使用Python实现k-近邻算法的一般流程为:
1、收集数据:提供文本文件
2、准备数据:使用Python解析文本文件,预处理
3、分析数据:可视化处理
4、训练算法:此步骤不适用与k——近邻算法
5、测试算法:使用海伦提供的部分数据作为测试样本。测试样本与非测试样本的区别在于:测试样本是已经完成分类的数据,如果预测分类与实际类别不一样,则标记为一个错误。
6、使用算法:产生简单的命令行程序,然后海伦可以输入一些特征数据来判断对方是否为自己喜欢的类型。
数据集介绍:
海伦女士一直使用在线约会网站寻找适合自己的约会对象。尽管约会网站会推荐不同的任选,但她并不是喜欢每一个人。经过一番总结,她发现自己交往过的人可以进行如下分类:
- 不喜欢的人
- 魅力一般的人
- 极具魅力的人
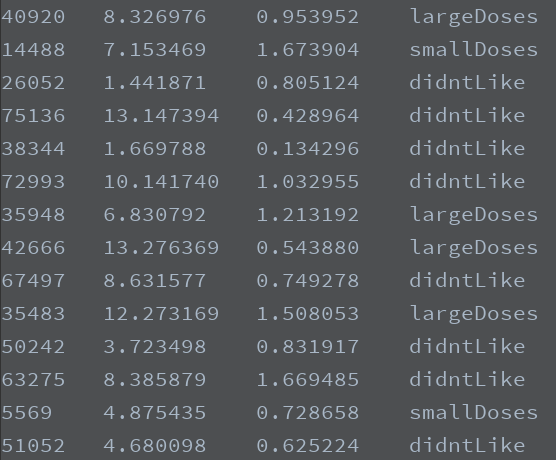
海伦收集约会数据已经有了一段时间,她把这些数据存放在文本文件datingTestSet.txt中,每个样本数据占据一行,总共有1000行。
海伦收集的样本数据主要包含以下3种特征:
- 每年获得的飞行常客里程数
- 玩视频游戏所消耗时间百分比
- 每周消费的冰淇淋公升数
数据展示如下:
准备数据
在将上述特征数据输入到分类器前,必须将待处理的数据的格式改变为分类器可以接收的格式。分类器接收的数据是什么格式的?从上小结已经知道,要将数据分类两部分,即特征矩阵和对应的分类标签向量。
代码如下:
1 import numpy as np 2 """ 3 函数说明: 4 打开文件并进行解析,对数据进行分类:1代表不喜欢,2代表魅力一般,3代表极具魅力 5 Parameters: 6 filename - 文件名 7 Returns: 8 returnMat - 特征矩阵 9 classLabelVector - 分类标签 10 """ 11 def file2matrix(filename): 12 fr = open(filename) 13 arrayOLines = fr.readlines() 14 numberOfLines = len(arrayOLines) 15 returnMat = np.zeros((numberOfLines, 3)) 16 classLabelVector = [] 17 index = 0 18 for line in arrayOLines: 19 line = line.strip() 20 listFromLine = line.split(' ') 21 returnMat[index, :] = listFromLine[0:3] 22 if listFromLine[-1] == 'didntLike': 23 classLabelVector.append(1) 24 elif listFromLine[-1] == 'smallDoses': 25 classLabelVector.append(2) 26 elif listFromLine[-1] == 'largeDoses': 27 classLabelVector.append(3) 28 index +=1 29 return returnMat, classLabelVector 30 31 if __name__ == "__main__": 32 filename = 'datingTestSet.txt' 33 datingData, datingLabel = file2matrix(filename) 34 print(datingData) 35 print(datingLabel)
运行程序之后,得到相应的数据,其中特征数据如下所示:

可以看到,我们已经顺利导入数据,并对数据进行解析,格式化为分类器需要的数据格式。接着我们需要了解数据的真正含义。可以通过直观的图形化的方式观察数据。
分析数据
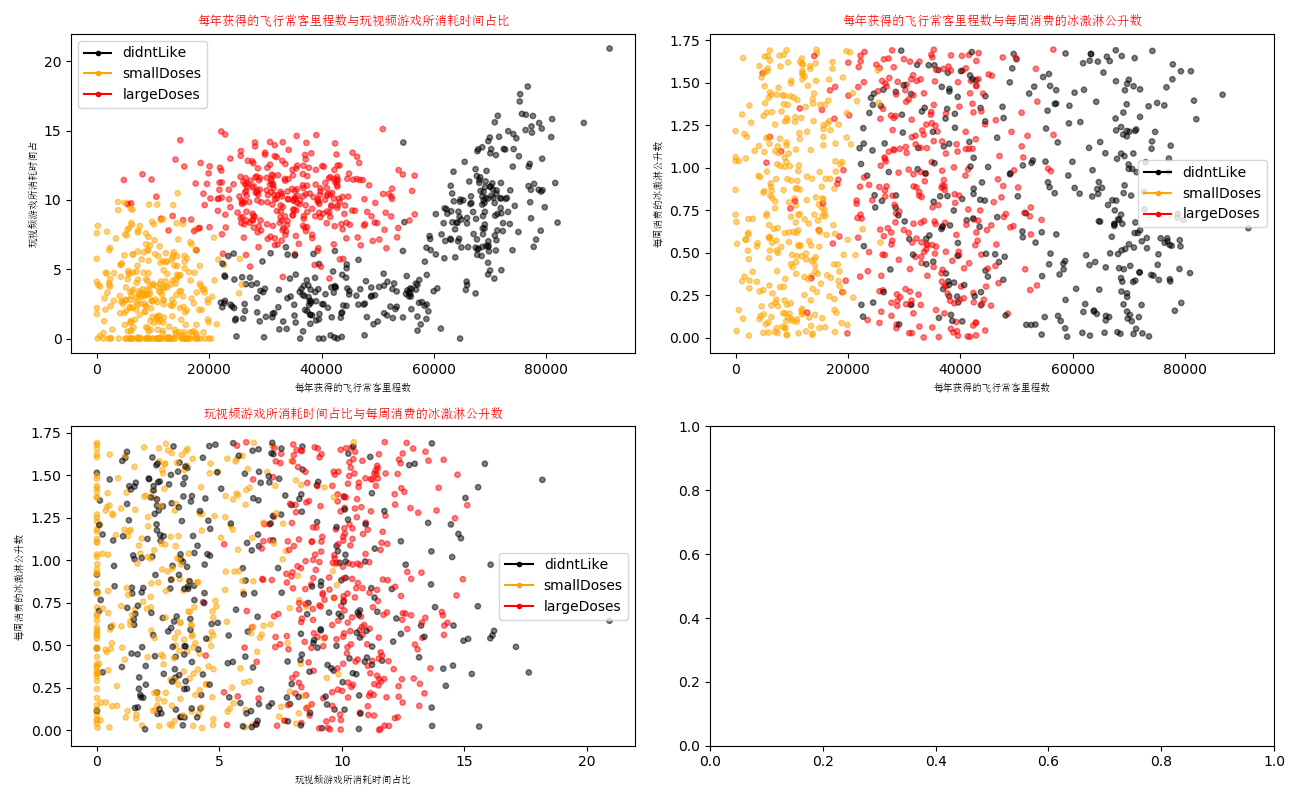
编写程序将数据可视化:
import numpy as np from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties import matplotlib.lines as mlines import matplotlib.pyplot as plt """ 函数说明: 打开文件并进行解析,对数据进行分类:1代表不喜欢,2代表魅力一般,3代表极具魅力 Parameters: filename - 文件名 Returns: returnMat - 特征矩阵 classLabelVector - 分类标签 """ def file2matrix(filename): fr = open(filename) arrayOLines = fr.readlines() numberOfLines = len(arrayOLines) returnMat = np.zeros((numberOfLines, 3)) classLabelVector = [] index = 0 for line in arrayOLines: line = line.strip() listFromLine = line.split(' ') returnMat[index, :] = listFromLine[0:3] if listFromLine[-1] == 'didntLike': classLabelVector.append(1) elif listFromLine[-1] == 'smallDoses': classLabelVector.append(2) elif listFromLine[-1] == 'largeDoses': classLabelVector.append(3) index +=1 return returnMat, classLabelVector """ 函数说明:可视化数据 Parameters: datingDataMat - 特征矩阵 datingLabels - 分类Label Returns: NO """ def showdata(datingData, datingLabel): font = FontProperties(fname="c:/windows/fonts/simsun.ttc", size=14) fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(13, 8)) numberOfLabel = len(datingLabel) labelsColors = [] for i in datingLabel: if i == 1: labelsColors.append('black') if i == 2: labelsColors.append('orange') if i == 3: labelsColors.append('red') axs[0][0].scatter(x=datingData[:, 0], y=datingData[:, 1], color=labelsColors, s=15, alpha=.5) axs0_title_text = axs[0][0].set_title(u'每年获得的飞行常客里程数与玩视频游戏所消耗时间占比', FontProperties=font) axs0_xlabel_text = axs[0][0].set_xlabel(u'每年获得的飞行常客里程数', FontProperties=font) axs0_ylabel_text = axs[0][0].set_ylabel(u'玩视频游戏所消耗时间占', FontProperties=font) plt.setp(axs0_title_text, size=9, weight='bold', color='red') plt.setp(axs0_xlabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') plt.setp(axs0_ylabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') axs[0][1].scatter(x=datingData[:, 0], y=datingData[:, 2], color=labelsColors, s=15, alpha=.5) axs1_title_text = axs[0][1].set_title(u'每年获得的飞行常客里程数与每周消费的冰激淋公升数', FontProperties=font) axs1_xlabel_text = axs[0][1].set_xlabel(u'每年获得的飞行常客里程数', FontProperties=font) axs1_ylabel_text = axs[0][1].set_ylabel(u'每周消费的冰激淋公升数', FontProperties=font) plt.setp(axs1_title_text, size=9, weight='bold', color='red') plt.setp(axs1_xlabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') plt.setp(axs1_ylabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') axs[1][0].scatter(x=datingData[:, 1], y=datingData[:, 2], color=labelsColors, s=15, alpha=.5) axs2_title_text = axs[1][0].set_title(u'玩视频游戏所消耗时间占比与每周消费的冰激淋公升数', FontProperties=font) axs2_xlabel_text = axs[1][0].set_xlabel(u'玩视频游戏所消耗时间占比', FontProperties=font) axs2_ylabel_text = axs[1][0].set_ylabel(u'每周消费的冰激淋公升数', FontProperties=font) plt.setp(axs2_title_text, size=9, weight='bold', color='red') plt.setp(axs2_xlabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') plt.setp(axs2_ylabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') didntLike = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='black', marker='.', markersize=6, label='didntLike') smallDoses = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='orange', marker='.', markersize=6, label='smallDoses') largeDoses = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='red', marker='.', markersize=6, label='largeDoses') axs[0][0].legend(handles=[didntLike, smallDoses, largeDoses]) axs[0][1].legend(handles=[didntLike, smallDoses, largeDoses]) axs[1][0].legend(handles=[didntLike, smallDoses, largeDoses]) plt.show() if __name__ == "__main__": filename = 'datingTestSet.txt' datingData, datingLabel = file2matrix(filename) showdata(datingData, datingLabel)
运行程序:
准备数据:归一化数值
在上面的数据中可以看出,如果想要计算某两个样本之间的距离,使用开根的方法就会得到一个数值,但是这样的话数字差值最大的属性对计算结果影响就会很大,换句话说:每年获取的飞行常客里程数对于计算结果的影响将远远大于其他特征的影响。而产生这种现象的原因仅仅是因为飞行常客里程数远远大于其他特征值。但是海伦认为这三个特征是同等重要的,因此作为三个等权重的特征之一,飞行常客里程数并不应该如此严重的影响到计算结果。
在处理这种不同取值范围的特征值时,我们通常采用的方法是讲数值归一化,如将数值范围处理为0到1或者-1到1之间。
编写名为autoNorm的函数,用该函数自动将数据归一化。代码如下:
import numpy as np from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties import matplotlib.lines as mlines import matplotlib.pyplot as plt """ 函数说明: 打开文件并进行解析,对数据进行分类:1代表不喜欢,2代表魅力一般,3代表极具魅力 Parameters: filename - 文件名 Returns: returnMat - 特征矩阵 classLabelVector - 分类标签 """ def file2matrix(filename): fr = open(filename) arrayOLines = fr.readlines() numberOfLines = len(arrayOLines) returnMat = np.zeros((numberOfLines, 3)) classLabelVector = [] index = 0 for line in arrayOLines: line = line.strip() listFromLine = line.split(' ') returnMat[index, :] = listFromLine[0:3] if listFromLine[-1] == 'didntLike': classLabelVector.append(1) elif listFromLine[-1] == 'smallDoses': classLabelVector.append(2) elif listFromLine[-1] == 'largeDoses': classLabelVector.append(3) index +=1 return returnMat, classLabelVector """ 函数说明:可视化数据 Parameters: datingDataMat - 特征矩阵 datingLabels - 分类Label Returns: NO """ def showdata(datingData, datingLabel): font = FontProperties(fname="c:/windows/fonts/simsun.ttc", size=14) fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(13, 8)) numberOfLabel = len(datingLabel) labelsColors = [] for i in datingLabel: if i == 1: labelsColors.append('black') if i == 2: labelsColors.append('orange') if i == 3: labelsColors.append('red') axs[0][0].scatter(x=datingData[:, 0], y=datingData[:, 1], color=labelsColors, s=15, alpha=.5) axs0_title_text = axs[0][0].set_title(u'每年获得的飞行常客里程数与玩视频游戏所消耗时间占比', FontProperties=font) axs0_xlabel_text = axs[0][0].set_xlabel(u'每年获得的飞行常客里程数', FontProperties=font) axs0_ylabel_text = axs[0][0].set_ylabel(u'玩视频游戏所消耗时间占', FontProperties=font) plt.setp(axs0_title_text, size=9, weight='bold', color='red') plt.setp(axs0_xlabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') plt.setp(axs0_ylabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') axs[0][1].scatter(x=datingData[:, 0], y=datingData[:, 2], color=labelsColors, s=15, alpha=.5) axs1_title_text = axs[0][1].set_title(u'每年获得的飞行常客里程数与每周消费的冰激淋公升数', FontProperties=font) axs1_xlabel_text = axs[0][1].set_xlabel(u'每年获得的飞行常客里程数', FontProperties=font) axs1_ylabel_text = axs[0][1].set_ylabel(u'每周消费的冰激淋公升数', FontProperties=font) plt.setp(axs1_title_text, size=9, weight='bold', color='red') plt.setp(axs1_xlabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') plt.setp(axs1_ylabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') axs[1][0].scatter(x=datingData[:, 1], y=datingData[:, 2], color=labelsColors, s=15, alpha=.5) axs2_title_text = axs[1][0].set_title(u'玩视频游戏所消耗时间占比与每周消费的冰激淋公升数', FontProperties=font) axs2_xlabel_text = axs[1][0].set_xlabel(u'玩视频游戏所消耗时间占比', FontProperties=font) axs2_ylabel_text = axs[1][0].set_ylabel(u'每周消费的冰激淋公升数', FontProperties=font) plt.setp(axs2_title_text, size=9, weight='bold', color='red') plt.setp(axs2_xlabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') plt.setp(axs2_ylabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') didntLike = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='black', marker='.', markersize=6, label='didntLike') smallDoses = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='orange', marker='.', markersize=6, label='smallDoses') largeDoses = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='red', marker='.', markersize=6, label='largeDoses') axs[0][0].legend(handles=[didntLike, smallDoses, largeDoses]) axs[0][1].legend(handles=[didntLike, smallDoses, largeDoses]) axs[1][0].legend(handles=[didntLike, smallDoses, largeDoses]) plt.show() """ 函数说明:对数据进行归一化 Parameters: dataSet - 特征矩阵 Returns: normDataSet - 归一化后的特征矩阵 ranges - 数据范围 minVals - 数据最小值 """ def autoNorm(dataset): minVal = dataset.min(0) maxVal = dataset.max(0) ranges = maxVal-minVal normDataSet = np.zeros(np.shape(dataset)) m = dataset.shape[0] normDataSet = dataset-np.tile(minVal, (m, 1)) normDataSet = normDataSet / np.tile(ranges, (m, 1)) return normDataSet, ranges, minVal if __name__ == "__main__": filename = 'datingTestSet.txt' datingData, datingLabel = file2matrix(filename) #showdata(datingData, datingLabel) normDataSet, ranges, minVals = autoNorm(datingData) print(normDataSet) print(ranges) print(minVals)
归一化之后的特征如下:

这样的话,我们已经顺利将数据归一化了,并且求出了数据的取值范围和数据的最小值,这两个值是在分类的时候需要用到的,直接先求解出来,也算是对数据预处理了。
测试算法:作为完整程序验证分类器
机器学习算法一个很重要的工作就是评估算法的正确率,通常我们只提供已有数据的90%作为训练样本来训练分类器,而使用其余的10%数据去测试分类器,检测分类器的正确率。需要注意的是,10%的测试数据应该是随机选择的,由于海伦提供的数据并没有按照特定目的来排序,所以我们可以随意选择10%数据而不影响其随机性。
创建datingClassTest函数:
import numpy as np from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties import matplotlib.lines as mlines import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import operator """ 函数说明: 打开文件并进行解析,对数据进行分类:1代表不喜欢,2代表魅力一般,3代表极具魅力 Parameters: filename - 文件名 Returns: returnMat - 特征矩阵 classLabelVector - 分类标签 """ def file2matrix(filename): fr = open(filename) arrayOLines = fr.readlines() numberOfLines = len(arrayOLines) returnMat = np.zeros((numberOfLines, 3)) classLabelVector = [] index = 0 for line in arrayOLines: line = line.strip() listFromLine = line.split(' ') returnMat[index, :] = listFromLine[0:3] if listFromLine[-1] == 'didntLike': classLabelVector.append(1) elif listFromLine[-1] == 'smallDoses': classLabelVector.append(2) elif listFromLine[-1] == 'largeDoses': classLabelVector.append(3) index +=1 return returnMat, classLabelVector """ 函数说明:可视化数据 Parameters: datingDataMat - 特征矩阵 datingLabels - 分类Label Returns: NO """ def showdata(datingData, datingLabel): font = FontProperties(fname="c:/windows/fonts/simsun.ttc", size=14) fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(13, 8)) numberOfLabel = len(datingLabel) labelsColors = [] for i in datingLabel: if i == 1: labelsColors.append('black') if i == 2: labelsColors.append('orange') if i == 3: labelsColors.append('red') axs[0][0].scatter(x=datingData[:, 0], y=datingData[:, 1], color=labelsColors, s=15, alpha=.5) axs0_title_text = axs[0][0].set_title(u'每年获得的飞行常客里程数与玩视频游戏所消耗时间占比', FontProperties=font) axs0_xlabel_text = axs[0][0].set_xlabel(u'每年获得的飞行常客里程数', FontProperties=font) axs0_ylabel_text = axs[0][0].set_ylabel(u'玩视频游戏所消耗时间占', FontProperties=font) plt.setp(axs0_title_text, size=9, weight='bold', color='red') plt.setp(axs0_xlabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') plt.setp(axs0_ylabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') axs[0][1].scatter(x=datingData[:, 0], y=datingData[:, 2], color=labelsColors, s=15, alpha=.5) axs1_title_text = axs[0][1].set_title(u'每年获得的飞行常客里程数与每周消费的冰激淋公升数', FontProperties=font) axs1_xlabel_text = axs[0][1].set_xlabel(u'每年获得的飞行常客里程数', FontProperties=font) axs1_ylabel_text = axs[0][1].set_ylabel(u'每周消费的冰激淋公升数', FontProperties=font) plt.setp(axs1_title_text, size=9, weight='bold', color='red') plt.setp(axs1_xlabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') plt.setp(axs1_ylabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') axs[1][0].scatter(x=datingData[:, 1], y=datingData[:, 2], color=labelsColors, s=15, alpha=.5) axs2_title_text = axs[1][0].set_title(u'玩视频游戏所消耗时间占比与每周消费的冰激淋公升数', FontProperties=font) axs2_xlabel_text = axs[1][0].set_xlabel(u'玩视频游戏所消耗时间占比', FontProperties=font) axs2_ylabel_text = axs[1][0].set_ylabel(u'每周消费的冰激淋公升数', FontProperties=font) plt.setp(axs2_title_text, size=9, weight='bold', color='red') plt.setp(axs2_xlabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') plt.setp(axs2_ylabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') didntLike = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='black', marker='.', markersize=6, label='didntLike') smallDoses = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='orange', marker='.', markersize=6, label='smallDoses') largeDoses = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='red', marker='.', markersize=6, label='largeDoses') axs[0][0].legend(handles=[didntLike, smallDoses, largeDoses]) axs[0][1].legend(handles=[didntLike, smallDoses, largeDoses]) axs[1][0].legend(handles=[didntLike, smallDoses, largeDoses]) plt.show() """ 函数说明:对数据进行归一化 Parameters: dataSet - 特征矩阵 Returns: normDataSet - 归一化后的特征矩阵 ranges - 数据范围 minVals - 数据最小值 """ def autoNorm(dataset): minVal = dataset.min(0) maxVal = dataset.max(0) ranges = maxVal-minVal normDataSet = np.zeros(np.shape(dataset)) m = dataset.shape[0] normDataSet = dataset-np.tile(minVal, (m, 1)) normDataSet = normDataSet / np.tile(ranges, (m, 1)) return normDataSet, ranges, minVal """ 函数说明:kNN算法,分类器 Parameters: inX - 用于分类的数据(测试集) dataSet - 用于训练的数据(训练集) labes - 分类标签 k - kNN算法参数,选择距离最小的k个点 Returns: sortedClassCount[0][0] - 分类结果 """ def classify0(inX, dataSet, labels, k): dataSetSize = dataSet.shape[0] diffMat = np.tile(inX, (dataSetSize, 1)) - dataSet sqDiffMat = diffMat**2 sqDistances = sqDiffMat.sum(axis=1) distances = sqDistances**0.5 sortedDistIndices = distances.argsort() classCount = {} for i in range(k): voteIlabel = labels[sortedDistIndices[i]] classCount[voteIlabel] = classCount.get(voteIlabel, 0) + 1 sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True) return sortedClassCount[0][0] """ 函数说明:分类器测试函数 Parameters: 无 Returns: normDataSet - 归一化后的特征矩阵 ranges - 数据范围 minVals - 数据最小值 """ def datingClassTest(): filename = "datingTestSet.txt" datingDataMat, datingLabels = file2matrix(filename) hoRatio = 0.10 normMat, ranges, minVals = autoNorm(datingDataMat) m = normMat.shape[0] numTestVecs = int(m * hoRatio) errorCount = 0.0 for i in range(numTestVecs): classifierResult = classify0(normMat[i, :], normMat[numTestVecs:m, :], datingLabels[numTestVecs:m], 4) print("分类结果:%d 真实类别:%d" % (classifierResult, datingLabels[i])) if classifierResult != datingLabels[i]: errorCount += 1.0 print("错误率:%f%%" % (errorCount / float(numTestVecs) * 100)) if __name__ == "__main__": datingClassTest()
运行结果显示:错误率为4%。
我们可以改变函数datingClassTest内变量hoRatio和分类器k的值,检测错误率是否随着变量值的变化而增加。依赖于分类算法、数据集和程序设置,分类器的输出结果可能有很大的不同。
使用算法:构建完整可用系统
上面我们已经在数据上对分类器进行了测试,现在可以使用这个分类器为海伦来对人们分类。我们会给海伦一个小程序,通过该程序,海伦可以在约会网站上找到某人并输入他的信息,程序会给出她对对方喜欢程度的预测值。
最终程序如下:
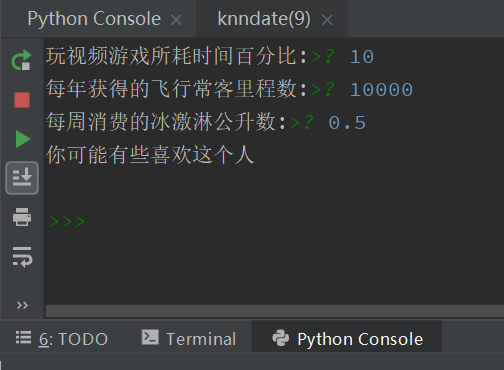
import numpy as np from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties import matplotlib.lines as mlines import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import operator """ 函数说明: 打开文件并进行解析,对数据进行分类:1代表不喜欢,2代表魅力一般,3代表极具魅力 Parameters: filename - 文件名 Returns: returnMat - 特征矩阵 classLabelVector - 分类标签 """ def file2matrix(filename): fr = open(filename) arrayOLines = fr.readlines() numberOfLines = len(arrayOLines) returnMat = np.zeros((numberOfLines, 3)) classLabelVector = [] index = 0 for line in arrayOLines: line = line.strip() listFromLine = line.split(' ') returnMat[index, :] = listFromLine[0:3] if listFromLine[-1] == 'didntLike': classLabelVector.append(1) elif listFromLine[-1] == 'smallDoses': classLabelVector.append(2) elif listFromLine[-1] == 'largeDoses': classLabelVector.append(3) index +=1 return returnMat, classLabelVector """ 函数说明:可视化数据 Parameters: datingDataMat - 特征矩阵 datingLabels - 分类Label Returns: NO """ def showdata(datingData, datingLabel): font = FontProperties(fname="c:/windows/fonts/simsun.ttc", size=14) fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(13, 8)) numberOfLabel = len(datingLabel) labelsColors = [] for i in datingLabel: if i == 1: labelsColors.append('black') if i == 2: labelsColors.append('orange') if i == 3: labelsColors.append('red') axs[0][0].scatter(x=datingData[:, 0], y=datingData[:, 1], color=labelsColors, s=15, alpha=.5) axs0_title_text = axs[0][0].set_title(u'每年获得的飞行常客里程数与玩视频游戏所消耗时间占比', FontProperties=font) axs0_xlabel_text = axs[0][0].set_xlabel(u'每年获得的飞行常客里程数', FontProperties=font) axs0_ylabel_text = axs[0][0].set_ylabel(u'玩视频游戏所消耗时间占', FontProperties=font) plt.setp(axs0_title_text, size=9, weight='bold', color='red') plt.setp(axs0_xlabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') plt.setp(axs0_ylabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') axs[0][1].scatter(x=datingData[:, 0], y=datingData[:, 2], color=labelsColors, s=15, alpha=.5) axs1_title_text = axs[0][1].set_title(u'每年获得的飞行常客里程数与每周消费的冰激淋公升数', FontProperties=font) axs1_xlabel_text = axs[0][1].set_xlabel(u'每年获得的飞行常客里程数', FontProperties=font) axs1_ylabel_text = axs[0][1].set_ylabel(u'每周消费的冰激淋公升数', FontProperties=font) plt.setp(axs1_title_text, size=9, weight='bold', color='red') plt.setp(axs1_xlabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') plt.setp(axs1_ylabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') axs[1][0].scatter(x=datingData[:, 1], y=datingData[:, 2], color=labelsColors, s=15, alpha=.5) axs2_title_text = axs[1][0].set_title(u'玩视频游戏所消耗时间占比与每周消费的冰激淋公升数', FontProperties=font) axs2_xlabel_text = axs[1][0].set_xlabel(u'玩视频游戏所消耗时间占比', FontProperties=font) axs2_ylabel_text = axs[1][0].set_ylabel(u'每周消费的冰激淋公升数', FontProperties=font) plt.setp(axs2_title_text, size=9, weight='bold', color='red') plt.setp(axs2_xlabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') plt.setp(axs2_ylabel_text, size=7, weight='bold', color='black') didntLike = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='black', marker='.', markersize=6, label='didntLike') smallDoses = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='orange', marker='.', markersize=6, label='smallDoses') largeDoses = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='red', marker='.', markersize=6, label='largeDoses') axs[0][0].legend(handles=[didntLike, smallDoses, largeDoses]) axs[0][1].legend(handles=[didntLike, smallDoses, largeDoses]) axs[1][0].legend(handles=[didntLike, smallDoses, largeDoses]) plt.show() """ 函数说明:对数据进行归一化 Parameters: dataSet - 特征矩阵 Returns: normDataSet - 归一化后的特征矩阵 ranges - 数据范围 minVals - 数据最小值 """ def autoNorm(dataset): minVal = dataset.min(0) maxVal = dataset.max(0) ranges = maxVal-minVal normDataSet = np.zeros(np.shape(dataset)) m = dataset.shape[0] normDataSet = dataset-np.tile(minVal, (m, 1)) normDataSet = normDataSet / np.tile(ranges, (m, 1)) return normDataSet, ranges, minVal """ 函数说明:kNN算法,分类器 Parameters: inX - 用于分类的数据(测试集) dataSet - 用于训练的数据(训练集) labes - 分类标签 k - kNN算法参数,选择距离最小的k个点 Returns: sortedClassCount[0][0] - 分类结果 """ def classify0(inX, dataSet, labels, k): dataSetSize = dataSet.shape[0] diffMat = np.tile(inX, (dataSetSize, 1)) - dataSet sqDiffMat = diffMat**2 sqDistances = sqDiffMat.sum(axis=1) distances = sqDistances**0.5 sortedDistIndices = distances.argsort() classCount = {} for i in range(k): voteIlabel = labels[sortedDistIndices[i]] classCount[voteIlabel] = classCount.get(voteIlabel, 0) + 1 sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True) return sortedClassCount[0][0] """ 函数说明:分类器测试函数 Parameters: 无 Returns: normDataSet - 归一化后的特征矩阵 ranges - 数据范围 minVals - 数据最小值 """ def datingClassTest(): filename = "datingTestSet.txt" datingDataMat, datingLabels = file2matrix(filename) hoRatio = 0.10 normMat, ranges, minVals = autoNorm(datingDataMat) m = normMat.shape[0] numTestVecs = int(m * hoRatio) errorCount = 0.0 for i in range(numTestVecs): classifierResult = classify0(normMat[i, :], normMat[numTestVecs:m, :], datingLabels[numTestVecs:m], 4) print("分类结果:%d 真实类别:%d" % (classifierResult, datingLabels[i])) if classifierResult != datingLabels[i]: errorCount += 1.0 print("错误率:%f%%" % (errorCount / float(numTestVecs) * 100)) """ 函数说明:通过输入一个人的三维特征,进行分类输出 """ def classifyPerson(): resultList = ['讨厌', '有些喜欢', '非常喜欢'] precentTats = float(input("玩视频游戏所耗时间百分比:")) ffMiles = float(input("每年获得的飞行常客里程数:")) iceCream = float(input("每周消费的冰激淋公升数:")) filename = "datingTestSet.txt" datingDataMat, datingLabels = file2matrix(filename) normMat, ranges, minVals = autoNorm(datingDataMat) inArr = np.array([ffMiles, precentTats, iceCream]) norminArr = (inArr - minVals) / ranges classifierResult = classify0(norminArr, normMat, datingLabels, 3) print("你可能%s这个人" % (resultList[classifierResult-1])) if __name__ == "__main__": #datingClassTest() classifyPerson()
运行程序,依次输入:10,10000,0.5.
得到结果:你可能有些喜欢这个人
如下图所示: