1. Task的划分
在flink中,划分task的依据是发生shuffle(也叫redistrubute),或者是并行度发生变化
- 1. wordcount为例

package cn._51doit.flink.day03; import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.FilterFunction; import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.FlatMapFunction; import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple; import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple2; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.KeyedStream; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment; import org.apache.flink.util.Collector; import java.util.Arrays; public class WordCount { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); DataStreamSource<String> lines = env.socketTextStream("feng05", 8888); SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple2<String, Integer>> wordAndOne = lines.flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<String, Tuple2<String, Integer>>() { @Override public void flatMap(String line, Collector<Tuple2<String, Integer>> out) throws Exception { Arrays.stream(line.split(" ")).forEach(w -> out.collect(Tuple2.of(w, 1))); } }); SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple2<String, Integer>> filtered = wordAndOne.filter(new FilterFunction<Tuple2<String, Integer>>() { @Override public boolean filter(Tuple2<String, Integer> value) throws Exception { return value.f1 != null; } }); KeyedStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>, Tuple> keyed = filtered.keyBy(0); //SingleOutputStreamOperator并行度为4 SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple2<String, Integer>> result = keyed.sum(1); result.print(); //sink的并行度也是2 env.execute(); } }
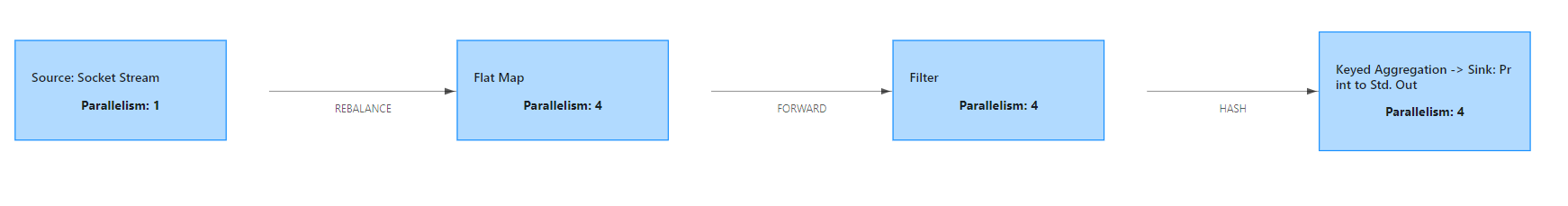
其dataflow图如下所示

socketTextStream是单并行度source,无论你将并行度设置成多少,其并行度都是1,所以到flatMap算子时,并行度就变成了自己设置的4.整个dataflow分成3个Task,9个subTask。
- 2. 改变1,在flatMap后加上startNewChain(),即开启一个新的链
按常理来讲,此处的flatMap算子和filter算子间的链是要断开的,但此处自己测试并没有端,暂时还不知道为什么
- 3. 改变2 在flatMap后加上disableChaining(),即将概算自前后的OperatorChain都断开,将该算子单独划分一个task
可以发现,Task数由3变成4,subTask也相应的编程了13个
注意:此处为什么要使用startNewChain、disablechaining呢?
我们在进行计算时,会存在一些计算密集型的算子(比如涉及排序的算子),可以将之独立出来,然后将其调度到某些机器上,这个算子就能独享该机器的cpu,内存的资源,提高效率。
总结:Task划分的依据
(1)并行度发生变化时
(2)keyBy() /window()/apply() 等发生 Rebalance 重新分配(即shuffle)
(3)调用startNewChain()方法,开启一个新的算子链
(4)调用diableChaining()方法,即告诉当前算子操作不适用算子链操作
2. 共享资源槽(Sharing slot)
2.1 简单概念
每一个TaskManager(Worker)是一个JVM进程,它可能会在独立的线程上执行一个或者多个subtask。为了控制一个worker能接收多少个task,worker通过task slot来进行控制
每个task slot表示TaskManager拥有资源的一个固定⼤大⼩小的⼦子集。假如⼀一个TaskManager有三个slot,那么它会将其管理理的内存分成三份给各个slot。资源slot化意味着⼀一个subtask将不不需要跟来⾃自其他job的subtask竞争被管理理的内存,取⽽而代之的是它将拥有⼀一定数量量的内存储备。需要注意的是,这⾥里里不不会涉及到CPU的隔离,slot⽬目前仅仅⽤用来隔离task的受管理理的内存。
默认情况下,flink允许subtasks共享slots,即使它们是不同tasks的subtasks,只要它们来自同一个job。因此,一个slot可能会负责这个job的某个管道(pipeline)。共享资源槽有如下两个优点:
- Flink 集群需要与 job 中使用的最高并行度一样多的 slots。若是没有sharing slot,就需要计算作业总共包含多少个 tasks,从而判断集群需要多少slots,非常麻烦。
- 更好的资源利用率。在没有 slot sharing 的情况下,简单的 subtasks(source/map())将会占用和复杂的 subtasks (window)一样多的资源。
如下:
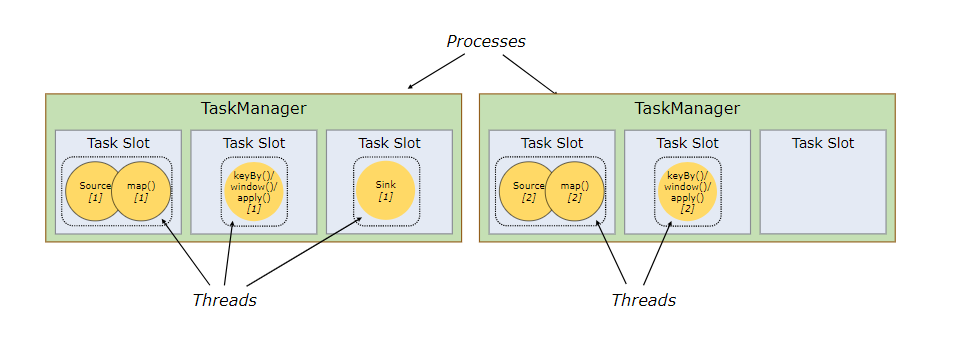
上图是没有采用sharing slot的情况,可见2个TaskManager只能使用两个并行,但若是换成sharing slot,则结果就大不一样,如下
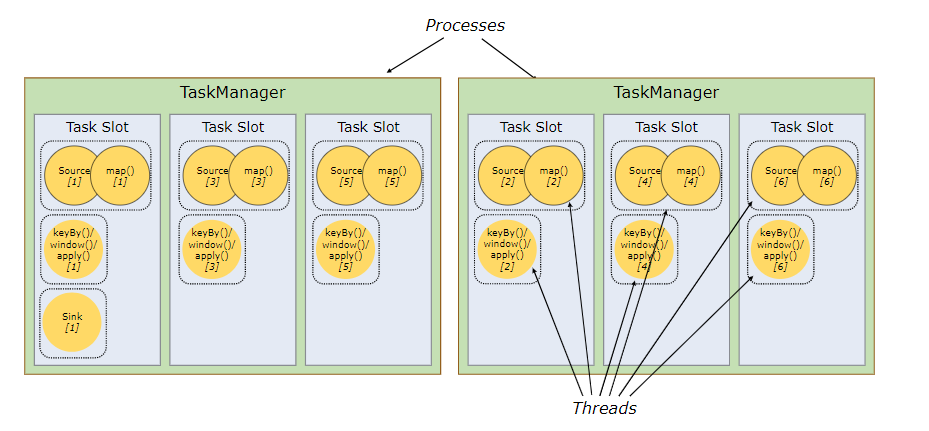
由图可明显看出,同样的slot数,使用sharing slot的情况并行度由2提高到6,这使得效率大大提高。
2.2 进一步理解
SlotSharingGroup是flink中用来实现slot共享的类,它尽可能的让subtasks共享一个slot。保证同一个group的sub-tasks共享一个slots。默认的slot sharing group名称为default,算子也有自己的名字,默认也是default并且算子只能进入与自己名字相同的slot sharing group(即默认一个job下的subtask都可以共享一个slot)。slot sharing group的名字由第一个进入该slot算子的名称而定,比如第一个进入该slot算子的名称为feng,则这个slot sharing group的名称就为feng。
有些时候不想使用资源共享槽,想让算子单独享用某个managerTask中的slot(比如一些计算密集型的算子,比如排序、机器学习等),即防止不合理的共享,这时候可以人为的强制指定operator的共享组。比如someStream.filter(...).slotSharingGroup("group1");就强制指定了filter的slot共享组为group1。
提交一个wordcount程序,并行度为4
代码如下

package cn._51doit.flink.day03; import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.FlatMapFunction; import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple; import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple2; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStream; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.KeyedStream; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment; import org.apache.flink.util.Collector; import java.util.Arrays; public class SharingGroupDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); //使用Socket创建DataStream //socketTextStream是一个非并行的Source,不论并行度设置为多少,总是一个并行 //DataStreamSourc并行度为1 DataStreamSource<String> lines = env.socketTextStream("node-1.51doit.cn", 8888); //DataStream的并行度默认是使用你设置的并行度 //DataStream并行度为4 DataStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>> wordAndOne = lines.flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<String, Tuple2<String, Integer>>() { @Override public void flatMap(String line, Collector<Tuple2<String, Integer>> out) throws Exception { Arrays.stream(line.split(" ")).forEach(w -> out.collect(Tuple2.of(w, 1))); } }); //keyBy属于shuffle(redistribute)算子 //KeyedStream并行度为4 KeyedStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>, Tuple> keyed = wordAndOne.keyBy(0); //SingleOutputStreamOperator并行度为4 SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple2<String, Integer>> result = keyed.sum(1); result.print(); env.execute(); } }
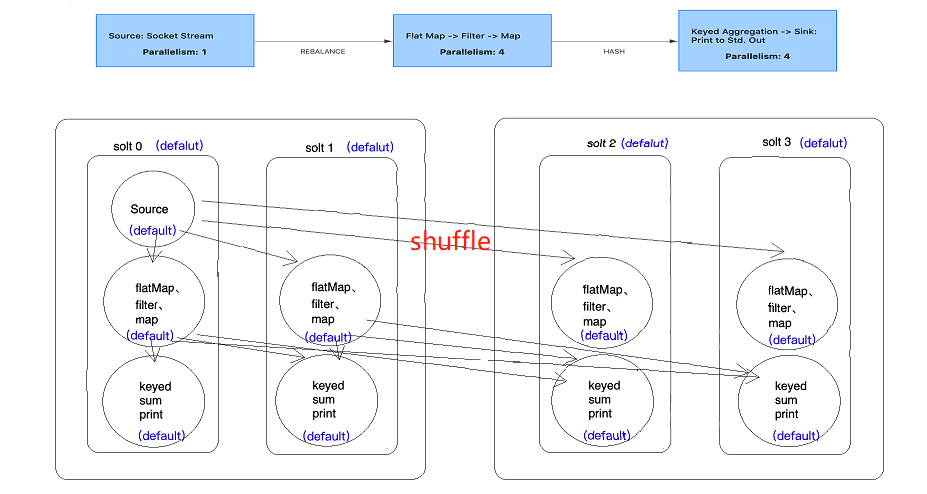
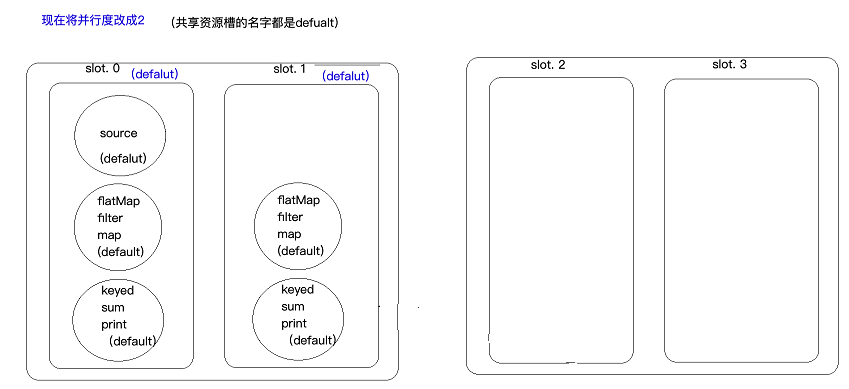
现将并行度沈设置成2,能发现有2个slot是空置的
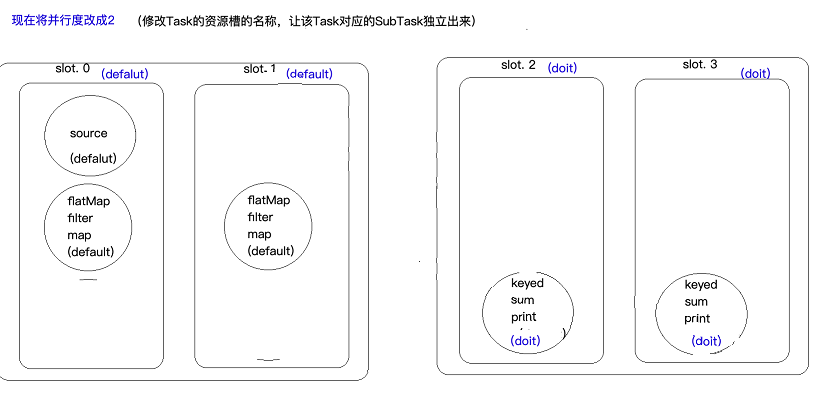
维持并行度为2,但是修改Task资源槽的名称,让该Task对应的subTask独立出来
此处在sum算子上打标签,即(sum.slotSharingGroup("doit")),sum包括其后面的算子名称都变为doit,但此处keyed为什么会变doit就不清楚了。
3.Flink的容错
3.1 State状态
Flink实时计算程序为了保证计算过程中,出现异常可以容错,就要将中间的计算结果数据存储起来,这些中间数据就叫做state。state可以是多种类型的,默认是保存在JobManager的内存中,也可以保存到TaskManager本地文件系统或HDFS这样的分布式文件系统。
3.2 StateBackEnd
用来保存的存储后端就叫做StateBackEnd,默认是保存在JobManager的内存中,也可以保存本地系统或HDFS这样的分布式文件系统。
3.3 CheckPointing
Flink实时计算为了容错,可以将中间数据定期保存下来,这种定期触发保存中间结果的机制叫CheckPointing,CheckPointing是周期性执行的,具体的过程是JobManager定期向TaskManager中的SubTask发送RPC消息,SubTask将其计算的State保存到StateBackEnd中,并且向JobManager响应Checkpoint是否成功。如果程序出现异常或者重启,TaskManager中的SubTask可以从上一次成功的CheckPointing的state恢复,具体见下图
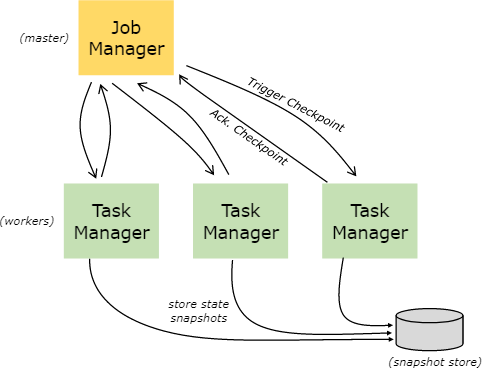
注意:JobManager只有在接收到所有subTask将计算结果的state成功保存到StateBackEnd的消息后,才会标记checkpoint成功。
3.4 重启策略
Flink实时计算程序为了容错,需要开启CheckPointing,一旦开启CheckPointing,如果没有重启策略,默认的重启策略是无限重启,也可以设置成其他的重启策略,如:重启固定次数以及重启间的间隔时间
3.5 CheckPointingMode
- exactly-once
精确一次性语义,可以保证数据消费且消费一次,但是要结合对应的数据源,比如Kafla支持exactly-once
- ar-least-once
至少消费一次,可能会重复消费,但是效率要比exactly-once高
4 state案例
4.1 简单概念
(1)state概念:
State是Flink计算过程的中间结果和状态信息,为了容错,必须把状态持久化到一个外部系统中去
(2)state的分类
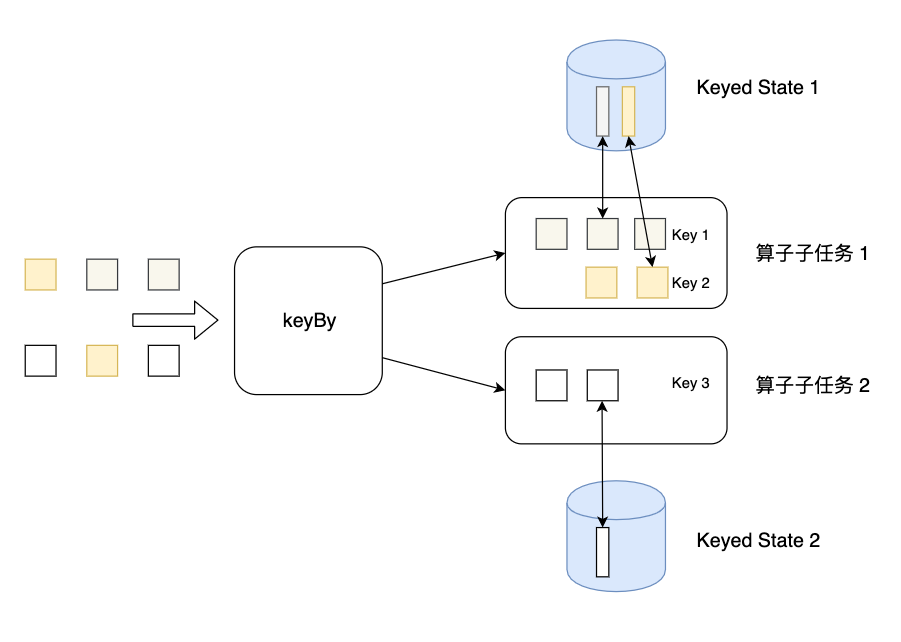
值得看的博客:https://www.lizenghai.com/archives/46460.html(下图来自此博客)
- KeyState:调用keyBy方法后,每个分区中相互独立的state
- Operatecast state:没有分组,每一个subTask自己维护一个状态
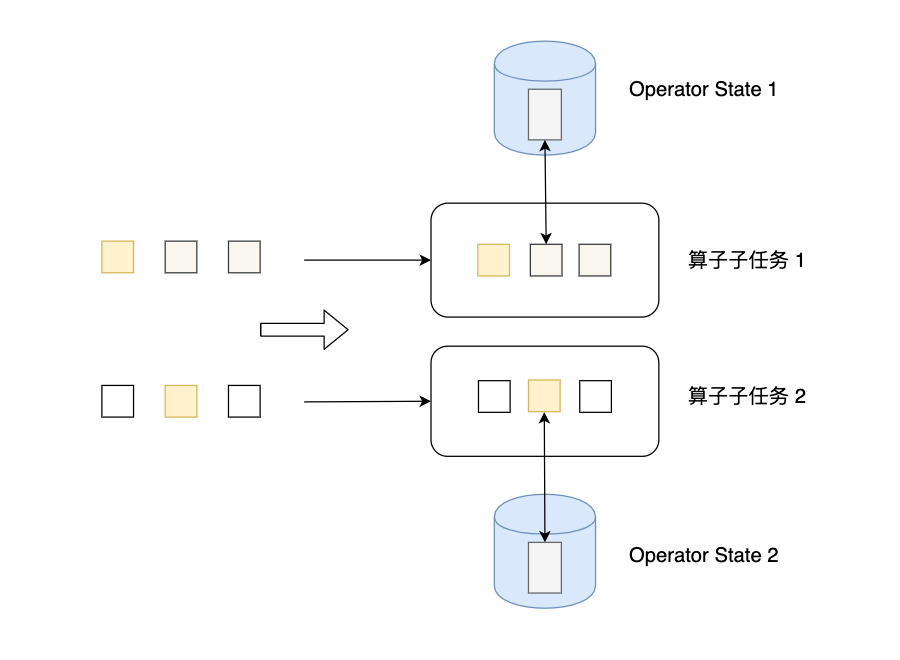
(3)state的使用
- 先定义一个状态描述器
- 通过context获取state
- 对数据处理后要更新数据
案例1:重启策略
RestartStrages

package cn._51doit.flink.day03; import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.FlatMapFunction; import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.MapFunction; import org.apache.flink.api.common.restartstrategy.RestartStrategies; import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple; import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple2; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.KeyedStream; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment; import org.apache.flink.util.Collector; import java.util.Arrays; public class RestartStrages { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); DataStreamSource<String> lines = env.socketTextStream("feng05", 8888); // 开启checkpoint,索九checkpoint一次 env.enableCheckpointing(5000); // 默认的重启策略就是无限重启 env.setRestartStrategy(RestartStrategies.fixedDelayRestart(3, 5000)); SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple2<String, Integer>> wordAndOne = lines.map(new MapFunction<String, Tuple2<String, Integer>>() { @Override public Tuple2<String, Integer> map(String word) throws Exception { if (word.equals("feng")) { int i = 1 / 0; } return Tuple2.of(word, 1); } }); //keyBy属于shuffle(redistribute)算子 //KeyedStream并行度为4 KeyedStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>, Tuple> keyed = wordAndOne.keyBy(0); //SingleOutputStreamOperator并行度为4 SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple2<String, Integer>> result = keyed.sum(1); result.print(); env.execute(); } }
发现程序中断后会重启,并且重启后,前面的计算结果还能被复用(sum算子内部实现了state的保存)
案例2:能否自己实现sum算子,既能正确的累加单词的次数,还能在程序出现异常时容错
MyHashMapDemo

package cn._51doit.flink.day03; import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.MapFunction; import org.apache.flink.api.common.restartstrategy.RestartStrategies; import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple; import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple2; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.KeyedStream; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment; import java.util.HashMap; public class MyHashMapDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); DataStreamSource<String> lines = env.socketTextStream("localhost", 8888); //开启checkpoint env.enableCheckpointing(5000); //开启checkpoint,默认的重启策略就是无限重启 env.setRestartStrategy(RestartStrategies.fixedDelayRestart(3, 5000)); SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple2<String, Integer>> wordAndOne = lines.map(new MapFunction<String, Tuple2<String, Integer>>() { @Override public Tuple2<String, Integer> map(String word) throws Exception { if (word.equals("laoduan")) { int i = 1 / 0; //模拟出现错误,任务重启 } return Tuple2.of(word, 1); } }); KeyedStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>, Tuple> keyed = wordAndOne.keyBy(0); SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple2<String, Integer>> result = keyed.map(new MapFunction<Tuple2<String, Integer>, Tuple2<String, Integer>>() { private HashMap<String, Integer> state = new HashMap<>(); @Override public Tuple2<String, Integer> map(Tuple2<String, Integer> input) throws Exception { String currentKey = input.f0; Integer currentCount = input.f1; Integer historyCount = state.get(currentKey); if (historyCount == null) { historyCount = 0; } int sum = historyCount + currentCount; //累加 //更新状态数据(我自己实现的计数器) state.put(currentKey, sum); return Tuple2.of(currentKey, sum); //输出结果 } }); result.print(); env.execute(); } }
此种定义hashMap的形式只能正确的累加单词的次数,并不能实现容错。
案例3:使用keyState实现sum,能满足需求

StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); DataStreamSource<String> lines = env.socketTextStream("localhost", 8888); //开启checkpoint env.enableCheckpointing(5000); //开启checkpoint,默认的重启策略就是无限重启 env.setRestartStrategy(RestartStrategies.fixedDelayRestart(3, 5000)); SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple2<String, Integer>> wordAndOne = lines.map(new MapFunction<String, Tuple2<String, Integer>>() { @Override public Tuple2<String, Integer> map(String word) throws Exception { if (word.equals("laoduan")) { int i = 1 / 0; //模拟出现错误,任务重启 } return Tuple2.of(word, 1); } }); KeyedStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>, Tuple> keyed = wordAndOne.keyBy(0); SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple2<String, Integer>> result = keyed.map(new RichMapFunction<Tuple2<String, Integer>, Tuple2<String, Integer>>() { private transient ValueState<Integer> countState; //在构造器方法之后,map方法之前执行一次 @Override public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception { //初始化状态或恢复状态 //使用状态的步骤: //1.定义一个状态描述器,状态的名称,存储数据的类型等 ValueStateDescriptor<Integer> stateDescriptor = new ValueStateDescriptor<>( "wc-state", Integer.class ); //2.使用状态描述从对应的StateBack器获取状态 countState = getRuntimeContext().getState(stateDescriptor); } @Override public Tuple2<String, Integer> map(Tuple2<String, Integer> input) throws Exception { String currentKey = input.f0; Integer currentCount = input.f1; Integer historyCount = countState.value(); if(historyCount == null) { historyCount = 0; } int sum = historyCount + currentCount; //更新state countState.update(sum); return Tuple2.of(currentKey, sum); } }); result.print(); env.execute();
案例4:OperatorState
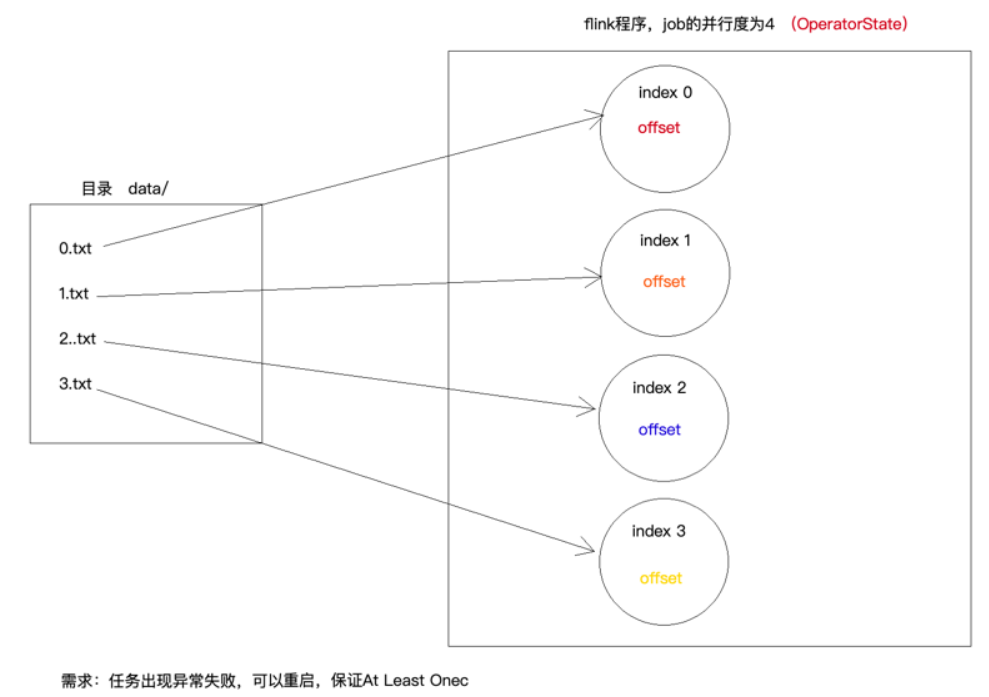
自定义Source
MyAtLeastOnceSource

package cn._51doit.flink.day03; import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ListState; import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ListStateDescriptor; import org.apache.flink.runtime.state.FunctionInitializationContext; import org.apache.flink.runtime.state.FunctionSnapshotContext; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.checkpoint.CheckpointedFunction; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.source.RichParallelSourceFunction; import java.io.RandomAccessFile; public class MyAtLeastOnceSource extends RichParallelSourceFunction<String> implements CheckpointedFunction { private transient ListState<Long> listState; private boolean flag = true; private Long offset = 0L; //在构造方法之后,open方法之前执行一次,用于初始化Operator State或恢复Operator State @Override public void initializeState(FunctionInitializationContext context) throws Exception { //定义一个状态描述器 ListStateDescriptor<Long> stateDescriptor = new ListStateDescriptor<>( "offset-state", Long.class ); //listState中存储的就是一个long类型的数值 listState = context.getOperatorStateStore().getListState(stateDescriptor); //从ListState中恢复数据 if(context.isRestored()) { for (Long first : listState.get()) offset = first; } } //snapshotState方法是在checkpoint时,会调用 @Override public void snapshotState(FunctionSnapshotContext context) throws Exception { //将上一次checkpoint的数据清除 listState.clear(); //将最新的偏移量保存到ListState中 listState.add(offset); } @Override public void run(SourceContext<String> ctx) throws Exception { int taskIndex = getRuntimeContext().getIndexOfThisSubtask(); RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("/Users/xing/Desktop/data/" + taskIndex + ".txt", "r"); //从指定的位置读取数据 raf.seek(offset); //获取一个checkpoint的锁 final Object checkpointLock = ctx.getCheckpointLock(); while (flag) { String line = raf.readLine(); if(line != null) { //获取最新的偏移量 synchronized (checkpointLock) { line = new String(line.getBytes("ISO-8859-1"), "UTF-8"); offset = raf.getFilePointer(); ctx.collect(taskIndex + ".txt => " + line); } } else { Thread.sleep(1000); } } } @Override public void cancel() { flag = false; } }
MyAtLeastOnceSourceDemo

package cn._51doit.flink.day03; import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.MapFunction; import org.apache.flink.api.common.restartstrategy.RestartStrategies; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStream; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment; public class MyAtLeastOnceSourceDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); env.setParallelism(4); env.enableCheckpointing(30000); env.setRestartStrategy(RestartStrategies.fixedDelayRestart(3, 5000)); //自定义一个多并行的Source DataStreamSource<String> lines1 = env.addSource(new MyAtLeastOnceSource()); DataStreamSource<String> lines2 = env.socketTextStream("localhost", 8888); SingleOutputStreamOperator<String> error = lines2.map(new MapFunction<String, String>() { @Override public String map(String line) throws Exception { if (line.startsWith("error")) { int i = 1 / 0; } return line; } }); DataStream<String> union = lines1.union(error); union.print(); env.execute(); } }
两次checkpoint之间的数据会被重复读,所以是AtListOnce
MyHashMaoDemo
