1. hive的简介(具体见文档)
Hive是分析处理结构化数据的工具
本质:将hive sql转化成MapReduce程序或者spark程序
Hive处理的数据一般存储在HDFS上,其分析数据底层的实现是MapReduce/spark,执行程序运行在Yarn上
其大致可以按如下图理解(具体可见HIVE文档)
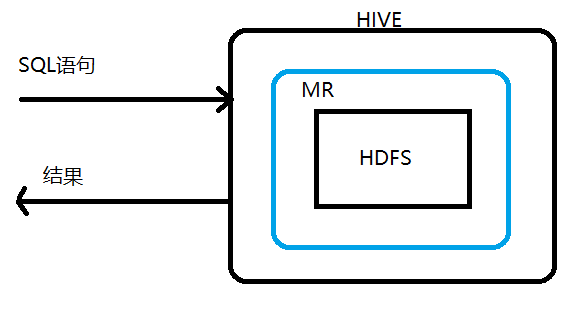
sql语句是对某个表进行操作,所以hive一定要创建一个表格,这个表格必须要映射到hdfs中某个具体的文件才行,而映射关系、表的结构数据以及hdfs中数据的存储结构都会在创建表时规定,这样就可以通过操作这个表格从而达到对hdfs中文件的处理(文档详细讲了这个过程)
2 hive的安装
2.0 安装mysql
见大数据学习day02,但是要注意,开启远程连接权限,如下
mysql > grant all privileges on *.* to 'root'@'%' identified by '密码' with grant option; mysql > flush privileges;
授权完成后,测试一下是否成功:在windows上用Navicat链接一下是否能成功
2.1 上传hive的安装包,解压
tar -zxvf apache-hive-2.3.5.tar.gz -C /usr/apps
2.2 修改hive-env.sh内容
(1)mv hive-env.sh.template hive-env.sh
(2)vi hive-env.sh
此文件中配置了hadoop的地址,所以hive能找到hadoop
vi /usr/apps/apache-hive-2.3.1-bin/conf/hive-env.sh

2.3 修改配置文件(conf文件夹下无此文件)
vi /usr/apps/apache-hive-2.3.1-bin/conf/hive-site.xml
修改内容如下

<configuration> <!-- 记录HIve中的元数据信息 记录在mysql中 --> <property> <name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionURL</name> <value>jdbc:mysql://doit01:3306/hive?createDatabaseIfNotExist=true&useSSL=false</value> </property> <property> <name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionDriverName</name> <value>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</value> </property> <property> <name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionUserName</name> <value>root</value> </property> <property> <name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionPassword</name> <value>123456</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.metastore.warehouse.dir</name> <value>/user/hive/warehouse</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.exec.scratchdir</name> <value>/user/hive/tmp</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.querylog.location</name> <value>/user/hive/log</value> </property> <!-- shell客户端连接的端口 --> <property> <name>hive.server2.thrift.port</name> <value>10000</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.server2.thrift.bind.host</name> <value>0.0.0.0</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.server2.webui.host</name> <value>0.0.0.0</value> </property> <!-- hive服务的页面的端口 --> <property> <name>hive.server2.webui.port</name> <value>10002</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.server2.long.polling.timeout</name> <value>5000</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.server2.enable.doAs</name> <value>true</value> </property> <property> <name>datanucleus.autoCreateSchema </name> <value>false</value> </property> <property> <name>datanucleus.fixedDatastore </name> <value>true</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.execution.engine</name> <value>mr</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.zookeeper.quorum</name> <value>doit01,doit02,doit03</value> </property> </configuration>
2.4 开启权限,即允许hive操作hdfs
/usr/apps/hadoop-2.8.5/etc/hadoop/core-site.xmld
2.5 拷贝一个mysql的jdbc驱动jar包到hive的lib目录中
2.6 重启hdp
stop-all.sh
start-all.sh
2.7 初始化hive的元数据库
${HIVE_HOME}/bin/schematool -initSchema -dbType mysql
此操作后即可在mysql中得到一个hive数据库,如下图

2.8 启动hive
(1)第一种方式
在本地启动一个客户端去连接本机器的hive1服务
/usr/apps/apache-hive-2.3.1-bin/bin/hive
即可得到下图所示

这种方式的格式不友好
(2)第二种方式(HiveJDBC访问)
a. 启动hiveserver2服务:hiveserver2
b. 启动beeline:beeline
c. 连接hiveserver2(可以在别的机器上连接feng05这台机器)
beeline> !connect jdbc:hive2://feng05:10000
bin/beeline -u jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000 -n root(补充)
补充:后台启动hiveserver2
HiveServer启动时可以选择启动为前台模式,也可以启动为后台模式:如何将一个程序启动为后台模式?如下
nohup bin/hiveserver2 1>/dev/null 2>&1 &
此处降 stdout和errout 送到 /dev/null 里面。那什麼是 /dev/null 呢,/dev/null 是 Unix/Linux 里的【无底洞】,任何的 output 送去了【无底洞】就再也没了。相信我,真的没了!那麼有人问,在什麼情况下要把 output 送去这无底洞呢?这里没有标准答案,不过一般呢,要是你不想看到 output 或者output 太多太大了,有可能把硬碟给挤爆了的时候,程序的设计就会考虑把 output 送到 /dev/null 了。
例子:
StdErr类
object StdErr{ def main(args:Array[String]):Unit = { var i = 0 while (true) { // out:标准输出通道 System.out.println("standard output..." + i) // err:错误输出通道 System.err.println("error output..." + i) Thread.sleep(10) i = i+1 } } }
控制台有两个输出通道:错误输出和标准输出,其中1表示标准输出,2表示错误输出
将改代码打成jar包放到linux上运行,此处自己写了运行脚本,如下所示
#!/bin/bash source /etc/profile java -cp /root/stderr.jar com.doit.demo.StdErr
当运行命令如下时:
./stderr //前台运行,输出会直接打印到控制台,打印时控制台不能操作 ./stderr & //后台运行,输出会直接打印到控制台,打印时控制台可以操作(影响操作,所以会将标准输出和错误输出写入指定文件中) ./stderr 1>/root/std.out 2>/root/err.out & //后台运行,“>”表示重定向,将标准输出写入到std.out文件,错误输出写入到err.out
3. 数据库的基本操作
(1)create database db_name ;
(2)drop database db_name (cascade强制删除);
(3)desc database mydb1 ; 显示数据库的信息

(4)desc database extended mydb1(与(3)的区别是此命令还可以显示属性信息(若有的话))

(5)alter database mydb set dbproperties ("author"="feng") ; 数据库的属性信息
(6)use db_name 切换数据库
(7)select current_database() ; 查看当前正在使用的数据库名称
总结:
数据库在hdfs中是一个文件夹,表在HDFS中对应一个文件夹
4. 建表
4.1 hive中支持的数据类型(常用)
int bigint string double Float
4.2 建表
4.2.1 创建内部表
create table tb_name(
列名 数据类型 ,
列名 数据类型 ,
.......
) ;
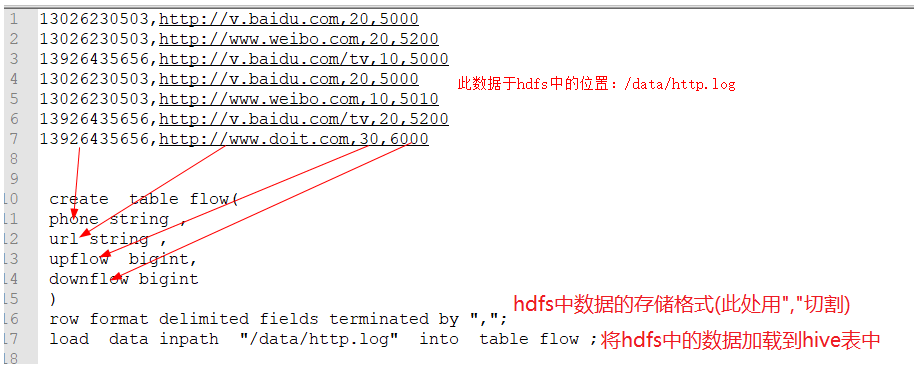
例1

这个时候tb_teacher表格在hdfs上对应的文件位置如下
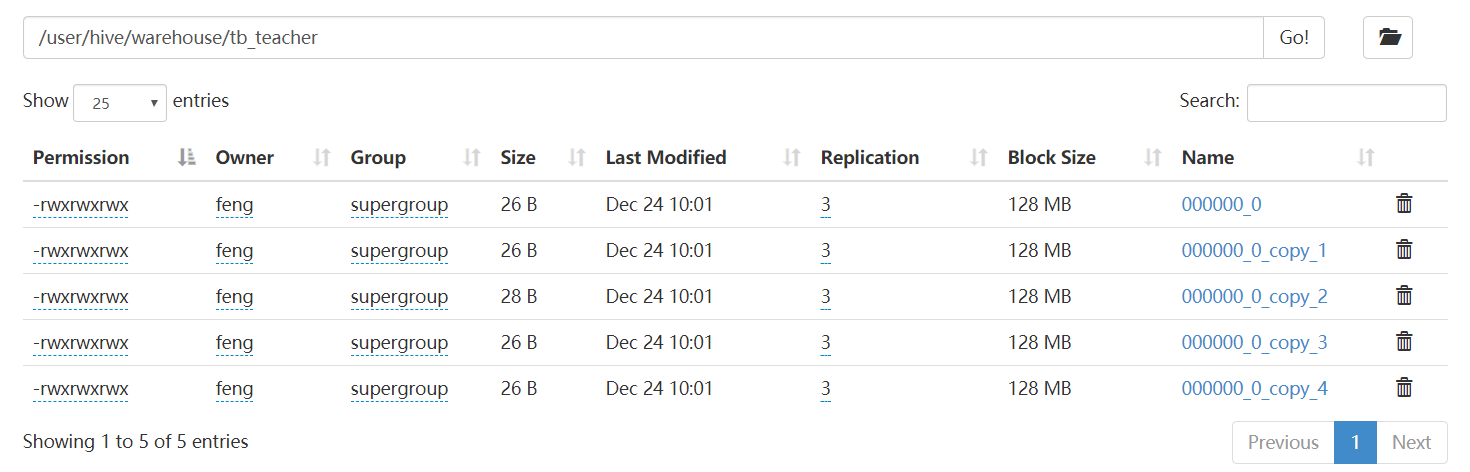
插入数据(建议不要插入数据,每次插入一条数据会有一个小文件产生,这样影响hdfs的效率)
insert into tb_teacher values (1001,'yangmi' , 34,230000.00,'F') ; insert into tb_teacher values (1002,'yangzi' , 24,220000.00,'F') ; insert into tb_teacher values (1003,'yangying' , 29,250000.00,'F') ;
如下
例2
(1)数据如下,并将这个数据上传至hdfs(hdfs://feng05:9000)

(2) 根据flow静态数据创建一个对应的hive表
create table flow( phone string , url string , upflow bigint, downflow bigint ) row format delimited fields terminated by ","; // 指定数据的分割规则
(3)加载hdfs中的数据到hive表中
0: jdbc:hive2://feng05:10000> load data inpath "/data/http.log" into table flow ;
注意,内部表进行加载数据的时候,hdfs中的原始数据就被移动到了相应表的文件中,当在shell端删除flow表时,发现hdfs中对应的文件(flow)也被删除了,这也意味着数据丢失了
(4)这个时候对表flow进行sql操作时,就能获取相应的结果
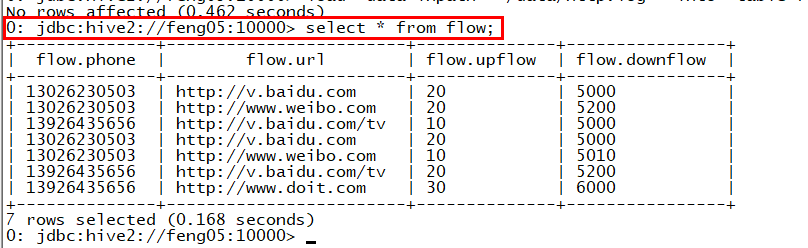
此时,进行一些数据处理会非常方便,如下

此时若是要达到同样的需求,用MR的话会很麻烦,但使用hive中的sql会相当的方便,节约开发时间
4.2.2 创建外部表
create external table tb_name( phone string , url string , upflow bigint, downflow bigint )
(1)创建一个外部表,删除表的时候数据不会被删除,但是数据会被移动到表文件夹下
create external table flow2( phone string , url string , upflow bigint, downflow bigint ) row format delimited fields terminated by ","; load data inpath "/data/http.log" into table flow2 ;
当删除flow表时,如下
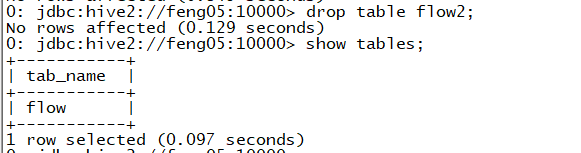
发现hdfs中的flow2中的http.log还是存在flow2的文件夹下。
但是,这样建表还是会移动数据,相当于原始数据丢失,该怎么解决呢?如下
(2)创建一个外部表 指定数据的位置(多个表可以指定同一个数据位置) 不会移动数据
由于此处的做法相当于在外部创建一个表指向数据,所以就不需要将数据加载至表中了
create external table flow3( phone string , url string , upflow bigint, downflow bigint ) row format delimited fields terminated by "," location "/log/" ;
同理创建flow4,得到如下结果

可以发现hdfs://9000/log下的http.log数据没有丢失,并且能进行相应的sql操作,当删除flow4时,数据也不会丢失
(3)内部表指定路径
create table manager_flow( phone string , url string , upflow bigint, downflow bigint ) row format delimited fields terminated by "," location "/log/"
这种情况,当删除内部表的时候,相应指定位置的数据也会被删除,即使这个数据所在的地址有外部表指定
注意:指定路径的形式创建表时,不会在hdfs上创建相应的文件夹(数据库和表)
4.2.3 内部表和外部表的相互转换
alter table tb_name set tblproperties("EXTERNAL"="TRUE") ;
显示表信息的两个命令
第一个

第二个

4.2.4 数据的导入(内部表和外部表一样)
create external table student( sid string , name string , age int , gender string ) row format delimited fields terminated by "," ; -- 导入本地数据 load data local inpath "/hive/student.txt" into table student ; -- 导入HDFS数据 load data inpath "/hive/student.txt" into table student ;
4.2.5 内部表和外部表的应用场景

大多数情况使用外部表(处理静态数据),但有些时候需要在hdfs上保存一些业务数据,当这个业务结束时,这些数据也就不起作用了,这个时候就会使用内部表,内部表随着业务的消失而删除时,业务数据也跟着删除
4.2.6 学生和分数的练习
学生数据和分数数据如下

创建student表和score表

create external table student( sid string , name string , age int , gender string ) row format delimited fields terminated by "," ; -- 导入本地数据 load data local inpath "/root/hive/student.txt" into table student ; -- 导入HDFS数据 load data inpath "/hive/student.txt" into table student ; create external table score( sid string , english int , chinese int , math int ) row format delimited fields terminated by "," ; load data local inpath "/root/hive/score.txt" into table score ;
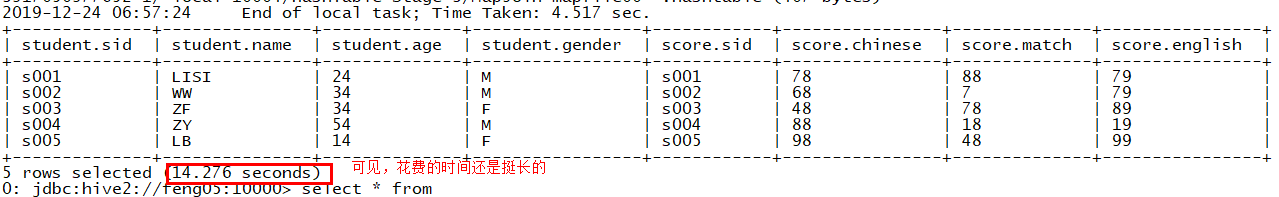
(1)查询学生信息并关联查询成绩
select student.*, score.* from student join score on student.sid = score.sid;
查询结果(此处若想将s6的成绩也查出来就使用右关联)
(2)查询每个人的总成绩,按照总分降序排列
select student.name, (score.english + score.chinese + score.match) as total_score from student join score on student.sid = score.sid order by total_score desc ;
结果

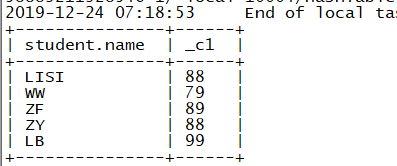
(3)查询每个人的最高成绩(此处使用greatest,max只能用于同一个字段取最大值,即纵向)
select student.name, greatest(score.english , score.chinese,score.match) from student join score on student.sid = score.sid;
结果
(4)查询男生和女生中英语最高分的那个人的名字 和英语成绩
分三步
- 第一步:获取name,gender,score.english信息
select student.name , student.gender , score.english from student join score on student.sid = score.sid
结果

- 第二步,获取性别以及各个性别中的最高分数
(select student.gender, max(score.english) ee from student join score on student.sid = score.sid group by student.gender) t
注意,此处一定要使用group by,因为select student.gender选出来的是2个类型,若不分组的话,max就不能聚合
结果
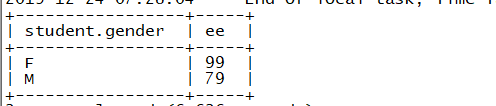
- 第三步, 结合第一第二步的结果求最终的结果

select t1.* from ( select student.name name, student.gender gender, score.english english from student join score on student.sid = score.sid )t1 join ( select student.gender gender, max(score.english) ee from student join score on student.sid = score.sid group by student.gender )t2 on t1.gender = t2.gender and t1.english = t2.ee ;
结果

(5)查询每个人的最高成绩以及科目
a 没查询科目

select student.name, greatest(score.english , score.chinese,score.math) from student join score on student.sid = score.sid;
结果

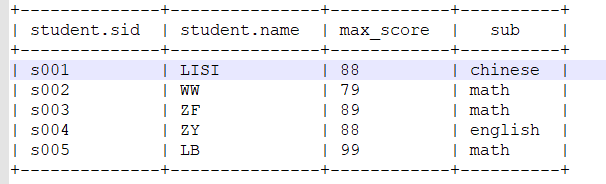
b 查询科目

select student.sid , student.name, greatest(score.english , score.chinese,score.math) max_score , --------------------------------- case when score.english == greatest(score.english , score.chinese,score.math) then "english" when score.chinese == greatest(score.english , score.chinese,score.math) then "chinese" when score.math == greatest(score.english , score.chinese,score.math) then "math" else "" end sub -------------- 所有的是一个字段 from student join score on student.sid = score.sid;
结果
5. 分区表(更加详细见文档)
5.1 静态分区
分区表实际上就是对应一个HDFS文件系统上的独立的文件夹,该文件夹下是该分区所有的数据文件。Hive中的分区就是分目录,把一个大的数据集根据业务需要分割成小的数据集。在查询时通过WHERE子句中的表达式选择查询所需要的指定的分区,而不是全局查询,这样的查询效率会提高很多。
手动将数据按需求分到不同的分区中
案例:
数据

(1)创建普通的表加载数据

create table log1( uid string , nane string , word string , age int , logday string ) row format delimited fields terminated by " " ; load data local inpath "/hive/log/" into table log1 ;
查询:查询数据的时候是全表检索 获取结果以后再where过滤
select * from log1 where logday="2019-11-29";
(2)优化 : 使用分区表 将不同日期的文件分到不同的区中[文件夹] ------->一级分区表
创建表的时候添加分区字段(partitioned by (分区名 分区名对应的数据类型))
create table log2( uid string , nane string , word string , age int , logday string ) partitioned by (myday string) -- 添加分区字段 row format delimited fields terminated by " " ;
导入数据
load data local inpath "/hive/log/2019-11-28.log" into table log2 partition(myday="2019-11-28") ; load data local inpath "/hive/log/2019-11-29.log" into table log2 partition(myday="2019-11-29") ;
查询
select * from log2 where myday="2019-11-29";
结果

(3)二级分区表
数据如下(4个)
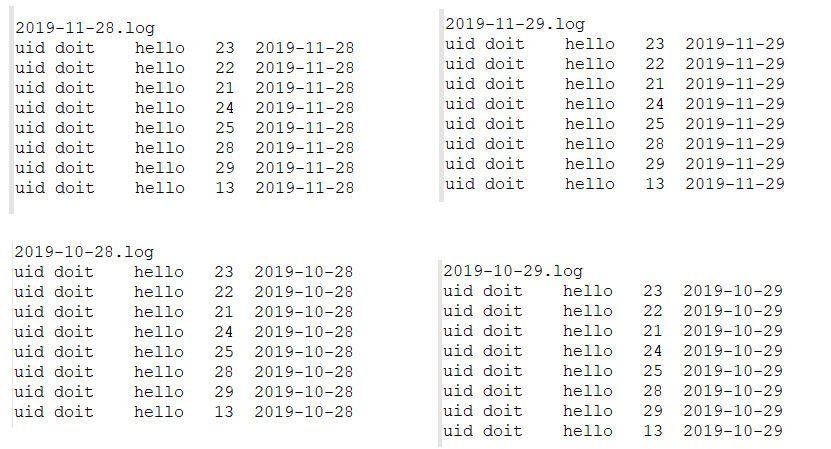
create table log3( uid string , nane string , word string , age int , logday string ) partitioned by (p_month string , p_day string) -- 分区字段 两个 二级分区 层级文件夹 row format delimited fields terminated by " " ;
导入数据
load data local inpath "/root/hive/log/2019-10-28.log" into table log3 partition(p_month="2019-10" ,p_day="10-28" ) ; load data local inpath "/root/hive/log/2019-10-29.log" into table log3 partition(p_month="2019-10" ,p_day="10-29" ) ; load data local inpath "/root/hive/log/2019-11-28.log" into table log3 partition(p_month="2019-11" ,p_day="11-28" ) ; load data local inpath "/root/hive/log/2019-11-29.log" into table log3 partition(p_month="2019-11" ,p_day="11-29" ) ;
(4)静态分区缺点
往hive分区表中插入数据时,如果需要创建的分区很多,比如以表中某个字段进行分区存储(如此例中的myday),则需要手动导入很多次数据,麻烦且效率低。
解决办法======>动态分区
5.2 动态分区
静态分区是在加载数据的时候将不同的文件数据导入到不同的分区文件夹中
动态分区是在一个普通表的基础上,按照某个或者某几个字段自动的将数据加载到指定的分区中
大体过程:首先创建一个普通的表,然后将需要的数据导入该表,然后根据查询普通表中的数据 按特定形式导入到动态分区表
案例
数据:

需求,按照日期分区
分析:若是使用静态分区的话,需要将上面文件按自己需求分成不同文件(此处是birthday),然后手动导入三次数据(比较麻烦),所以使用动态分区
(1)创建普通表并导入数据
create table demo1( id int , birthday string , cost int ) row format delimited fields terminated by ' ' ; load data local inpath "/hive/demo1.txt" into table demo1 ;
(2)创建一个分区表
create table demo2( id int , birthday string , cost int ) partitioned by(bd string) row format delimited fields terminated by ' ' ;
(3)开启动态分区的设置参数
set hive.exec.dynamic.partition=true ; #开启动态分区,默认是false set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode=nonstrick; #开启允许所有分区都是动态的,否则必须要有静态分区才能使用
(4)查询普通的表,得到数据,将数据根据指定的字段导入到分区中
--- partition(bd) bd 代表动态分区表的分区字段的名称 --- 查询的数据的最后一个字段会导入到分区字段中 insert into table demo2 partition(bd) select id , birthday ,cost , birthday from demo1 ;
6. 加载数据的方式
6.1 load方式(可以导入本地也可以导入hdfs中的数据)
(1)导入本地数据
创建表

create table tb_user ( uid string , name string , gender string , age int ) row format delimited fields terminated by "," ;
导入数据
- 非覆盖导入
load data local inpath "/hive/user.txt" into table tb_user ; load data local inpath "/hive/user.txt" into table tb_user ; 导入两次 表中存在两份数据
- 覆盖导入
load data local inpath "/root/hive/user.txt" overwrite into table tb_user ;
(2)导入hdfs中的数据(去掉local)
load data inpath "/root/hive/user.txt" into table tb_user ;
load data inpath "/root/hive/user.txt" overwrite into table tb_user ;
6.2 location
见前面
此外,直接将文件移动到目标表的路径下,数据符合要求的话,会自动加载数据
6.3 insert方式 将查询到的数据导入到hive表中
建表
create EXTERNAL table tb_user2 ( uid string , name string , gender string , age int ) ;
-- 通过查询插入数据 insert into tb_user2 select * from tb_user where age >15 ; -- 通过查询覆盖数据 insert overwrite table tb_user2 select * from tb_user where age >15 ;
6.4 create 建表的时候根据查询的数据和字段
create table tb_user3 as select name , gender from tb_user ; -- 常用的方式 将查询的业务数据 导入到一张新表中 , 字段不用自己定义 create external table if not exists tb_user3 as select name , gender from tb_user ;
6.5 import导入 export导出的特殊的文件数据
导出数据 export table tb_user2 to "/data/user2/" ; create table tb_user10 ( uid string , name string , gender string , age int ) ; 导入数据 import table tb_user10 from "/data/user2/" ;
