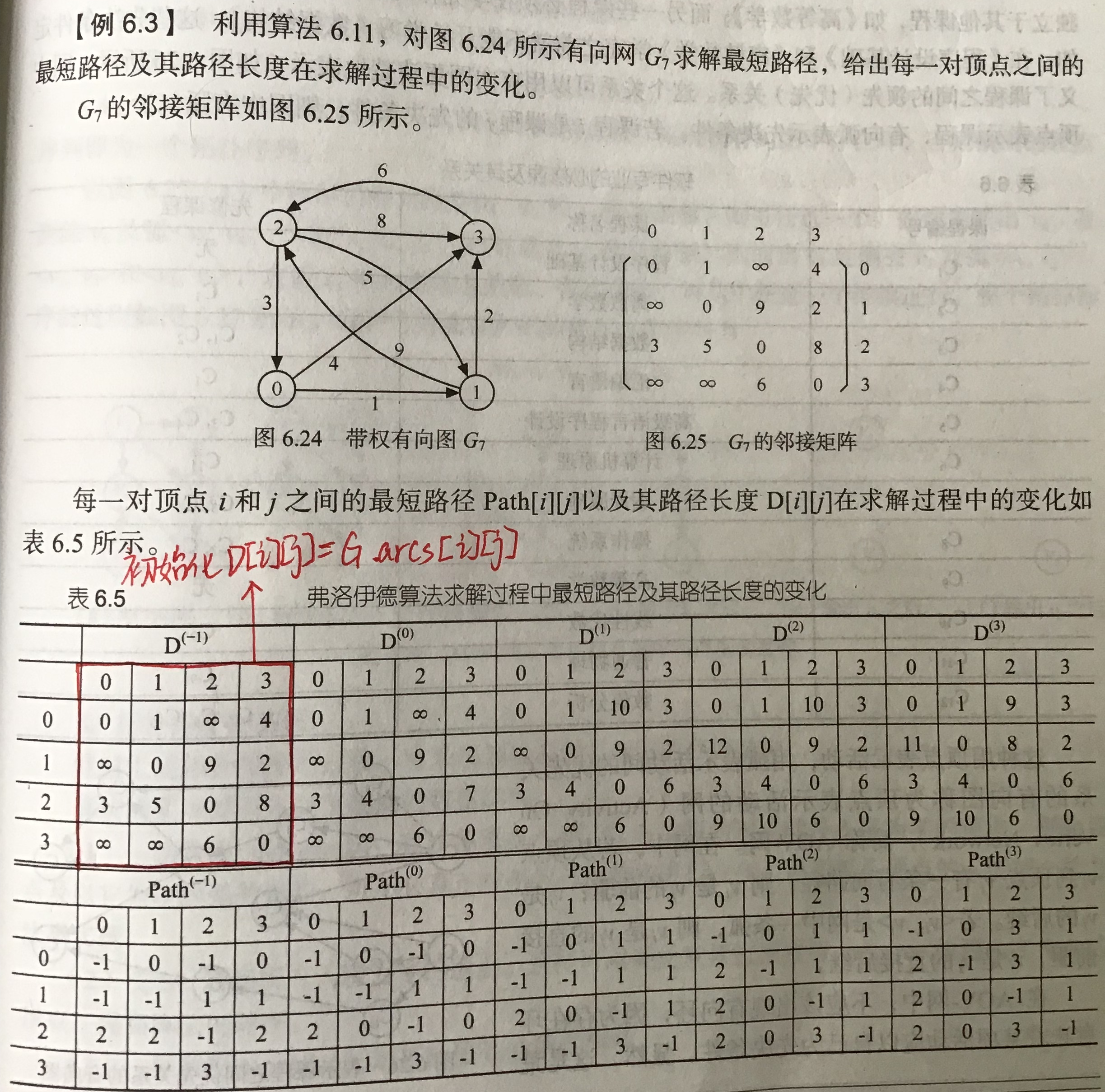
1 Floyd算法
1.1 解决问题/提出背景
- 多源最短路径(带权有向图中,求每一对顶点之间的最短路径)
- 方案一:弗洛伊德(Floyd算法)算法
- 方案二:分别以图中的每个顶点为源点,共调用【n次】【迪杰斯特拉(Dijkstra)算法】
- 算法思想:贪心算法
- 时间复杂度:O(n^3)
- 补充
- Dijkstra算法主要应用于:求解【单源最短路径】
1.2 算法描述
1.3 编程复现
- 1> 定义图模型(邻接矩阵表示法)的基本存储结构体
# define MaxInt 32767 // 表示极大值 即 ∞ (无穷大)
# define MVNum 100 // 最大顶点数
typedef int VertexType; // 假设顶点的数据类型为整型
typedef int ArcType; // 假设Vi与Vj之边的权值类型为整型
typedef struct {
VertexType vexs[MVNum]; // 顶点表 (存储顶点信息)
ArcType arcs[MVNum][MVNum]; // 邻接矩阵
int vexnum,arcnum; // 图的当前顶点数与边数
}AMGraph; // Adjacent Matrix Graph 邻接矩阵图
ArcType D[MVNum][MVNum]; // 记录顶点Vi和Vj之间的最短路径长度
int Path[MVNum][MVNum]; // 最短路径上顶点Vj的前一顶点的序号
void InitAMGraph(AMGraph &G){
cout<<"Please Input Vertexs Number:";
cin>>G.vexnum;
cout<<"
Please Directed Edge Number:";
cin>>G.arcnum;
for(int i=0;i<MVNum;i++){
for(int j=0;j<MVNum;j++){
if(i!=j){ // 【易错】 初始化<Vi, Vj>时: <Vi,Vj> 路径长度无穷大 (i!=j)
G.arcs[i][j] = MaxInt;
} else { // 【易错】 初始化<Vi, Vj>时: <Vi,Vi>【自回环】路径长度为0 (i==i)
G.arcs[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++){
G.vexs[i] = i;
}
cout<<"
Please Input All Directed Edges and their Weight now:";
cout<<"
Directed Edges(i,j,weight): "<<endl;
int i,j;
int weight;
for(int k=0;k<G.arcnum;k++){
cin>>i;cin>>j;cin>>weight;
G.arcs[i][j] = weight;
}
cout<<endl;
}
void ShortestPath_Floyd(AMGraph G){
//step1 初始化各对结点的已知路径和距离
for(int i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++){
for(int j=0;j<G.vexnum;j++){
D[i][j] = G.arcs[i][j]; //D[i][j] 初始化
if(D[i][j]<MaxInt && i!=j){ // 【易漏】 i != j (防止产生自回环)
Path[i][j] = i; // 若 Vi与Vj之间存在弧(有序顶点对): 将Vj的前驱置为 Vi
} else {
Path[i][j] = -1;
}
}
}
//step2 动态规划(DP)动态更新: <Vi,Vj>更短的最短路径的距离和路径
for(int k=0;k<G.vexnum;k++){ // 【易错】 中间结点Vk的循环 是在最外层
for(int i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++){
for(int j=0;j<G.vexnum;j++){
if(D[i][k] + D[k][j] < D[i][j]){ // 若从Vi【经Vk】到Vj的一条路径更短
D[i][j] = D[i][k] + D[k][j]; // 更新D[i][j]
Path[i][j] = Path[k][j]; // 【易错】 更改Vj的前驱为 Vk
}
}
}
}
}
- 5> 输出结果 D[i][j] 、Path[i][j]
- 二维数组D[i][j]【最短路径长度】、二维数组Path[i][j]【最短路径权重】
void OutputD(AMGraph G){
cout<<"Shortest Distance Weight of the Pair of Directed Vertices:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++){
for(int j=0;j<G.vexnum;j++){
cout<<D[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
void OutputPath(AMGraph G){
cout<<"Shortest Distance Path(i,j) of the Pair of Directed Vertices:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++){
for(int j=0;j<G.vexnum;j++){
cout<<Path[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
int main(){
AMGraph G;
InitAMGraph(G);//易错处
ShortestPath_Floyd(G); // 【重/难点】易错处
OutputD(G);
OutputPath(G);
return 0;
}
Please Input Vertexs Number:4
Please Directed Edge Number:8
Please Input All Directed Edges and their Weight now:
Directed Edges(i,j,weight):
0 1 1
1 3 2
2 0 3
0 3 4
2 1 5
3 2 6
2 3 8
1 2 9
Shortest Distance Weight of the Pair of Directed Vertices:
0 1 9 3
11 0 8 2
3 4 0 6
9 10 6 0
Shortest Distance Path(i,j) of the Pair of Directed Vertices:
-1 0 3 1
2 -1 3 1
2 0 -1 1
2 0 3 -1
2 参考文献
- 《数据结构(C语言版/ 严蔚敏 李冬梅 吴伟民 编)》