一、概念:
一般我们都知道 ArrayList* 由一个数组后推得到的 List。作为一个常规用途的对象容器使用,用于替换原先的 Vector。允许我们快速访问元素,但在从列表中部插入和删除元素时,速度却嫌稍慢。一般只应该用ListIterator 对一个 ArrayList 进行向前和向后遍历,不要用它删除和插入元素;与 LinkedList 相比,它的效率要低许多LinkedList 提供优化的顺序访问性能,同时可以高效率地在列表中部进行插入和删除操作。但在进行随机访问时,速度却相当慢,此时应换用 ArrayList。
二、测试
本来自己写了一些测试类想测试下 ArrayList 和 LinkedList 的性能比较,发现怎么写都差强人意,今天在《Thinking in Java》中看到了这样的一段代码,个人觉得写得不赖。
public class ListPerformance { private static final int REPS = 100; private abstract static class Tester//内部抽象类,作为List测试。 { String name; int size; Tester(String name, int size) { this.name = name; this.size = size; } abstract void test(List a); } private static Tester[] tests = {new Tester("get", 300)//一个测试数组,存储get(随机取)、iteration(顺序遍历)、insert(中间插入)、remove(随机删除) { void test(List a) { for (int i = 0; i < REPS; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < a.size(); j++) { a.get(j); } } } }, new Tester("iteration", 300) { void test(List a) { for (int i = 0; i < REPS; i++) { Iterator it = a.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) it.next(); } } }, new Tester("insert", 1000) { void test(List a) { int half = a.size() / 2; String s = "test"; ListIterator it = a.listIterator(half); for (int i = 0; i < size * 10; i++) { it.add(s); } } }, new Tester("remove", 5000) { void test(List a) { ListIterator it = a.listIterator(3); while (it.hasNext()) { it.next(); it.remove(); } } }, }; public static void test(List a) { System.out.println("Testing " + a.getClass().getName());//输出测试的类名称 for (int i = 0; i < tests.length; i++) { fill(a, tests[i].size);//填充空集合 System.out.print(tests[i].name); long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); tests[i].test(a);//进行测试 long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.print(":" + (t2 - t1)+" ms "); } } public static Collection fill(Collection c, int size) { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { c.add(Integer.toString(i)); } return c; } public static void main(String[] args) { test(new ArrayList()); System.out.println(); test(new LinkedList()); } }
三、总结
首先,真的夸一下,这段代码写得真是好啊,无论是内部类的应用还是对面向对象的认识,都考虑的恰到好处,用到了设计模式中的模板方法模式。
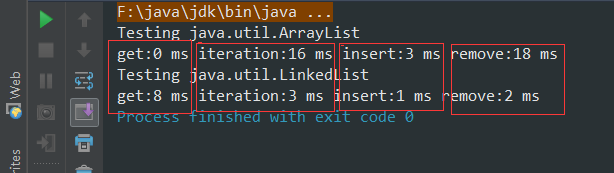
测试结果每次都有些许的差异,但不难得出以下的结论:
1、在 ArrayList 中进行随机访问(即 get())以及循环反复是最划得来的 。原因在于,ArrayList是基于数组而来的,所以每个元素都有其对应的index,所以随机定位一个元素要快捷的多。
2、在 LinkedList 中进行顺序访问、插入、删除动作的话还是比较高效的。原因在于,插入、删除的话对于LinkedList来说只需要改变其排列的一个node结点就可以了,而对于ArrayList来说删除一个元素,需要不断把后面的元素移到前面的位置上。
3、至于顺序访问,之前一直认为ArrayList 基于数组排列,在内存中是连续排列的,应该会快得多,然后多次测试发现并不是想象的那样,或者说ArrayList没有表现出它该有的优势,甚至还不如LinkedList的访问速度。原因在于:LinkedList 提供了优化的顺序访问性能。
4、ArrayList 是线程安全的,LinkedList 是线程不安全的。这个原因也导致了我们在平常编程中比较少看到 LinkedList 。