub repo, that would be super awesome.
Install
Assuming that you already have OpenCV (with Python bindings) and NumPy installed, the easiest way to install is use to use pip:
$pip install color_transfer
The Code Explained
I have created a PyPI package that you can use to perform color transfer between your own images. The code is also available on GitHub.
Anyway, let’s roll up our sleeves, get our hands dirty, and see what’s going on under the hood of the color_transfer package:
# import the necessary packages import numpy as np import cv2 def color_transfer(source, target): # convert the images from the RGB to L*ab* color space, being # sure to utilizing the floating point data type (note: OpenCV # expects floats to be 32-bit, so use that instead of 64-bit) source = cv2.cvtColor(source, cv2.COLOR_BGR2LAB).astype("float32") target = cv2.cvtColor(target, cv2.COLOR_BGR2LAB).astype("float32")
Lines 2 and 3 import the packages that we’ll need. We’ll use NumPy for numerical processing and cv2 for our OpenCV bindings.
From there, we define our color_transfer function on Line 5. This function performs the actual transfer of color from the source image (the first argument) to the target image (the second argument).
The algorithm detailed by Reinhard et al. indicates that the L*a*b* color space should be utilized rather than the standard RGB. To handle this, we convert both the source and the target image to the L*a*b* color space on Lines 9 and 10 (Steps 1 and 2).
OpenCV represents images as multi-dimensional NumPy arrays, but defaults to the uint8datatype. This is fine for most cases, but when performing the color transfer we could potentially have negative and decimal values, thus we need to utilize the floating point data type.
Now, let’s start performing the actual color transfer:
# compute color statistics for the source and target images (lMeanSrc, lStdSrc, aMeanSrc, aStdSrc, bMeanSrc, bStdSrc) = image_stats(source) (lMeanTar, lStdTar, aMeanTar, aStdTar, bMeanTar, bStdTar) = image_stats(target) # subtract the means from the target image (l, a, b) = cv2.split(target) l -= lMeanTar a -= aMeanTar b -= bMeanTar # scale by the standard deviations l = (lStdTar / lStdSrc) * l a = (aStdTar / aStdSrc) * a b = (bStdTar / bStdSrc) * b # add in the source mean l += lMeanSrc a += aMeanSrc b += bMeanSrc # clip the pixel intensities to [0, 255] if they fall outside # this range l = np.clip(l, 0, 255) a = np.clip(a, 0, 255) b = np.clip(b, 0, 255) # merge the channels together and convert back to the RGB color # space, being sure to utilize the 8-bit unsigned integer data # type transfer = cv2.merge([l, a, b]) transfer = cv2.cvtColor(transfer.astype("uint8"), cv2.COLOR_LAB2BGR) # return the color transferred image return transfer
Lines 13 and 14 make calls to the image_stats function, which I’ll discuss in detail in a few paragraphs. But for the time being, know that this function simply computes the mean and standard deviation of the pixel intensities for each of the L*, a*, and b* channels, respectively (Steps 3 and 4).
Now that we have the mean and standard deviation for each of the L*a*b* channels for both the source and target images, we can now perform the color transfer.
On Lines 17-20, we split the target image into the L*, a*, and b* components and subtract their respective means (Step 5).
From there, we perform Step 6 on Lines 23-25 by scaling by the ratio of the target standard deviation, divided by the standard deviation of the source image.
Then, we can apply Step 7, by adding in the mean of the source channels on Lines 28-30.
Step 8 is handled on Lines 34-36 where we clip values that fall outside the range [0, 255] (in the OpenCV implementation of the L*a*b* color space, the values are scaled to the range [0, 255], although that is not part of the original L*a*b* specification).
Finally, we perform Step 9 and Step 10 on Lines 41 and 42 by merging the scaled L*a*b* channels back together, and finally converting back to the original RGB color space.
Lastly, we return the color transferred image on Line 45.
Let’s take a quick look at the image_stats function to make this code explanation complete:
We make the assumption that the image is already in the L*a*b* color space, prior to calling cv2.split on Line 49 to break our image into its respective channels.
From there, Lines 50-52 handle computing the mean and standard deviation of each of the channels.
Finally, a tuple of mean and standard deviations for each of the channels are returned on Line 55.
Examples
To grab the example.py file and run examples, just grab the code from the GitHub project page.
You have already seen the beach example at the top of this post, but let’s take another look:
$python example.py--source images/ocean_sunset.jpg--target images/ocean_day.jpg
After executing this script, you should see the following result:
Figure 1: The image on the left is the source, the middle image is the target, and the right is the output image after applying the color transfer from the source to the target. Notice how a nice sunset effect is created in the output image.
Notice how the oranges and reds of the sunset photo has been transferred over to the photo of the ocean during the day.
Awesome. But let’s try something different:
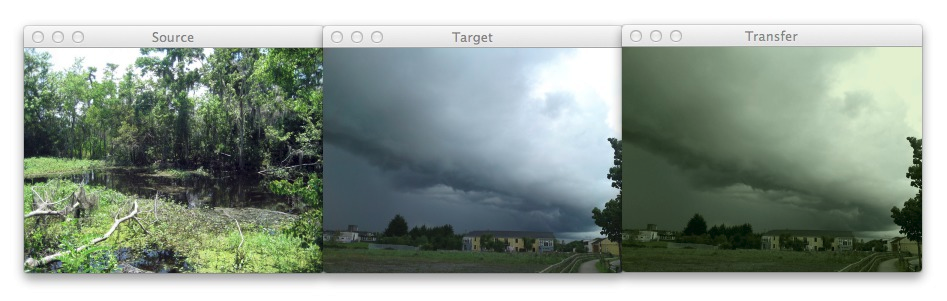
$python example.py--source images/woods.jpg--target images/storm.jpg
Figure 2: Using color transfer to make storm clouds look much more ominous using the green foliage of a forest scene.
Here you can see that on the left we have a photo of a wooded area — mostly lots of green related to vegetation and dark browns related to the bark of the trees.
And then in the middle we have an ominous looking thundercloud — but let’s make it more ominous!
If you have ever experienced a severe thunderstorm or a tornado, you have probably noticed that the sky becomes an eerie shade of green prior to the storm.
As you can see on the right, we have successfully mimicked this ominous green sky by mapping the color space of the wooded area to our clouds.
Pretty cool, right?
One more example:
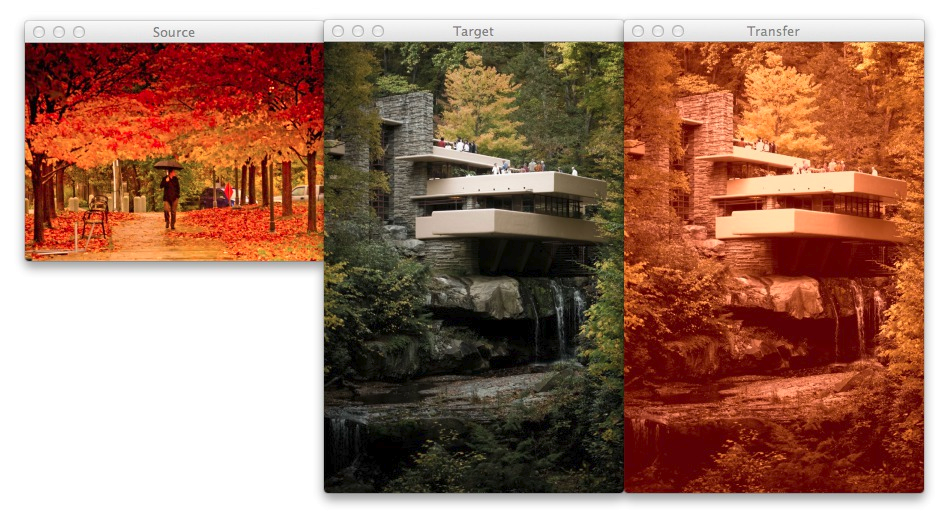
Figure 3: Using color transfer between images to create an autumn style effect on the output image.
Here I am combining two of my favorite things: Autumn leaves (left) and mid-century modern architecture, in this case, Frank Lloyd Wright’s Fallingwater (middle).
The middle photo of Fallingwater displays some stunning mid-century architecture, but what if I wanted to give it an “autumn” style effect?
You guessed it — transfer the color space of the autumn image to Fallingwater! As you can see on the right, the results are pretty awesome.
Ways to Improve the Algorithm
While the Reinhard et al. algorithm is extremely fast, there is one particular downside — it relies on global color statistics, and thus large regions with similar pixel intensities values can dramatically influence the mean (and thus the overall color transfer).
To remedy this problem, we can look at two solutions:
Option 1: Compute the mean and standard deviation of the source image in a smaller region of interest (ROI) that you would like to mimic the color of, rather than using the entire image. Taking this approach will make your mean and standard deviation better represent the color space you want to use.
Option 2: The second approach is to apply k-means to both of the images. You can cluster on the pixel intensities of each image in the L*a*b* color space and then determine the centroids between the two images that are most similar using the Euclidean distance. Then, compute your statistics within each of these regions only. Again, this will give your mean and standard deviation a more “local” effect and will help mitigate the overrepresentation problem of global statistics. Of course, the downside is that this approach is substantially slower, since you have now added in an expensive clustering step.
Summary
In this post I showed you how to perform a super fast color transfer between images using Python and OpenCV.
I then provided an implementation based (loosely) on the Reinhard et al. paper.
Unlike histogram based color transfer methods which require computing the CDF of each channel and then constructing a Lookup Table (LUT), this method relies strictly on the mean and standard deviation of the pixel intensities in the L*a*b* color space, making it extremely efficient and capable of processing very large images quickly.
If you are looking to improve the results of this algorithm, consider applying k-means clustering on both the source and target images, matching the regions with similar centroids, and then performing color transfer within each individual region. Doing this will use local color statistics rather than global statistics and thus make the color transfer more visually appealing.
Code Available on GitHub
Looking for the source code to this post? Just head over to the GitHub project page!