一.数据基本类型之set集合
set和dict类似,也是一组key的集合,但不存储value。由于key不能重复,所以,在set中,没有重复的key
set集合,是一个无序且不重复的元素集合
1.创建
s = set() #创建空集合 s = {'values1','values2'} #非空集合
2.转换
l = [1,2,5,11] t = (11,22,12) #元组转集合 st2 = set(t) #列表转集合 st = set(l) print(st) print(st2)
3.常用支持操作
添加元素-->add(key)
s = set() s.add(1) print(s)
删除元素-->remove(key)
s = set([1,2,3]) s.remove(1) print(s)
清除元素-->clear()
s = set([1,2,3,4,5]) print(s) s.clear() print(s)
比较元素-->difference()
set1 = {1,44,87,23,55}
set2 = {1,44,88,23,67}
#set1中有而set2中没有的值
ret = set1.difference(set2)
print(ret)
删除两集合中相同的元素-->difference_update()
set1 = {1,44,87,23,55}
set2 = {1,44,88,23,67}
#从set1中删除和set2中相同的元素
set1.difference_update(set2)
print(set1)
print(set2)
移除元素-->discard(values)
set1 = {1,44,87,23,55}
set2 = {1,44,88,23,67}
#移除指定元素,不存在不会报错,remove()不存在会报错,建议discard
set1.discard(44)
print(set1)
取交集值-->intersection()
set1 = {1,44,87,23,55}
set2 = {1,44,88,23,67}
#取两个set集合的交集值
ret = set1.intersection(set2)
print(ret)
取交集并更新-->intersection_update()
set1 = {1,44,87,23,55}
set2 = {1,44,88,23,67}
#取交集并更新到set1中
set1.intersection_update(set2)
print(set1)
判断是否交集-->isdisjoint()
set1 = {1,44,87,23,55}
set2 = {1,44,88,23,67}
#如果两个集合有交集返回false,反之返回true
print(set1.isdisjoint(set2))
子序列-->issubset()
set1 = {1,44,87,23,55}
set2 = {1,44,88,23,67}
#判断是否是子集,是返回true,反之返回Flase
print(set1.issubset(set2))
父序列-->issuperset()
set1 = {1,44,87,23,55}
set2 = {1,44,88,23,67}
#是否是父序列,是返回True,反之返回Flase
print(set1.issuperset(set2))
对称交集-->symmetric_difference()
set1 = {1,44,87,23,55}
set2 = {1,44,88,23,67}
#对称交集,取两个集合中互不存在的元素,生成一个新的集合
ret = set1.symmetric_difference(set2)
print(ret)
对称交集并更新-->symmetric_difference_update()
set1 = {1,44,87,23,55}
set2 = {1,44,88,23,67}
#对称交集,并更新元素到set1中
set1.symmetric_difference_update(set2)
print(set1)
并集-->union()
set1 = {1,44,87,23,55}
set2 = {1,44,88,23,67}
#并集并更新到新的集合中
ret = set1.union(set2)
print(ret)
二.深浅拷贝
1.数字和字符串
对于 数字 和 字符串 而言,赋值、浅拷贝和深拷贝无意义,因为其永远指向同一个内存地址
import copy # ######### 数字、字符串 ######### n1 = 123 # n1 = "i am alex age 10" print(id(n1)) # ## 赋值 ## n2 = n1 print(id(n2)) # ## 浅拷贝 ## n2 = copy.copy(n1) print(id(n2)) # ## 深拷贝 ## n3 = copy.deepcopy(n1) print(id(n3))
二,其他数据类型
对于list dict,tuple 浅拷贝只拷贝最外一层,深拷贝除了最后一层(因最后一层是字符串)其余的都拷贝
- 赋值
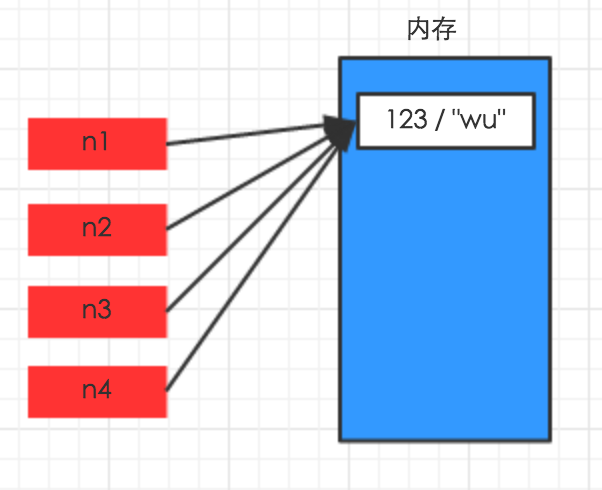
赋值,只是创建一个变量,该变量指向原来内存地址,如
n1 = {"k1": "wu", "k2": 123, "k3": ["alex", 456]}
n2 = n1
解析图如下:
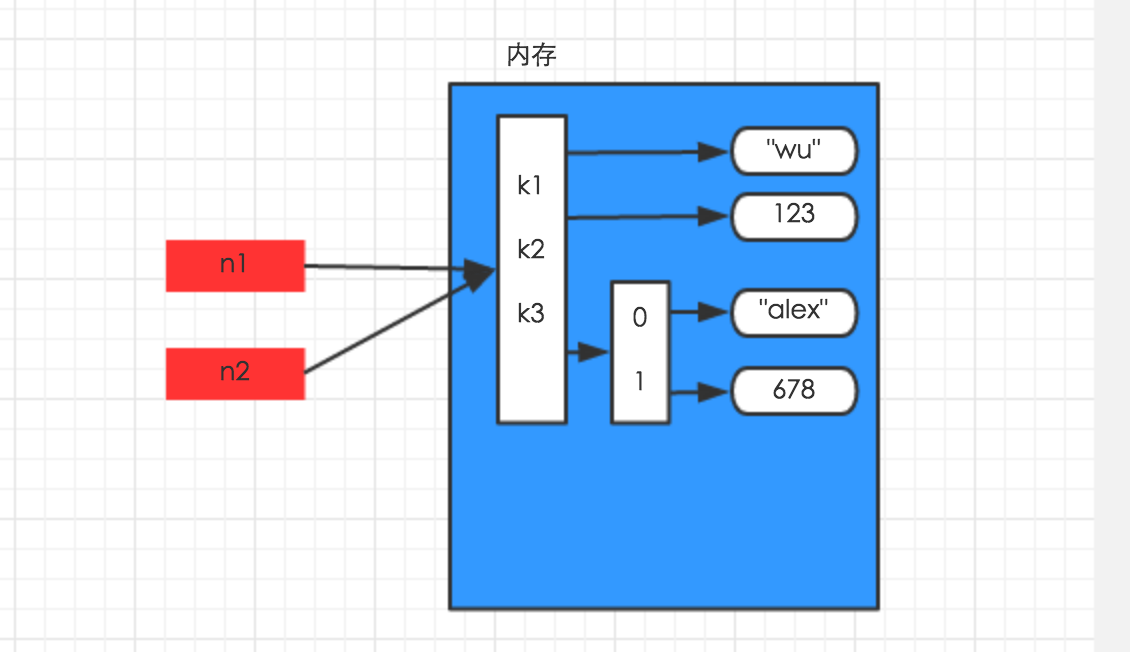
- 浅拷贝
浅拷贝,在内存中只额外创建第一层数据
import copy n1 = {"k1": "wu", "k2": 123, "k3": ["alex", 456]} n3 = copy.copy(n1)
解析图如下:
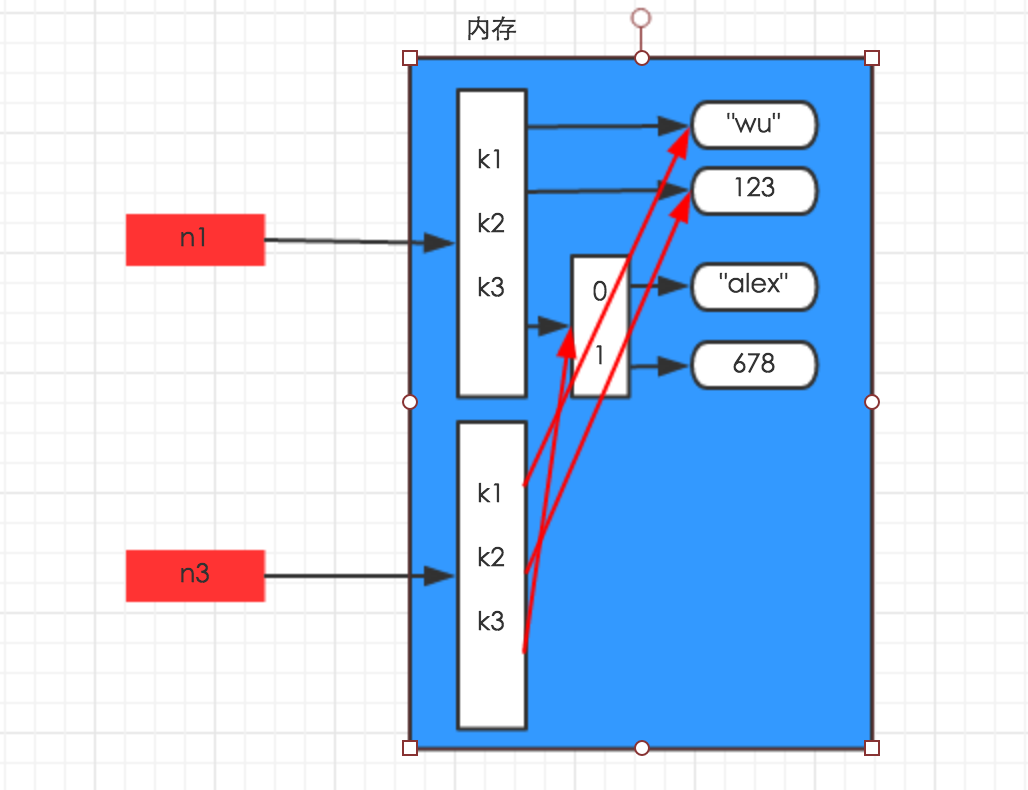
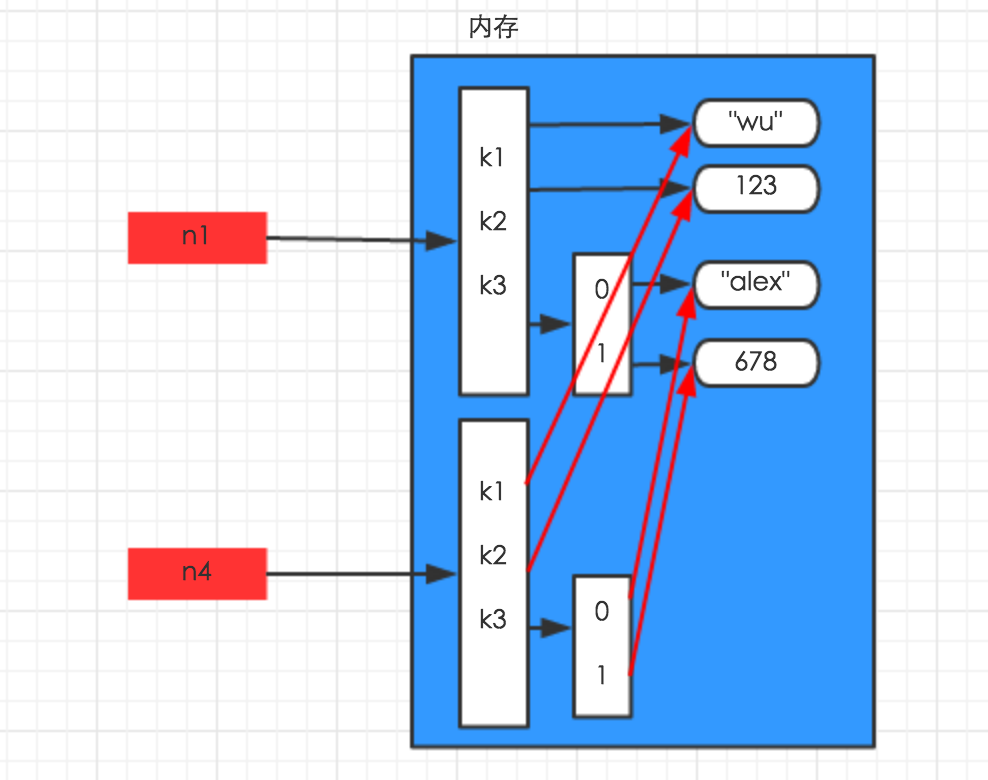
- 深拷贝:
深拷贝,在内存中将所有的数据重新创建一份(排除最后一层,即:python内部对字符串和数字的优化)
import copy n1 = {"k1": "wu", "k2": 123, "k3": ["alex", 456]} n4 = copy.deepcopy(n1)
解析图如下:
三.集合作业
1.寻找差异,并将new_dict的值更新到old_dict中
old_dict = { "#1":11, "#2":22, "#3": 100 } new_dict = { "#1":33, "#4":22, "#7": 100 }
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
old_dict = { "#1":11, "#2":22, "#3": 100 } new_dict = { "#1":33, "#4":22, "#7": 100 } old_keys = old_dict.keys() new_keys = new_dict.keys() old_set = set(old_keys) new_set = set(new_keys) #old存在new不存在,并删除new中不存在,old 中存在的元素 del_set = old_set.difference(new_set) for i in del_set: del old_dict[i] #new存在old不存在 add_set = new_set.difference(old_set) for a in add_set: old_dict[a] = new_dict[a] #更新旧数据表 update_set = old_set.intersection(new_set) for u in update_set: old_dict[u] = new_dict[u] print(old_dict)