类与对象


- 引入类
// 类与对象
// 一个程序就是一个世界,有很多事物(对象[属性, 行为])
public class Object01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
张老太养了两只猫,一只猫的名字叫小白,今年三岁,白色
一只叫小花,今年100岁,请编写一个程序,当用户输入小猫的名字时,
就显示这个猫的年龄,名字,颜色,如果用户的输入小猫名有误
显示 张老太没有这只猫
*/
// 单独变量来解决 => 不利于数据的管理(把一只猫的数据拆解)
// 第一只猫的信息
String cat1Name = "小白";
int cat1Age = 3;
String cat1Color = "白色";
// 第二只猫的信息
String cat2Name = "小花";
int cat2Age = 100;
String cat2Color = "花色";
// 数组 ===> 数据类型不能体现出来,
// 只能通过下标获取信息,造成变量名字和内容对应关系不明确
// 不能体现猫的行为
// 第一只猫的信息
// String[] cat1 = {"小白", "3", "白色"};
// String[] cat2 = {"小花", "100", "花色"};
// 现有技术的缺点
// 不利于数据的管理
// 效率低,引出我们新的知识点,类和对象
// java的设计者引入类与对象(OOP),根本原因是现有的技术不能完美的解决新的需求
//
//
//
// 使用OOP面向对象解决
// 实例化一只猫【创建一个猫对象】
// 1.new Cat() 创建一只猫
// 2.Cat cat1 = new Cat();把创建的猫赋值给cat1
Cat cat1 = new Cat();
cat1.name = "小白";
cat1.age = 3;
cat1.color = "白色";
cat1.weight = 10;
// 创建第二只猫对象
Cat cat2 = new Cat();
cat2.name = "小花";
cat2.age = 100;
cat2.color = "花色";
cat2.weight = 23.9;
// 怎么使用,怎么访问对象的属性
System.out.println("第一只猫的信息" + cat1.name + " " + cat1.age + " " + cat1.color + " " + cat1.weight);
System.out.println("第一只猫的信息" + cat2.name + " " + cat2.age + " " + cat2.color + " " + cat2.weight);
}
}
// 使用面向对象的方式解决养猫问题
// 定义一个猫类 Cat - > 自定义数据类型
//
class Cat{
// 属性
String name;
int age;
String color;
double weight;
}
- 类在内存中的存在形式(重要)
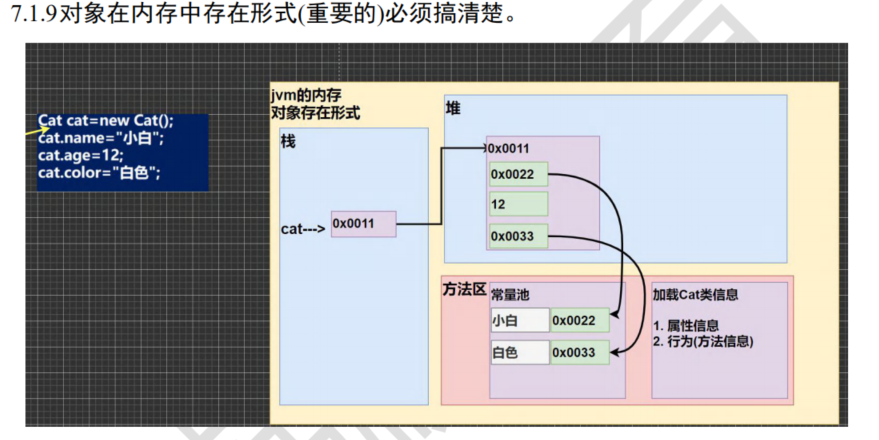
public class Object02{
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
class Car{
String name; // 属性 成员变量 字段 field
double price;
String color;
String[] master; // 属性可以是基本数据类型,也可以是引用类型
}
- 属性的注意事项
- 属性的定义语法同变量,示例:访问修饰符 属性类型 属性名;
这里老师简单的介绍访问修饰符: 控制属性的访问范围 有四种访问修饰符 public, proctected, 默认, private ,后面我会详细介绍 - 属性的定义类型可以为任意类型,包含基本类型或引用类型
- 属性如果不赋值,有默认值,规则和数组一致。具体说: int 0,short 0, byte 0, long 0, float 0.0,double 0.0,char \u0000, boolean false,String null
public class Properties{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建对象
// p1 是对象名(对象引用
// new Perso() 创建的对象空间才是真正的对象
Person p1 = new Person();
// 对象的属性默认值,遵守数据的规则
System.out.println("当前人的信息");
System.out.println("age=" + p1.age + " name = " + p1.name + " sal=" + p1.sal + " isPass " + p1.isPass);
}
}
class Person{
int age;
String name;
double sal;
boolean isPass;
}
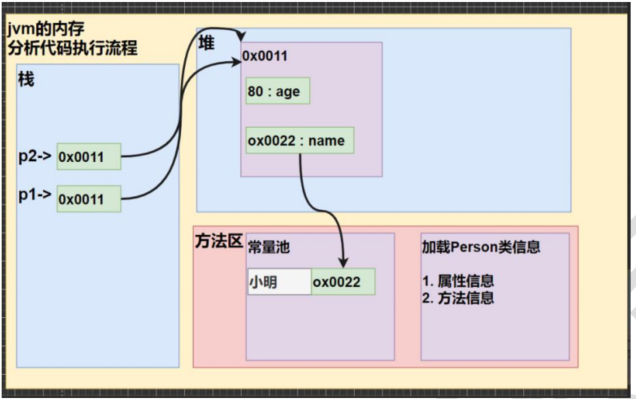
- 类的内存结构
- 栈: 一般存放基本数据类型(局部变量)
- 堆: 存放对象(Cat cat , 数组等)
- 方法区:常量池(常量,比如字符串), 类加载信息
- 示意图 [Cat (name, age, price)]
public class Object03{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person();
p1.age = 10;
p1.name = "小明";
Person p2 = p1;
p2.age = 80;
System.out.println(p1.age); // 10
}
}
class Person{
String name;
int age;
}
成员方法
- 成员方法入门
public class Method01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 方法写好了,如果不去调用,不会输出
// 如何使用方法,先创建一个对象,然后调用方法即可
Person p1 = new Person();
p1.speak(); // 调用方法
p1.cal01();
p1.cal02(5);
p1.cal02(100);
// 调用getSum方法,同时num1,num2
// 把方法 getSum 返回的值赋给变量 returnRes
int returnRes = p1.getSum(10, 20); //
System.out.println("getSum 方法返回的值:" + returnRes);
}
}
class Person{
String name;
int age;
// 方法,成员方法
// 输出我是一个好人
// 1.public 表示方法是公开的
// 2. void 表示方法没有返回值
// 3. speak(),speak就是方法的名称,()形参列表,当前没有任何值在里面
// 4.{}方法体,可以写我们要执行的代码
//
public void speak(){
System.out.println("我是一个好人");
}
public void cal01(){
// 循环完成
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 1000; i++){
sum += i;
}
System.out.println("cal01计算结果:" + sum);
}
// 接受一个参数n, 计算1 + 2 + ... + n
// 形参列表,当前有个形参n,形参就是形式参数,可以接收用户的输入
public void cal02(int n){
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
sum += i;
}
System.out.println("cal02计算结果:" + sum);
}
// 添加getSum方法,可以计算两个数的和
// 1.public 表示方法是公开的
// 2. int 表示返回一个int值
// 3.(int num1, int num2) 形参列表,2个形参
// 4.return res 表示把res的值返回
public int getSum(int num1, int num2){
int result = num1 + num2;
return result;
}
}
- 方法的内存调用机制
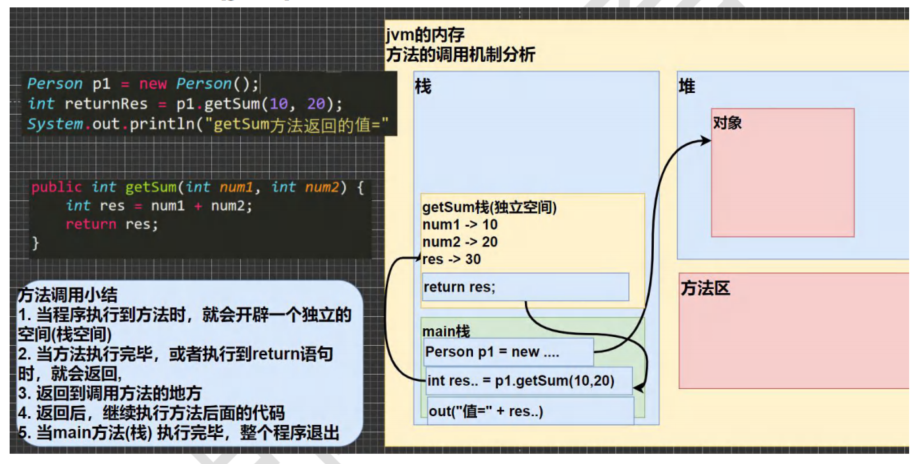
- 提高了代码的复用性,方法的最大优势,就是实现一个模块,可以多次复用
- 可以将实现的细节封装起来,然后共其他用户调用即可
public class Method02{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 遍历一个二维数组,输出数组的各个元素值
int[][] map = {{0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 1}, {1, 2, 3}};
// for(int i = 0; i < map.length; i++){
// for(int j = 0; j < map[i].length; j++){
// System.out.print(map[i][j] + " ");
// }
// System.out.println();
// }
// // 要求再次遍历这个map数组
// for(int i = 0; i < map.length; i++){
// for(int j = 0; j < map[i].length; j++){
// System.out.print(map[i][j] + " ");
// }
// System.out.println();
// }
// // 再次遍历,在复制一次
// for(int i = 0; i < map.length; i++){
// for(int j = 0; j < map[i].length; j++){
// System.out.print(map[i][j] + " ");
// }
// System.out.println();
// }
//
// 使用方法进行输入
myTools tool = new myTools();
tool.printArray(map);
}
}
// 把输入的功能,写入到类的方法中,然后调用这个方法即可
class myTools{
// 接受一个二维数组
//
public void printArray(int[][] map){
// 对传入的map数组进行遍历
for(int i = 0; i < map.length; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < map[i].length; j++){
System.out.print(map[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
- 成员方法的定义
public 返回数据类型 方法名(形参){
语句;
返回值
}
成员方法注意事项
- 访问控制符,作用是控制方法使用的范围,默认有四种(public protected, 默认,private)
- 一个方法最多有一个返回值
- 返回类型可以为任意类型,包含基本类型或引用类型(数组,对象)
- 如果方法要求有返回数据类型,则方法体中最后的执行语句必须为 return 值; 而且要求返回值类型必须和 return 的 值类型一致或兼容
- 如果方法是 void,则方法体中可以没有 return 语句,或者 只写 return ;
public class MethodDetail{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1个方法最多有一个返回值,思考如何返回多个值,数组
// 2.返回类型可以为任何类型,包含基本类型和引用类型,数组,对象
// 3.如果方法要求有返回值类型,则必须有return值
// 而且要求return的值必须与return的值类型一致或者兼容
//
// 4.如果是void,可以不写return或者return ,不能写其他
AA a = new AA();
int[] res = a.getSumAndSub(1, 4);
double b = a.f1();
System.out.println("和=" + res[0]);
System.out.println("差=" + res[1]);
}
}
class AA{
public int[] getSumAndSub(int n1, int n2){
int[] resArr = new int[2];
resArr[0] = n1 + n2;
resArr[1] = n1 - n2;
return resArr;
}
public double f1(){
double d1 = 1.1 * 3;
int n = 100;
return n;
}
}

方法的注意细节
- 同一个类的方法直接调用, 不需要创建对象
- 不同类之间的方法调用,需要在该类创建一个新的对象,才能使用别的方法

public class MethodDetail02{
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
a.sayOk();
a.m1();
}
}
class A{
// 同一个类的方法直接调用, 不需要创建对象
//
public void print(int n){
System.out.println("print方法被调用 n = " + n);
}
public void sayOk(){
print(10);
System.out.println("继续执行sayOk");
}
// 跨类中的A类调用B类方法:需要通过对象名进行调用
//
public void m1(){
// 创建B对象
System.out.println("A类中的m1被调用");
B b = new B();
b.hi();
System.out.println("M1方法继续执行");
}
}
class B{
// 跨内的方法,需要创建方法
//
public void hi(){
System.out.println("B类的hi方法执行");
}
}
- 练习1 返回一个数是否是奇数
public class MethodEx01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//
AA a = new AA();
boolean isRight = a.isOdd(5);
System.out.println("5是奇数?" + isRight);
}
}
class AA{
// 思路
// 1 方法的返回类型是 boolean
// 2 方法的名字是 isOdd
// 3 方法的形参是 int num
// 4 方法体进行判断
public boolean isOdd(int num){
// boolean isRight = false;
// if(n % 2 == 1){
// isRight = true;
// }
// return isRight;
//
// return num % 2 != 0 ? true: false;
//
return num % 2 != 0;
}
}
- 练习2 输出一个行, 列,字符,打印这些字符
public class MethodEx01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//
AA a = new AA();
boolean isRight = a.isOdd(5);
// System.out.println("5是奇数?" + isRight);
// 调用方法
a.printChar(4, 5, '*');
}
}
class AA{
// 思路
// 1 方法的返回类型是 boolean
// 2 方法的名字是 isOdd
// 3 方法的形参是 int num
// 4 方法体进行判断
public boolean isOdd(int num){
// boolean isRight = false;
// if(n % 2 == 1){
// isRight = true;
// }
// return isRight;
//
// return num % 2 != 0 ? true: false;
//
return num % 2 != 0;
}
// 思路
// 1 没有返回值
// 2 参数是三个,一个是行,一个是列,一个是字符
// 3 打印二维数组的思想
public void printChar(int row, int col, char chara){
for(int i = 0 ; i < row; i++){
for(int j=0; j < col; j++){
System.out.print(chara + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
成员变量传参机制
- 传入的是基本数据类型,不会改变数据
public class MethodParameter01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
// 创建AA对象
AA obj = new AA();
obj.swap(a, b); // 调用swap方法
System.out.println("a和b经过swap的值a=" + a + "\tb=" + b);
}
}
class AA{
public void swap(int a , int b){
System.out.println("a和b交换前的值a=" + a + "\tb=" + b);
// 完成a和b的交换
//
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
System.out.println("a和b交换后的值a=" + a + "\tb=" + b);
}
}
- 传入的是引用数据类型
传入的是引用类型,由于传入的是地址,所以引用数据类型会改变
public class MethodParameter02{
public static void main(String[] args) {
B b = new B();
int[] arr01 = {1, 2, 3};
b.test100(arr01);
System.out.println("main中的arr数组");
for(int i= 0; i < arr01.length; i++){
System.out.print(arr01[i] + "\t");
}
}
}
class B{
// 接受一个数组,修改这个数组
public void test100(int[] arr){
arr[0] = 200;
// 遍历数组
System.out.println("类B中test100方法中");
for(int i= 0; i < arr.length; i++){
System.out.print(arr[i] + "\t");
}
}
}
- 练习1,如何复制一个新的空间的类
public class MethodEx02{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//
Person p = new Person();
p.name = "Tom";
p.age = 12;
MyTools tools = new MyTools();
Person p2 = tools.copyPerson(p);
System.out.println("p2的name值:" + p2.name + " p2的age值:" + p2.age);
p2.name = "小明";
// 提示,可以通过hashCode看看对象是否是同一个
// 可以通过对象比较看看是否是同一个
System.out.println(p == p2);
System.out.println("p1.name = " + p.name);
}
}
class Person{
String name;
int age;
}
class MyTools{
// 编写一个方法 copyPerson,可以复制一个 Person 对象,返回复制的对象。克隆对象,
// 注意要求得到新对象和原来的 对象是两个独立的对象,只是他们的属性相同
// 思路
// 确定返回类型为Person
// 方法的形参也是 Person p
// 完成一个复制,创建一个新对象,并复制属性,返回即可
//
//
public Person copyPerson(Person p){
// 创建一个person对象
Person p2 = new Person();
p2.name = p.name;
p2.age = p.age;
return p2;
}
}
递归方法
递归就是方法自己调用自己,每次调用时传入不同的变量.递归有助于编程者解决复杂问题,同时可以让代码变 得简洁

- 递归入门,递归适合逻辑清晰,能够通过不断迭代来减少问题规模的场景,比如
- f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2)
- 汉诺塔等
public class Recursion01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
T t1 = new T();
t1.test(4);
}
}
class T{
public void test(int n){
if (n > 2){
test(n-1);
}
System.out.println("n=" + n);
}
}
- 递归的联系,数据的阶乘
public class Recursion01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
T t1 = new T();
// t1.test(4);
int res = t1.factorial(5);
System.out.println("res = " + res);
}
}
class T{
public void test(int n){
if (n > 2){
test(n-1);
}
System.out.println("n=" + n);
}
//### factorial 阶乘
public int factorial(int n){
if(n == 1){
return 1;
}
return n* factorial(n-1);
}
}
递归的注意细节

- 课堂练习1:求出斐波拉列数
public class RecursionEx01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
T t1 = new T();
int res = t1.fibonacci(7);
System.out.println("当n=7是的斐波那契数:" + res);
}
}
class T{
/*
使用递归的方法求出斐波那契数列,1,1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 给你一个整数n,求它的值是多少?
思路分析:
n = 1 斐波那契是 1
n = 2 斐波那契是 1
n >= 3 斐波那契是 前面两个数的和
这里就是递归的思路,n = 7 ,我就需要得到前面两个数,我得到前面两个数,就需要得到前面两个数,直到第一个和第二个数
*/
public int fibonacci(int n){
if(n >= 1){
if(n == 1 || n == 2){
return 1;
}
else{
return fibonacci(n-1) + fibonacci(n - 2);
}
}
else{
System.out.println("输入的数据有误");
return -1;
}
}
}
- 练习2 猴子吃桃子问题,有一堆桃子,猴子第一天吃了一把,并多吃一个,每天都是这样,当到第10天,只剩下一个桃子,求最初多少个桃子
这个重点是在在于前一天的桃子 = (后一天的桃子+1) * 2
public class RecursionEx02{
public static void main(String[] args) {
T t1 = new T();
int day = 0;
int peachNum = t1.peach(day);
System.out.println(day + "的桃子是" + peachNum);
}
}
class T{
/*
猴子吃桃子,每天吃了其中的一半,然后多吃一个,直到第十天,只剩下一个桃子
请问最初有几个桃子
思路分析:
逆推:
第十天 1个桃子
第九天 最初 4个 桃子 4/2-1
第八天 10 个桃子 10/2 -1
......
*/
public int peach(int day){
if(day == 10){
return 1;
}
else if(day >=1 && day <= 9){
return (peach(day+1) + 1) * 2;
}
else{
System.out.println("day在1-10");
return -1;
}
}
}
- 练习3 老鼠出迷宫问题
很有意思的一个递归题,对后面数,图的算法理解很有帮助
public class RecursionEx03{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 思路
// 1.先创建迷宫,用二维数组表示, int[][] map = new int[8][7];
// 2.先规定map数组的元素:0表示可以走,1表示障碍物
int[][] map = new int[8][7];
// 3.将上下两行,左右两列都设置为1
// 也可以用两个for循环进行设置,更快一点
for(int i = 0; i < map.length; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < map[i].length; j++){
if(i == 0 || i == map.length-1){
map[i][j] = 1;
}
else if (j == 0 || j == map[i].length-1){
map[i][j] = 1;
}
}
}
// map[2][1] = 1;
// map[2][2] = 1;
// map[1][2] = 1;
map[3][1] = 1;
map[3][2] = 1;
// 输出地图情况
System.out.println("=====地图=======");
for(int i = 0; i < map.length; i++){
for(int j=0; j <map[i].length; j++){
System.out.print(map[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// 使用findway找路
MiGong t1 = new MiGong();
t1.findWay(map, 1, 1);
// 输出找路的情况
System.out.println("\n=====找路的情况=======");
for(int i = 0; i < map.length; i++){
for(int j=0; j <map[i].length; j++){
System.out.print(map[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
class MiGong{
/*
使用递归回溯的思想来解决老鼠出迷宫
1. findway专门找到迷宫的路径
2.找到,就返回true,找不到返回false
3.map就是二维数组,表示迷宫
4. i,j就是老鼠的位置,初始化的位置为(1,1),终点位置(6,5);
5.因为是递归找路,我们规定map数组各个值的含义,
0:表示可以走,1:表示障碍物,
2:表示可以走 3:表示走过但是不通
退出递归:
6.当走到终点(6,5) = 2 就说明找到通路,就可以退出递归,否则就继续找
7.先确定老鼠找路的策略 下->右->上->左
*/
public boolean findWay(int[][]map, int i, int j){
if(map[6][5] == 2){ // 说明已经找到
return true;
}
else{
if(map[i][j] == 0){ // 当前位置为0,表示可以走通
// 我们假定可以走通
map[i][j] = 2;
// 使用找路策略,确定该位置是否真的走通
if (findWay(map, i+1, j)){
return true;
}
else if(findWay(map, i, j+1)){
return true;
}
else if(findWay(map, i-1, j)){
return true;
}
else if(findWay(map, i, j-1)){
return true;
}
else{
map[i][j] = 3;
return false;
}
}
else{ // map[i][j] = 1, 2, 3
return false;
}
}
}
}
- 汉诺塔问题
汉诺塔问题是递归的经典问题,对于每一个塔来说,只解决三步,
把最后一个塔以上的所有塔借助第三个针移到第二个针上
把最后的塔移动第三个针上
把第二个针上的塔借助第一个针移到第三个针上
public class HanoiTower{
public static void main(String[] args) {
HanTower tower = new HanTower();
tower.move(10, 'A', 'B', 'C');
}
}
class HanTower{
// 方法
// num 表示要移动的个数, a,b,c表示A塔,B塔,C塔
//
//
public void move(int num, char a, char b, char c){
// 如果只有一个盘
if(num == 1){
System.out.println(a + "->" + c);
}
else{
// 如果有多个盘,可以 看出两个,最下面的,和上面所有盘
// 1.先移动上面所有盘到 B, 借助c
move(num - 1, a, c, b);
// 2.把最下面的盘移动到c
System.out.println(a + "->" + c);
// 再把b塔的所有盘移动到c,借助a
move(num - 1, b, a, c);
}
}
}
方法重载
Java允许在一个类中多个同名的方法存在,但是形不一致,根据形参的数量自动调取需要的方法
public class OverLoad01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(100);
System.out.println("hello world");
System.out.println('h');
System.out.println(true);
}
}
- 自己类中定义的重载
public class OverLoad01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// System.out.println(100);
// System.out.println("hello world");
// System.out.println('h');
// System.out.println(true);
//
MyCalculator mc = new MyCalculator();
System.out.println(mc.calculate(1, 2));
System.out.println(mc.calculate(1.2, 3.4));
System.out.println(mc.calculate(1, 2, 3));
}
}
class MyCalculator{
// 下面四个方法构成了重载
// 两个整数的和
public int calculate(int n1, int n2){
return n1 + n2;
}
public double calculate(int n1, double n2){
return n1 + n2;
}
public double calculate(double n1, double n2){
return n1 + n2;
}
public int calculate(int n1, int n2, int n3){
return n1 + n2 + n3;
}
}
- 方法重载的注意事项和使用细节
- 方法名要一样
- 形参必须不一样,比如类型或者数量
- 返回值没有要求,返回值类型不同不属于方法重载
public class OverLoadEx01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Methods m1 = new Methods();
m1.m(3);
m1.m(3, 4);
m1.m("hello");
}
}
class Methods{
public void m(int a){
System.out.println(a*a);
}
public void m(int a, int b){
System.out.println(a * b);
}
public void m(String s){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
- 练习2,利用重载完成对两个数的比较
public class OverLoadEx02{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Methods m1 = new Methods();
System.out.println(m1.max(4, 5));
System.out.println(m1.max(4.5, 6.7));
System.out.println(m1.max(7.8, 8.8, 10));
}
}
class Methods{
public int max(int a, int b){
if(a > b){
return a;
}
else{
return b;
}
}
public double max(double a, double b){
if(a > b){
return a;
}
else{
return b;
}
}
public double max(double a, double b, double c){
if(a > b){
if (a > c){
return a;
}
else{
return c;
}
}
else{
if(b > c){
return b;
}
else{
return c;
}
}
}
}
可变参数
java 允许将同一个类中多个同名同功能但参数个数不同的方法,封装成一个方法。
就可以通过可变参数实现
public class VarParameter02{
public static void main(String[] args) {
HspMethod m = new HspMethod();
m.sum();
System.out.println(m.sum(1, 3, 4));
}
}
class HspMethod{
// 计算多个可变参数的值
// 解读
// 1. int... 表示接受的可变参数,类型是int,可以接收多个int
// 2. 使用可变参数时,可以当做数组来使用,即 nums 可以当做数组
// 3. 遍历求和即可
//
public int sum(int... nums){
System.out.println("接受的参数个数=" + nums.length);
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
res += nums[i];
}
return res;
}
}
- 可变参数的使用细节

- 可变参数的实参可以为数组
- 实参可以为0个或者多个
- 可变参数可以跟普通参数放在新参列表,但是必须保证可变参数放在最后
- 一个形参列表中,只能有一个可变参数
public class VarParameterDetail{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 细节:可变参数的实参可以为数组
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
T t1 = new T();
t1.f1(arr);
}
}
class T{
public void f1(int... nums){
System.out.println("长度=" + nums.length);
}
// 细节:可变参数可以跟普通参数放在新参列表,但是必须保证可变参数放在最后
public void f2(String str, double... nums){
}
}
- 练习01,利用可变参数完成多个数据的相加
public class VarParameterEx01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
HspMethod score = new HspMethod();
String[] newInfo = score.showScore("jack", 1.2, 3.4, 6.7);
for(int i = 0; i < newInfo.length; i++){
System.out.print(newInfo[i] + " ");
}
}
}
class HspMethod{
public String[] showScore(String name, double... scores){
String[] info = new String[2];
info[0] = name;
double sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < scores.length; i++){
sum += scores[i];
}
info[1] = sum + " ";
return info;
}
}
作用域

public class VarScope{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat myCat = new Cat();
myCat.cry();
}
}
class Cat{
// 全局变量,也就是属性,作用域在整个Cat类,cry eat 等方法使用属性
//
// 属性定义时,可以直接赋值
int age = 10;
// 全局变量可以不赋值,直接使用,因为有默认值
// 局部变量必须赋值后,才能使用,因为没有默认值
//
double weight; // 默认值是0.0
public void cry(){
// 1.局部变量一般是在成员方法中定义的变量
// 2.这里的n和name都是局部变量
// 3.n和name的作用域都在cry方法中
//
int n = 10;
String name = "jack";
double year;
System.out.println("在cry中使用属性age = " + age);
System.out.print(year); // 报错,没有初始化不能使用,但是如果只有变量,但是不使用,也不会报错
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("在eat中使用属性age = " + age);
}
}
- 作用域使用细节
- 就近原则
- 同一个作用域下的变量不能重名
- 局部变量的生命周期随着作用域的不同而不同,局部变量的生命周期较短
- 不同的方法可以调用
public class VarScopeDetail{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person();
p1.say(); //方法结束后,name就销毁了,但是类还在,因此类中的全局变量还存在
T t1 = new T();
t1.test();
}
}
class T{
// 全局变量,可以在本类中使用,也可以在其他类使用,对象调用
public void test(){
Person p2 = new Person();
p2.say();
System.out.println(p2.name);
}
}
class Person{
String name = "jack";
public void say(){
// String name = "king";
System.out.println("say() name = " + name);
}
}
构造器
1.构造器没有返回值,也不能写void
2.构造器的名字和类名必须一致
3.构造器形参列表,规则与成员方法一致
public class Constructor{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 当我们new一个对象,直接通过构造器指定名字和年龄
Person p1 = new Person("smith", 90);
System.out.println("p1的信息如下");
System.out.println("p1对象的name=" + p1.name);
}
}
class Person{
String name;
int age;
// 构造器
//
// 1.构造器没有返回值,也不能写void
// 2.构造器的名字和类名必须一致
// 3.构造器形参列表,规则与成员方法一致
public Person(String pName, int pAge){
System.out.println("构造器被调用~~");
name = pName;
age = pAge;
}
}
- 构造器的使用细节
- 一个类可以有多个构造器,即构造器的重载
- 构造器名字必须跟类名一致
- 构造器没有返回值
- 构造器是完成对象的初始化,不是创建对象
- 创建对象时,系统会自动的创建该类的构造方法
- 如果程序员没有定义构造 ,系统会自动给类生成一个默认无参构造方法,也叫默认构造方法
- 一旦定义了自己的构造器,就覆盖了默认的构造器,就不能使用无参的方法,除非显示的定义一下

public class ConstructorDetail{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 当我们new一个对象,直接通过构造器指定名字和年龄
Person p1 = new Person("smith", 90);
Person p2 = new Person("king");
System.out.println("p1的信息如下");
System.out.println("p1对象的name=" + p1.name);
System.out.println("p2对象的name=" + p2.name);
}
}
class Person{
String name;
int age;
// 构造器
//
// 1.构造器没有返回值,也不能写void
// 2.构造器的名字和类名必须一致
// 3.构造器形参列表,规则与成员方法一致
public Person(String pName, int pAge){
System.out.println("构造器被调用~~");
name = pName;
age = pAge;
}
public Person(String pName){
name = pName;
}
}
- 练习 ,构造器练习
public class ConstructorEx01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person();
System.out.println("输出所有人:" + p1.age);
Person p2 = new Person("jack", 199);
System.out.println("输出" + p2.name + "年龄:" + p2.age);
}
}
class Person{
String name;
int age;
public Person(){
age = 18;
}
public Person(String pName, int pAge){
name = pName;
age = pAge;
}
}
对象创建的流程分析
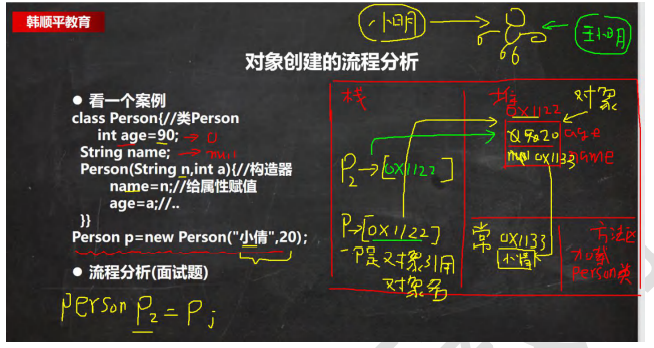

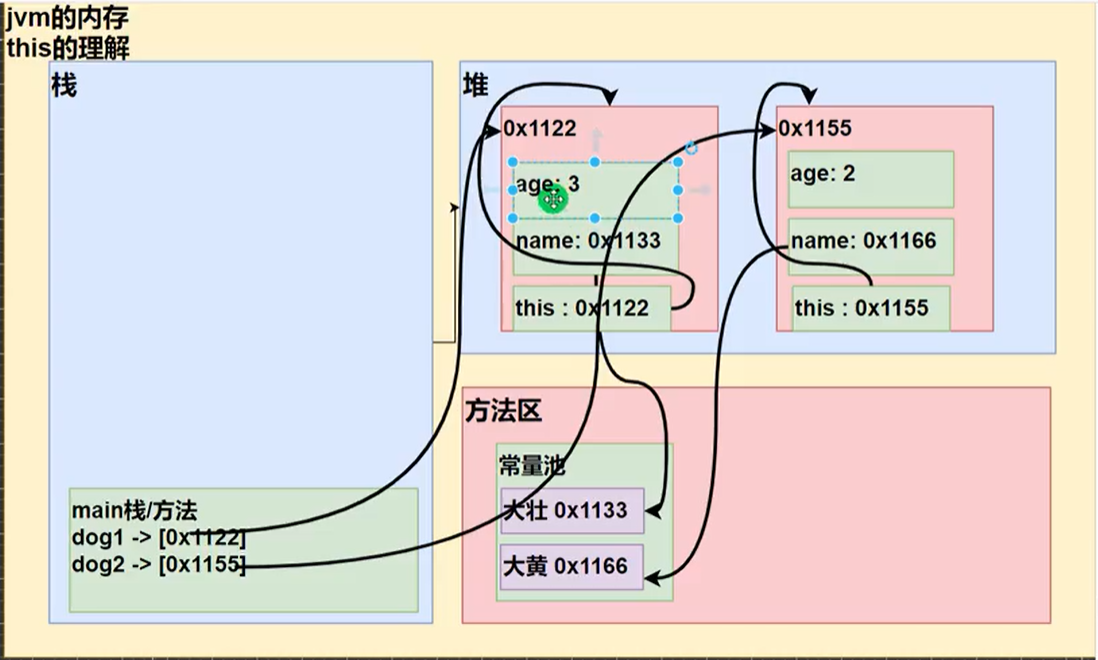
this关键字
- 什么是this?
java虚拟机会给每个对象分配this,代表当前对象
使用this解决变量命名问题
public class This01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog1 = new Dog("tom", 12);
System.out.println("dog1的hashCode=" + dog1.hashCode());
dog1.info();
Dog dog2 = new Dog("jack", 6);
dog2.info();
}
}
class Dog{
String name;
int age;
// public Dog(String dName, int dAge){
// name = dName;
// age = dAge;
// }
// 如果我们构造器的形参,能够直接写成属性名就更好了
// 构造器的name是局部变量,age也是局部变量,而不是属性
//
// ==> 引出this关键字来解决
public Dog(String name, int age){
// this.name 就是当前对象的属性
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
System.out.println("this.hashCode=" + this.hashCode());
}
// 成员方法,输出属性的信息
public void info(){
System.out.println(name + "\t" + age + "\t");
}
}
this 是在创建对象的时候,this的地址与创建对象的地址是一致的
this就是哪个对象调用,就是值哪个对象
- this使用细节
- this 关键字可以用来访问本类的属性、方法、构造器
- this 用于区分当前类的属性和局部变量
- 访问成员方法的语法:this.方法名(参数列表)
- 访问构造器语法:this(参数列表); 注意只能在构造器中使用(即只能在构造器中访问另外一个构造器, 必须放在第一条语句)
- this 不能在类定义的外部使用,只能在类定义的方法中使用
public class ThisDetail{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// T t1 = new T();
// t1.f2();
T t2 = new T();
//this
t2.f1();
}
}
class T{
/*
细节,访问构造器语法,只能在构造器中使用,this(参数列表),且必须放在第一条
*/
String name = "jack";
int age = 12;
public T (){
// 访问这个构造器
this("jack", 100);
System.out.println("T() 构造器");
}
public T(String name, int age){
System.out.println("T(String, int) 构造器");
}
public void f1(){
// this("jack", 100);
String name = "jin";
System.out.println("f1方法");
System.out.println("name = " + name + " age = " + age);
System.out.println("name = " + this.name + " age = " + this.age);
}
public void f2(){
System.out.println("f2方法");
f1();
this.f1();
}
}
- this 课堂练习
定义 Person 类,里面有 name、age 属性,并提供 compareTo 比较方法,用于判断是否和另一个人相等,提供测试类 TestPerson
用于测试, 名字和年龄完全一样,就返回 true, 否则返回
public class TestPerson{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person("小花", 12);
Person p2 = new Person("小白", 12);
System.out.println("是否一样" + p2.compareTo(p1));
}
}
class Person{
String name;
int age;
public Person(String name, int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public boolean compareTo(Person p1){
if(this.name.equals(p1.name) && this.age == p1.age){
return true;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
}
- 类的作业1,返回一个max的方法
public class Homework01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
A01 a01 = new A01();
double arr[] = {};
Double res = a01.max(arr);
System.out.println("arr的最大值是:" + a01.max(arr));
}
}
class A01{
/*
思路分析:
1.类名 A01
2.方法名 max
3.形参 double[]
4.返回值 double
先完成业务,然后在考虑代码的健壮性
*/
public Double max(double[] arr){
// 保证arr至少有一个元素
//
if(arr.length > 0){
double maxNum = arr[0];
for(int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++){
if(arr[i] > maxNum){
maxNum = arr[i];
}
}
return maxNum;
}
else{
return null;
}
}
}
- 作业2:返回字符串数组的元素查找,返回索引
public class Homework02{
public static void main(String[] args) {
A02 a02 = new A02();
String[] arr = {"you", "here", "are", "right"};
System.out.println("返回的索引:" + a02.find(arr, "are"));
}
}
class A02{
/*
思路:
方法名 find
形参 字符串数组
返回值 int
*/
public int find(String[] arr, String findThing){
int findPath = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
if(arr[i].equals(findThing)){
findPath = i;
break;
}
}
return findPath;
}
}
- 作业3,定义一个类,包含书名和价格,可以实现自动对价格进行调整
public class Homework03{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book bookPrice = new Book("岁月神偷", 200);
bookPrice.udpatePrice();
bookPrice.info();
}
}
class Book{
/*
构造一个书类
实现改变数的价格
;类型,diuble
返回值 int
*/
String name;
double price;
// 构造器
public Book(String name, double price){
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public void udpatePrice(){
if(this.price > 150){
this.price = 150;
}
else if(this.price > 100){
this.price = 100;
}
}
// 显示书籍情况
public void info(){
System.out.println("书名:" + this.name + " 价格 = " + this.price);
}
}
- 作业4: 编写一个类,实现数组的copy功能,输入旧数组,返回一个新数组
public class Homework04{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 方法返回值
int[] oldArr = {10, 30, 40};
A03 a3 = new A03();
int[] newArr = a3.copyArr(oldArr);
// 遍历
for(int i = 0; i < newArr.length; i++){
System.out.print(newArr[i] + "\t");
}
}
}
class A03{
/*
编写编写一个类,实现数组的copy功能,输入旧数组,返回一个新数组
实现一个方法,copyArr
返回一个新数组,元素和就数组一样
*/
public int[] copyArr(int[] oldArr){
int[] newArr = new int[oldArr.length];
for(int i=0; i < oldArr.length; i++){
newArr[i] = oldArr[i];
}
return newArr;
}
}
- 作业5 定义一个圆类,定义属性半径,提供显示圆周长的方法
public class Homework05{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cricle cl = new Cricle(2.5);
cl.circumference();
cl.area();
}
}
class Cricle{
double radius;
public Cricle(double radius){
this.radius = radius;
}
// 计算周长
public void circumference(){
double circleCum = 2*radius*Math.PI;
System.out.println("圆的周长为=" + circleCum);
}
// 计算面积
public void area(){
double circleArea = Math.PI * radius * radius;
System.out.println("圆的面积为=" + circleArea);
}
}
- 作业6 实现一个Cale计算类,输出两个变量表示两个操作数,定义加减乘除
public class Homework06{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cale cale = new Cale(5, 0);
System.out.println("和=" + cale.add());
System.out.println("减=" + cale.sub());
System.out.println("乘=" + cale.mul());
System.out.println("除=" + cale.div());
}
}
class Cale{
double a;
double b;
public Cale(double a, double b){
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
public double add(){
return a + b;
}
public double sub(){
return a - b;
}
public double mul(){
return a * b;
}
public Double div(){
if ( b == 0){
System.out.println("除数不能为0");
return null;
}
else{
return a / b;
}
}
}
- 作业7 设计一个Dog类,显示其信息
public class Homework07{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog bai = new Dog("小白", "白色", 23);
bai.show();
}
}
class Dog{
String name;
String color;
int age;
public Dog(String name, String color, int age){
this.name = name;
this.color = color;
this.age = age;
}
public void show(){
System.out.println("名字:" + name + "颜色" + color + "年龄" + age);
}
}
-
作业8 答案是

-
作业12 复用构造器
public class Homework12{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee employee = new Employee("小金", "男", 12000);
}
}
class Employee{
// 先写少的
String name;
String gender;
int age;
String position;
double salary;
public Employee(String name, String gender, int age){
this.name = name;
this.gender = gender;
this.age = age;
}
public Employee(String position, double salary){
this.position = position;
this.salary = salary;
}
public Employee(String name, String gender, int age, String position, double salary){
// this.name = name;
// this.gender = gender;
// this.age = age;
this(name, gender, age);
this.position = position;
this.salary = salary;
}
}
- 作业13 类进行调用

public class Homework13{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Circle cl = new Circle();
PassObject ps = new PassObject();
ps.printAreas(cl, 5);
}
}
class Circle{
double radius;
public double findArea(){
return radius * radius * Math.PI;
}
}
class PassObject{
public void printAreas(Circle cl, int times){
System.out.println("Radius" + "\t\t" + "Area");
for(int i = 1; i <=times; i++){
cl.radius = i;
System.out.println(cl.radius + "\t\t" + cl.findArea());
}
}
}
- 作业14 电脑和Tom进行猜拳
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Homework14{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tom tom = new Tom();
tom.times = 3;
int sum = tom.Game();
}
}
class Tom{
/*
思路分析:
石头 0, 剪刀 1, 布 2
属性,出一个数
方法:可以跟电脑猜拳,并显示Tom输赢次数
*/
int guessTom;
int times;
public int Game(){
Scanner myScanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int count = 0;
for(int i=0; i< times; i++){
int guessComputer = (int)(Math.random() * 3);
System.out.println("请输入Tom的值");
int guessTom = myScanner.nextInt();
if(guessTom == guessComputer){
System.out.println(i + "次平手");
continue;
}
else if (guessTom == 0 && guessComputer == 1 || guessTom == 1 && guessComputer ==2 || guessTom == 2 && guessComputer == 0){
count+=1;
System.out.println(i +"次\tTom赢了" + "电脑出的" + guessComputer + "Tom出的" + guessTom);
}
else{
System.out.println(i+ "Tom输了");
}
}
return count;
}
}