C#数组,索引器与集合
数组
数组是具有索引的同类型对象的集合。
声明数组
类型[] 数组名;
[]会告诉编译器,这是声明了一个数组,类型指定了数组包含的元素的类型。
可以用new关键字来实例化数组。
默认值
值类型数组,每个元素默认是所存类型的默认值;引用类型不能初始化为默认值,而是初始化为null。
class Person
{
}
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
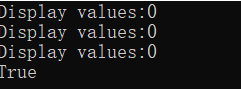
int[] myIntArray = new int[3];
Person[] myPersons = new Person[3];
DisplayVals(myIntArray);
Console.WriteLine(myPersons[0] == null);
}
public static void DisplayVals(params int[] intValues)
{
foreach (var i in intValues)
{
Console.WriteLine("Display values:{0}", i);
}
}
}
params关键字
以下代码中,DisplayVals只接受整数数组:
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
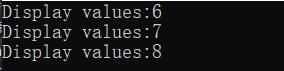
int[] explicitArray = new int[3] { 6, 7, 8 };
DisplayVals(explicitArray);
}
public static void DisplayVals(int[] intValues)
{
foreach (var i in intValues)
{
Console.WriteLine("Display values:{0}", i);
}
}
}
而使用params关键字,就不必显式地创建数组再传入可变数用的参数:
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
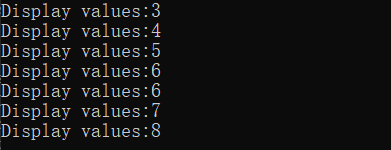
DisplayVals(3, 4, 5, 6);
int[] explicitArray = new int[3] { 6, 7, 8 };
DisplayVals(explicitArray);
}
public static void DisplayVals(params int[] intValues)
{
foreach (var i in intValues)
{
Console.WriteLine("Display values:{0}", i);
}
}
}
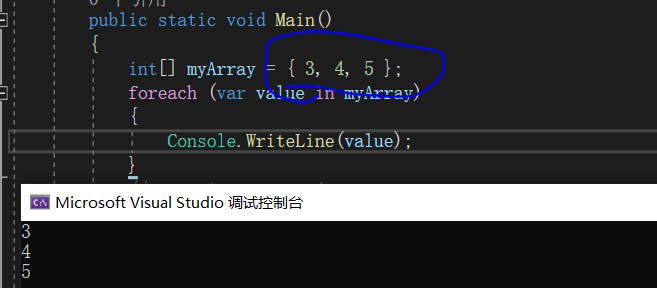
一维数组的初始化
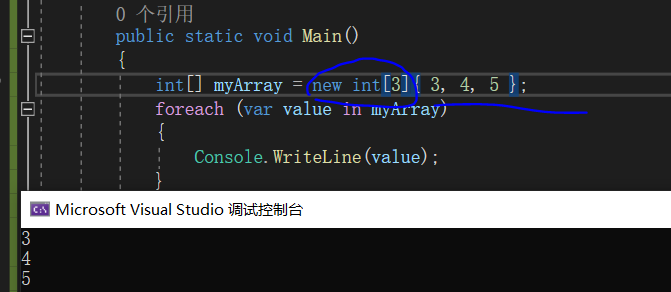
多维数组
- 规则数组
规则数组是指两维或多维的数组,在经典的二维数组中,第一维是行数,第二维是列数。
声明语法如下:
类型[,] 数组名;
public static void Main()
{
const int rows = 4;
const int columns = 3;
int[,] regularArray = new int[rows, columns];
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < columns; j++)
{
regularArray[i, j] = i + j;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
for (int j=0; j < columns; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"regularArray[{i},{j}]:{regularArray[i, j]}");
}
}
}
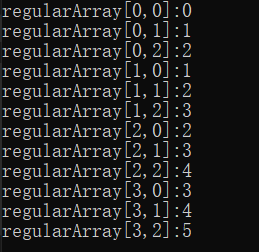
int[,]表明这是二维整数数组,实例实现是new int[rows,columns]。
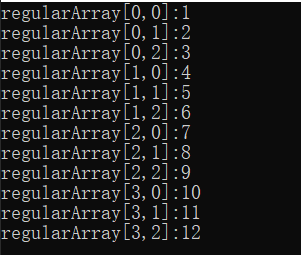
正如可以用一系列大括号的值来初始化一维数组,对二维数组也可以用相似的语法来初始化:
public static void Main()
{
const int rows = 4;
const int columns = 3;
int[,] regularArray = new int[rows, columns]
{
{1,2,3 },
{4,5,6 },
{7,8,9 },
{10,11,12 }
};
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < columns; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"regularArray[{i},{j}]:{regularArray[i, j]}");
}
}
}
public static void Main()
{
const int rows = 4;
const int columns = 3;
int[,] regularArray =
{
{1,2,3 },
{4,5,6 },
{7,8,9 },
{10,11,12 }
};
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < columns; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"regularArray[{i},{j}]:{regularArray[i, j]}");
}
}
}
以上两种方法。
- 不规则数组
由数组组成的数组称为不规则的数组,因为每行不必和其他的大小一致,因此它的几何表示将不是矩形。
声明语法:
类型[][]...
中括号的数量代表了维数。
这点与规则数组不一样,同样地,访问数组元素也是[][]的形式来访问。
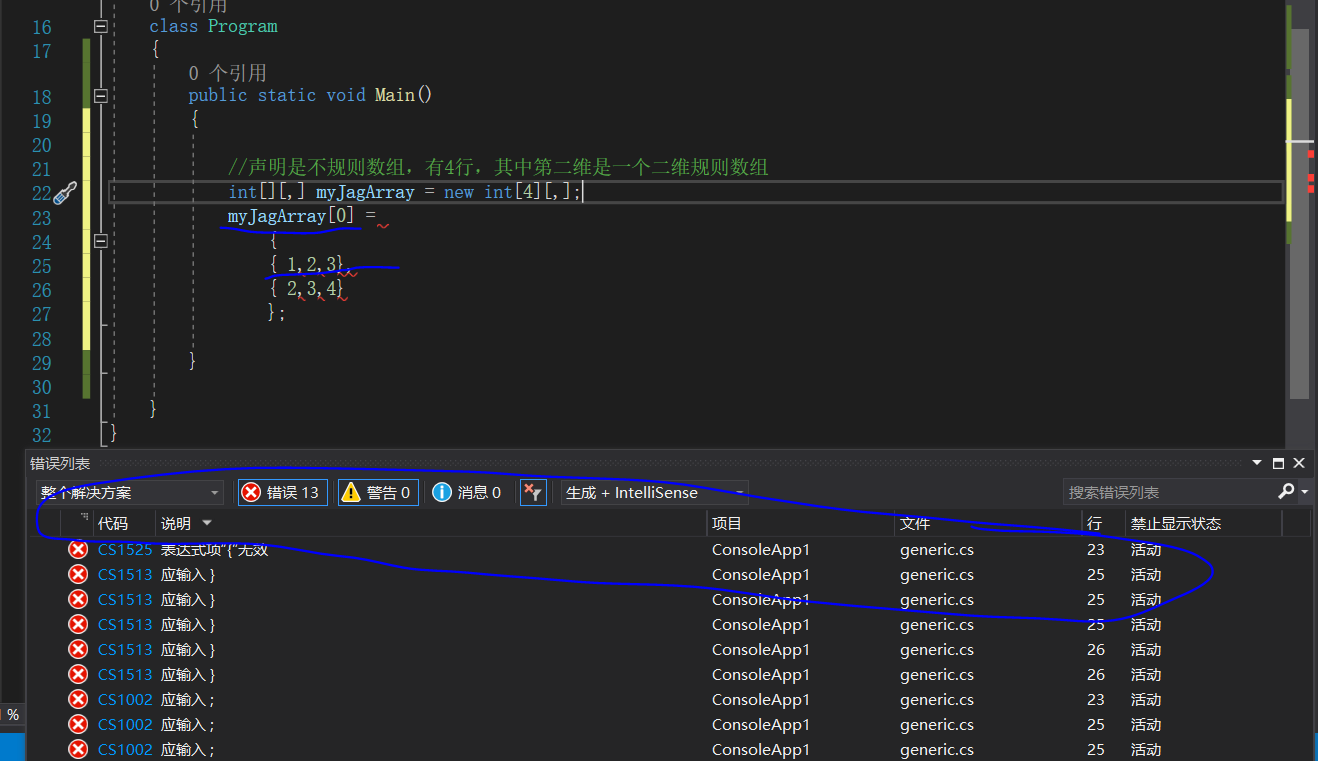
public static void Main() { //声明是不规则数组,有4行,其中第二维是一个二维规则数组 int[][,] myJagArray = new int[3][,]; //因为是不规则数组,所以对于其子数组的规模而言,都是不确定的,所以必须要用new int[,]或者new int[2,3]来实例化,使用简单的初始化是非法的 myJagArray[0] = new int[,] { { 1,2,3}, { 2,3,4} }; myJagArray[1] = new int[,] { {2,3 }, {4,5 }, }; myJagArray[2] = new int[,] { {1,2,3,4 } }; for (int i = 0; i < myJagArray.GetLength(0); i++)//myJagArray的第一维的长度 { for (int j = 0; j < myJagArray[i].GetLength(0); j++)//myJagArray[0]的第一维的长度 { for(int k = 0; k < myJagArray[i].GetLength(1); k++) { Console.WriteLine($"myJagArray[i][j,k] is {myJagArray[i][j, k]}"); } } } } }
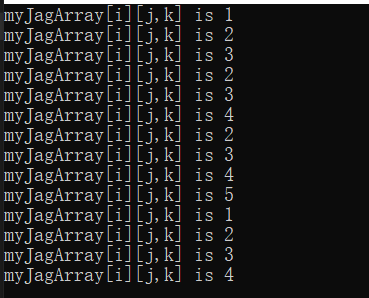
- 初始化快捷语法
int[] arr1=new int[3]{10,20,30};//传统的方法
int[] arr1={10,20,30};
- 隐式类型数组
int[] intArr1=new int[]{1,2,3,4};//传统
var intArr1=new []{1,2,3,4};//隐式类型数组,从初始化推断出是int[]
- 误区
var intArr1={1,2,3,4};//错误;推断不出来类型
Array类
用方括号声明数组是C#使用Array的表示法,在后台使用C#语法,会创建一个派生自抽象基类Array的新类,就可以使用Array类为每个C#数组定义的方法和属性了,比如使用Length或者foreach,实际上是使用了Array类的GetEnumerator()方法。
- 创建数组
Array intArray = Array.CreateInstance(typeof(int), 5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
intArray.SetValue(i * 2, i);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(intArray.GetValue(i));
}

还可以将已创建的数组强制转换为声明为int[]的数组:
int[] intArray2 = (int[])intArray;
class Program
{
public static void CreateArrayWithBounds()
{
int[] lengthsArray = new int[2] { 3, 5 };
int[] boundsArray = new int[2] { 2, 3 };
Array multiDimensionalArray = Array.CreateInstance(
typeof(string),
lengthsArray,
boundsArray); //3行5列,行数从2开始,列数从3开始
Console.WriteLine("Bounds: Lower Upper");
for (int i = 0; i < multiDimensionalArray.Rank; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(
"{0}: {1} {2}",i, multiDimensionalArray.GetLowerBound(i), multiDimensionalArray.GetUpperBound(i));
}
Console.WriteLine("***********************");
//赋值
for (int i = multiDimensionalArray.GetLowerBound(0); i <= multiDimensionalArray.GetUpperBound(0); i++)
{
for (int j = multiDimensionalArray.GetLowerBound(1); j <= multiDimensionalArray.GetUpperBound(1); j++)
{
int[] indexs = new int[2] { i, j }; //multiDimensionalArray的索引数组
multiDimensionalArray.SetValue(i.ToString() + j, indexs);
}
}
PrintValue(multiDimensionalArray);
}
public static void PrintValue(Array myArray)
{
var enumator = myArray.GetEnumerator();
var cols = myArray.GetLength(myArray.Rank - 1);//获取列数
int i = 0;
while (enumator.MoveNext()) //不断的往下读取数字,直到最后一个,返回false,结束while语句
{
if (i < cols)
{
i++;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(); //超过列数,进入下一行,从头计数
i = 1;
}
Console.Write("{0} ", enumator.Current);
}
}
public static void Main()
{
CreateArrayWithBounds();
}
}
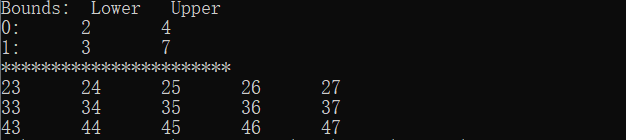
- 复制数组
数组实现了ICloneable接口,这个接口定义的Clone方法会创建数组的浅表副本。
如果数组的元素是值类型,就复制数组中元素的值,如果元素是引用类型,则不复制元素,复制元素的引用:
int[] intArray1 = { 1, 2 };
int[] intArray2 = (int[])intArray1.Clone();
Console.WriteLine(object.ReferenceEquals(intArray2, intArray1));
Console.WriteLine(object.ReferenceEquals(intArray2[0],intArray1[0]));
test[] test1 = { new test(),new test() };
var test2 =(test[]) test1.Clone();
Console.WriteLine(object.ReferenceEquals(test1, test2));
Console.WriteLine(object.ReferenceEquals(test1[0],test2[0]));

Copy有几个重载函数:
//从第一个元素开始复制Array中的一系列元素,将它们粘贴到另一Array中(从第一个元素开始)。长度为32位整数
public static void Copy(Array sourceArray, Array destinationArray, int length)
//从第一个元素开始复制Array中的一系列元素,将它们粘贴到另一Array中(从第一个元素开始)。长度为64位整数
public static void Copy(Array sourceArray, Array destinationArray, long length)
//从指定的源索引开始,复制Array中的一系列元素,将它们粘贴到另一Array中(从指定的目标索引开始)。长度和索引指定为32位整数
public static void Copy(Array sourceArray, int sourceIndex,Array destinationArray, int destinationIndex,int length)
//从指定的源索引开始,复制Array中的一系列元素,将它们粘贴到另一Array中(从指定的目标索引开始)。长度和索引指定为64位整数
public static void Copy(Array sourceArray, long sourceIndex,Array destinationArray, long destinationIndex,long length)
例:
Array myIntArray=Array.CreateInstance( typeof(System.Int32), 5 );
for ( int i = myIntArray.GetLowerBound(0); i <= myIntArray.GetUpperBound(0); i++ )
{myIntArray.SetValue( i+1, i );}
Array myObjArray = Array.CreateInstance( typeof(System.Object), 5 );
for ( int i = myObjArray.GetLowerBound(0); i <= myObjArray.GetUpperBound(0); i++ )
{myObjArray.SetValue( i+26, i );}
// Copies the first element from the Int32 array to the Object array.
Array.Copy( myIntArray, myIntArray.GetLowerBound(0), myObjArray, myObjArray.GetLowerBound(0), 1 );
// Copies the last two elements from the Object array to the Int32 array.
Array.Copy( myObjArray, myObjArray.GetUpperBound(0) - 1, myIntArray, myIntArray.GetUpperBound(0) - 1, 2 );
区别:
Clone()返回值是Object,Copy返回值为void
Clone()是非静态方法,Copy为静态方法。
Clone()会创建一个新数组,Copy方法必须传递阶数相同且有足够元素的已有数组。
int[] intArray1 = { 1, 2,3,4 };
int[] intArray2 = new int[6] { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
Array.Copy(intArray1, 1, intArray2, 3, 3);
foreach(var a in intArray2)
{
Console.Write(a+",");
}

int[] intArray1 = { 1, 2,3,4 };
int[] intArray2 = new int[6] { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
intArray1.CopyTo(intArray2, 1);
foreach(var a in intArray2)
{
Console.Write(a+",");
}
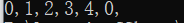
如果需要包含引用类型的数组的深层副本,就必须迭代数组并创建新对象。
- 搜索
在一维数组中,Array类提供了一系列的方法来找元素。
(1)BinarySearch:对于有序数组,迅速的搜索一个特定的元素
(2)IndexOf/LastIndex:对于无序数组,搜索特定元素
(3)Find/FindLast/FindIndex/FindLastIndex/FindAll/Exists/TruForAll:对于无序数组,搜索满足给定条件Predicate<T>的元素,其中Predicate<T>是一个委托,接受一个object,返回true,或false.
public delegate bool Predicate<T>(T object)
以上搜索方法都不会抛出异常,如果没找到,对于返回类型是int的,就返回-1。发返回泛型的方法返回的是默认类型。
string[] names = { "Rodney", "Jack", "jill" };
string match = Array.Find(names, n => n.Contains("a"));
Console.WriteLine(match);
或
string[] names = { "Rodney", "Jack", "jill" };
string match = Array.Find(names, delegate(string name) { return name.Contains("a"); });
Console.WriteLine(match);
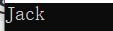
Sort
(1)对单个数组排序
public static void Sort<T> (T[] array);
public static void Sort(Array array);
(2)对一对数组排序
public static void Sort<Tkey,TValue>(Tkeyy[] keys,TValue[] items);
public static void Sort(Array keys,Array items);
例子:
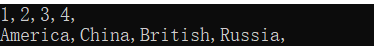
int[] num = { 2, 1, 4,3};
string[] words = { "China", "America", "Russia", "British" };
Array.Sort(num, words);
foreach(var s in num)
{
Console.Write("{0},", s);
}
Console.WriteLine();
foreach(var s in words)
{
Console.Write("{0},", s);
}
- Copy
四个浅层拷贝:Clone,CopyTo,Copy,ConstrainedCopy,其中前两个是实例方法,后两个是静态方法。
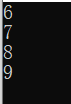
对于拷贝多维数组,需要将多维数组的索引转换为一个线性的索引,比如33的数组,其中心位置,postion[1,1]的索引就是13+1=4.
int[,] a=
{
{1,2,3 },
{4,5,6 },
{7,8,9 }
};
int[,] b = new int[2,2];
Array.Copy(a,5,b,0,4);
foreach(var s in b)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
ConstraintedCopy是一种原子操作:如果所有元素不能成功的拷贝,那么该操作就一个都不操作,回滚到之前的状态。
int[,] a=
{
{1,2,3 },
{4,5,6 },
{7,8,9 }
};
int[,] b = new int[2,2];
Array.ConstrainedCopy(a, 5, b,0, 4);
foreach(var s in b)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
}

Convert And Resize
Array.ConvertAll创建和返回了TOutput类型的数组,调用了Converter委托,来沿着元素全部复制转换,其中Converter定义如下:
public delegate TOutput Converter<IIput,TOutput>(TInput input);
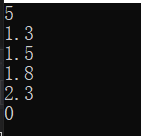
float[] reals = { 1.3f, 1.5f, 1.8f };
int[] wholes = Array.ConvertAll(reals, r => Convert.ToInt32(r));
foreach(var s in wholes)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
}

float[] reals = { 1.3f, 1.5f, 1.8f,2.3f };
Array.Resize(ref reals, 5);
Console.WriteLine(reals.Length);
foreach(var s in reals)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
ArraySegment<T>
ArraySegment<T>是结构类型(struct),表示数组的一段,如果需要使用不同的方法来处理某个大型数组的不同部分,可以将整个数组传给不同的方法,这些方法只使用数组的某个部分。方法的参数除了数组外,还应包括数组内的偏移量和应使用的元素数。
class Program
{
public static int SumOfSegments(ArraySegment<int>[] segments)
{
int sum = 0;
foreach(var segment in segments)
{
for(int i = segment.Offset; i < segment.Offset + segment.Count; i++)
{
sum += segment.Array[i];
segment.Array[i] -= 1;//数组段不复制数组元素,如果数组段中的元素改变了,这些变化就会反映到原数组中
}
}
return sum;
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr1 = { 1, 4, 5, 11, 13, 18 };
int[] arr2 = { 3, 4, 5, 18, 21, 27, 33 };
var segments = new ArraySegment<int>[2]
{
new ArraySegment<int>(arr1,0,3),
new ArraySegment<int>(arr2,3,3)
};
var sum = SumOfSegments(segments);
Console.WriteLine(sum);
foreach(var a in arr1)
{
Console.WriteLine(a);
}
}
}
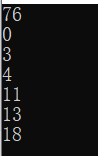
class Program
{
public static void change(ArraySegment<int> b)
{
b.Array[b.Offset] = 100;
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] a = { 1, 2, 3,4 };
ArraySegment<int> b = new ArraySegment<int>(a, 1, 2);
change(b);
Console.WriteLine(a[1]);
}
}

上例表明,ArraySegment虽然是结构,但是传入其中的数组,被修改时,即被修改,因为数组本身就是引用类型。
本质上与下例相似:
public struct a
{
public b bb;
}
public class b
{
public int x;
}
class Program
{
public static void change(a aa)
{
aa.bb.x = 100;
}
public static void Main()
{
var c = new a();
c.bb = new b();
change(c);
Console.WriteLine(c.bb.x);
}
}

数组转换
如果维数相同,且引用元素类型之间可以转换,那么可以进行数组间的转换。如果元素类型可以隐式转换,则可以进行隐式转换,否则,必须进行显式转换。
class Program
{
public class Employee
{
private int empID;
public Employee(int empID)
{
this.empID = empID;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return empID.ToString();
}
}
public class Tester
{
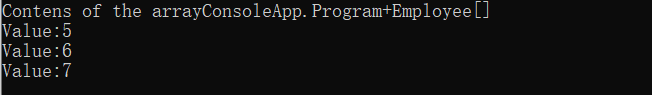
public static void PrintArray(object[] theArray)
{
Console.WriteLine("Contens of the array{0}", theArray.ToString());
foreach(var obj in theArray)
{
Console.WriteLine("Value:{0}", obj);
}
}
}
public static void Main()
{
Employee[] myArray = new Employee[3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
myArray[i] = new Employee(i + 5);
}
Tester.PrintArray(myArray);//将myArray隐式转换为object[]类型,因为employee可隐式转换为object
}
}
索引器
索引器是类的成员,它能使类看起来像某种数组,可以用来索引类中的数据。
语法:
类型 this[类型 参数]{get;set;}
第一个类型当然是返回类型,第二个类型,参数是索引的类型和参数,它和属性非常像,都有set和get访问器,this是对索引器所指对象的引用。
public class ListBoxText
{
private int ctr = 0;
private string[] strings;
public int GetNumEntries()
{
return ctr;
}
public ListBoxText(params string[] initialStrings)
{
strings = new string[256];
foreach(var s in initialStrings)
{
strings[ctr++] = s;
}
}
public void Add(string theString)
{
if (ctr >= strings.Length)
{
Console.WriteLine("已经满了...");
}
else
{
strings[ctr++] = theString;
}
}
public string this[int index]
{
get
{
if (index<0|| index > strings.Length)
{
Console.WriteLine("索引{0}不对", index);
}
return strings[index];
}
set
{
if (index >= ctr)
{
Console.WriteLine("只能Add增加,索引只能更改已经有的数据");
}
else
{
strings[index] = value;
}
}
}
}
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
var lbt = new ListBoxText("Hello", "world");
lbt.Add("Who");
lbt.Add("is");
lbt.Add("John Yang");
for (int i = 0; i < lbt.GetNumEntries(); i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"lbt[{i}]:{lbt[i]}");
}
}
}

索引其他值
C#并不要求我们必须使用整数作为集合的索引,索引值其实可以重载。
public class ListBoxText
{
private int ctr = 0;
private string[] strings;
public int GetNumEntries()
{
return ctr;
}
public ListBoxText(params string[] initialStrings)
{
strings = new string[256];
foreach(var s in initialStrings)
{
strings[ctr++] = s;
}
}
public void Add(string theString)
{
if (ctr >= strings.Length)
{
Console.WriteLine("已经满了...");
}
else
{
strings[ctr++] = theString;
}
}
public string this[int index]
{
get
{
if (index<0|| index > strings.Length)
{
Console.WriteLine("索引{0}不对", index);
}
return strings[index];
}
set
{
if (index >= ctr)
{
Console.WriteLine("只能Add增加,索引只能更改已经有的数据");
}
else
{
strings[index] = value;
}
}
}
private int findString(string searchString)
{
for (int i = 0; i < ctr; i++)
{
if (strings[i].StartsWith(searchString))
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//重载索引器
public string this[string index]
{
get
{
if (index.Length == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("请输入要搜索的字符串");
return "Null";
}
var locater = findString(index);
if (locater == -1)
{
return "Null";
}
return this[locater];
}
set
{
var locater = findString(index);
if (locater == -1)
{
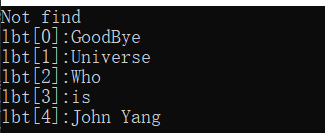
Console.WriteLine("Not find");
}
else
{
strings[locater] = value;
}
}
}
}
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
var lbt = new ListBoxText("Hello", "world");
lbt.Add("Who");
lbt.Add("is");
lbt.Add("John Yang");
lbt[1] = "Universe";
lbt["Hel"] = "GoodBye";
lbt["yang"]="jsfdk" ;
for (int i = 0; i < lbt.GetNumEntries(); i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"lbt[{i}]:{lbt[i]}");
}
}
}

集合接口
| 接口 | 目的 |
|---|---|
| ICollection |
泛型集合的基接口,the Count property |
| IEnumerator |
用foreach语句枚举集合,enumeration only |
| ICollection |
所有集合都要实现,以提供CopyTo()方法,以及Count,IsSynchronized和SynRoot属性 |
| IComparer |
比较集合中的两个对象以对集合排序 |
| IList |
用于数组可索引的集合,random access by index |
| IDictionary<K,V> | 用于基于键值对的集合,如Dictionary,random access by key |
ICollection<T> 和ICollection
public interface ICollection<T>:IEnumerable<T>,IEnumerable
{
int Count{get;}
bool Contains(T item);//查
void CopyTo(T[] array,int arrayIndex);
bool IsReadOnly{get;};
void Add(T item);//增
bool Remove(T item);//删
void Clear();//删
}
public interface ICollection:IEnumerable
{
int Count{get;}
bool IsSynchronized{get;}
object SynRoot{get;}
void CopyTo(Array array,int index);
}
如果ICollection是read-only的(ReadOnlyCollection),那么Add,Remove,Clear都会抛出NotSupportedException异常.
这些接口经常与IList或者IDictionary接口一起联合使用。
定制集合和代理(Customizable collections and proxies)
定义的集合虽然可以快速实例化使用,但它们不能控制当元素被添加或者移除后所触发的事情。有时候,我们可能会需要这种控制:
- 当元素被添加/删除所触发的事件
- 因为增加的/删除的元素,而更新属性
- 监测增加/删除的”合法性“,如果”非法“,则抛出异常
.NET Framework在System.Collections.ObjectModel中提供了这种目的的集合类。
Collection<T>和CollectionBase
Collection<T>是对List<T>的可定制化的包装。
public class Collection<T>:
IList<T>,ICollection<T>,IEnumerable<T>,IList,ICollection,IEnumerable
{
protected virtual void ClearItems();//删
protected virtual void InsertItem(int index,T item);//增
protected virtual void RemoveItem(int index);//删
protected virtual void SetItem(int index,T item);//改
protected IListt<T> Items{get;}//查
}
这些虚方法提供了你可以改变或者提升列表的正常行为的方法,protected意味着它的实例不能对这些方法进行使用,只能由其派生类使用这些方法。
这些虚方法不需要被覆盖,直到有必要去改变列表的默认行为。下面例子展示了其典型应用的构架:
public class Animal
{
public string Name;
public int Popularity;
public Animal(string name,int popularity)
{
Name = name;
Popularity = popularity;
}
}
public class AnimalCollection : Collection<Animal>
{
//AnimalCollection is already a fully functioning list of animals
//no extra code is required.
}
public class Zoo
{
public readonly AnimalCollection Animals = new AnimalCollection();
}
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
Zoo zoo = new Zoo();
zoo.Animals.Add(new Animal("Kangaroo", 10));
zoo.Animals.Add(new Animal("Tiger", 20));
foreach (var a in zoo.Animals) Console.WriteLine(a.Name);
}
}
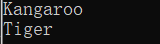
正如上例所示,AnimalCollection所起的作用与简单的List<Animal>一样,但它却为将来的功能延申提供了基础。
public class Animal
{
public string Name;
public int Popularity;
public Zoo Zoo { get; internal set; }
public Animal(string name,int popularity)
{
Name = name;
Popularity = popularity;
}
}
public class AnimalCollection : Collection<Animal>
{
Zoo zoo;
public AnimalCollection(Zoo zoo) { this.zoo = zoo; }
protected override void InsertItem(int index, Animal item)
{
base.InsertItem(index, item);
item.Zoo = zoo;
Console.WriteLine("Index {0} insert Item {1}", index, item.Name);
}
protected override void SetItem(int index, Animal item)
{
base.SetItem(index, item);
item.Zoo = zoo;
Console.WriteLine("Index {0} has been reset as {1}", index, item.Name);
}
protected override void RemoveItem(int index)
{
this[index].Zoo = null;
Console.WriteLine("index {0} has been removed", index);
base.RemoveItem(index);
}
protected override void ClearItems()
{
foreach (var a in this) a.Zoo = null;
base.ClearItems();
Console.WriteLine("All has been removed now...");
}
}
public class Zoo
{
public readonly AnimalCollection Animals;
public Zoo() { Animals = new AnimalCollection(this); }
}
class Program
{
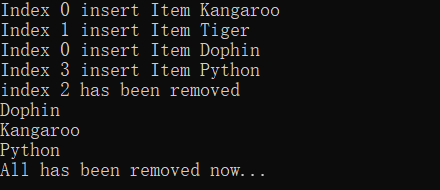
public static void Main()
{
Zoo zoo = new Zoo();
zoo.Animals.Add(new Animal("Kangaroo", 10));
zoo.Animals.Add(new Animal("Tiger", 20));
zoo.Animals.Insert(0, new Animal("Dophin", 23));
zoo.Animals.Add(new Animal("Python", 25));
zoo.Animals.RemoveAt(2);
foreach (var a in zoo.Animals) Console.WriteLine(a.Name);
zoo.Animals.Clear();
}
}
CollectionBase
CollectionBase是Collection<T>的非泛型版本,它也有Collection<T>的特定,但使用更加臃肿,它没有InsertItem,RemoveItem,SetItem,ClearItem方法,取而代之的是OnInsert,OnInsertComplete,OnClear,OnClearComplete。
KeyedCollection<TKey,TItem>和DictionaryBase
可以认为KeyedCollection<TKey,TItem>是Collection<TItem>加上通过键快速查找。
与字典不同的是,它并没有”键-值对“的概念,它的键是从存储元素自身里获取的:通过抽象方法GetKeyForItem实现的(注意抽象方法必须被派生类override而实现,除非派生类本身也是抽象类)
public abstractt class KeyedCollection<TKey,TItem>:Collection<TItem>
{
//...
protected abstract TKey GetKeyForItem(TItem item);//抽象方法,非抽象类派生类必须覆盖之
protected void ChangeItemKey(TItem item,TKey newKey);
//Fast lookup by key--this is in addition to lookup by index.
public TItem this[TKey key]{get;}
protected IDictionary<TKey,TItem> Dictionary{get;}
}
GetKeyForItem作为抽象方法,是非抽象派生类所必须覆写的方法,其作用就是从加入的元素里抽取出信息,作为该元素的”键“。ChangeItemKey方法在元素的键被改变时候,必须被调用,以此来更新它的内部字典。而内部字典是由Dictionary只读属性维护的,当第一个元素被添加,内部字典就被创建。
KeyedCollection<TKey,TItem>的应用场景就是可以通过索引和”键“来对集合进行访问。
public class Animal
{
string name;
public string Name
{
get { return name; }
set
{
if (Zoo != null) Zoo.Animals.NotifyNameChange(this, value);
name = value;
}
}
public int Popularity;
public Zoo Zoo { get; internal set; }
public Animal(string name,int popularity)
{
Name = name;Popularity = popularity;
}
}
public class AnimalCollection :KeyedCollection<string,Animal>
{
Zoo zoo;
public AnimalCollection(Zoo zoo) { this.zoo = zoo; }
internal void NotifyNameChange(Animal a,string newName)
{
this.ChangeItemKey(a, newName);
Console.WriteLine("{0} has been changed as {1}", a.Name, newName);
}
protected override string GetKeyForItem(Animal item)//当重写时,不能更改其访问修饰符,也就是也必须为protected
{
Console.WriteLine("Get {0}", item.Name);
return item.Name;
}
protected override void InsertItem(int index, Animal item)
{
base.InsertItem(index, item);
item.Zoo = zoo;
Console.WriteLine("Index {0} insert Item {1}", index, item.Name);
}
protected override void SetItem(int index, Animal item)
{
base.SetItem(index, item);
item.Zoo = zoo;
Console.WriteLine("Index {0} has been reset as {1}", index, item.Name);
}
protected override void RemoveItem(int index)
{
this[index].Zoo = null;
Console.WriteLine("index {0} has been removed", index);
base.RemoveItem(index);
}
protected override void ClearItems()
{
foreach (var a in this) a.Zoo = null;
base.ClearItems();
Console.WriteLine("All has been removed now...");
}
}
public class Zoo
{
public readonly AnimalCollection Animals;
public Zoo() { Animals = new AnimalCollection(this); }
}
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
Zoo zoo = new Zoo();
zoo.Animals.Add(new Animal("Kangaroo", 10));
zoo.Animals.Add(new Animal("Mr sea lion", 20));
Console.WriteLine(zoo.Animals[0].Popularity);
Console.WriteLine(zoo.Animals["Kangaroo"].Popularity);
zoo.Animals["Mr sea lion"].Name = "Mr Roo";
Console.WriteLine(zoo.Animals["Mr Roo"].Popularity);
}
}

由上面的例子,可以看出,当添加第一个元素时候,内部字典同时也被创建,并调用GetKeyForItem方法,求得该元素在内部字典中的键,显示的Get Kangroo也佐证了这点,然后紧接着,被添加到内部列表中。再添加第二个元素,同样的,调用GetKeyForItem,求得第二个元素在内部字典中的键,紧接着被加到内部列表中。当被改变元素的”键“时候,这儿是Name属性,就调用ChangeItemKey方法来改变元素的”键“,由于ChangeItemKey是protected,因此实例不能直接访问,需要通过派生类在类内调用,这也是NotifyNameChange出现的原因。
IList<T>和IList
IList<T>是关于在位置上,用索引进行增删查改的接口,它继承了ICollection<T>,和IEnumeratble<T>。
public interface IList<T>:ICollection<T>,IEnumerable<T>,IEnumerable
{
T this[int index]{get;set;}//查,改
void Insert(int index,T item);//增
void RemoveAt(int index);//删
int IndexOf(T item);//查
}
public interface IList:ICollection,IEnumerable
{
object this[int index]{get;set;}
bool IsFixedSize{get;}
bool IsReadOnly{get;}
int Add(object value);
void Clear();
bool Contains(object value);
int IndexOf(object value);
void Insert(int index,object value);
void Remove(object value);
void RemoveAt(int index);
}
List<T>就是既有IList<T>又有ILIst的典型类。
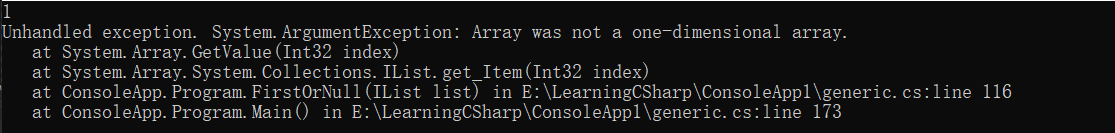
如果试图通过 IList的索引来访问多维数组,那么ArgumentException将会被抛出。
可能会写出这样的代码:
public object FirstOrNull(IList list)
{
if(list==null || list.Count==0) return null;
return list[0];
}
如果传入多维数组,那么就会抛出异常。
var a = new int[,]
{
{1,2,3 },
{3,4,5 }
};
var b = new int[] { 1, 2, 3 };
var c = FirstOrNull(b as IList);
Console.WriteLine(c);
var d = FirstOrNull(a as IList);
Console.WriteLine(d);
public class ListBoxText
{
private int ctr = 0;
private string[] strings;
public int GetNumEntries()
{
return ctr;
}
public ListBoxText(params string[] initialStrings)
{
strings = new string[256];
foreach(var s in initialStrings)
{
strings[ctr++] = s;
}
}
public void Add(string theString)
{
if (ctr >= strings.Length)
{
Console.WriteLine("已经满了...");
}
else
{
strings[ctr++] = theString;
}
}
public string this[int index]
{
get
{
if (index<0|| index > strings.Length)
{
Console.WriteLine("索引{0}不对", index);
}
return strings[index];
}
set
{
if (index >= ctr)
{
Console.WriteLine("只能Add增加,索引只能更改已经有的数据");
}
else
{
strings[index] = value;
}
}
}
private int findString(string searchString)
{
for (int i = 0; i < ctr; i++)
{
if (strings[i].StartsWith(searchString))
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//重载索引器
public string this[string index]
{
get
{
if (index.Length == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("请输入要搜索的字符串");
return "Null";
}
var locater = findString(index);
if (locater == -1)
{
return "Null";
}
return this[locater];
}
set
{
var locater = findString(index);
if (locater == -1)
{
Console.WriteLine("Not find");
}
else
{
strings[locater] = value;
}
}
}
}
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
var lbt = new ListBoxText("Hello", "world");
lbt.Add("Who");
lbt.Add("is");
lbt.Add("John Yang");
lbt[1] = "Universe";
lbt["Hel"] = "GoodBye";
lbt["yang"]="jsfdk" ;
for (int i = 0; i < lbt.GetNumEntries(); i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"lbt[{i}]:{lbt[i]}");
}
}
}
约束
以下面的单链表为例,所谓单链表就是当增加新节点时候,链表自动实现排序;为此,需要定义一个Node类,此类包裹数据,并需要实现IComparable接口,有next,prev字段,保存了它的前一个Node,和后一个Node,然后定义一个Add方法,使得每次调用都返回起始端的Node,这就需要将本节点与Add传入的参数Node作比较,如果传入参数的Node比本节点靠前,那么就要调整相互关系,即调整next,prev字段,返回传入参数的Node,如果传入的参数的Node 比本节点靠后,返回本节点,直接用Add方法操作传入参数的Node,让其找到自己在链表中的合适的位置,即它的后一个节点一定是在它后面,也就是说不再调用Add向后传播。
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Xml.Linq;
namespace ConsoleApp
{
public class Employee : IComparable<Employee>
{
private string name;
public Employee(string name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return this.name;
}
public int CompareTo(Employee rhs)
{
return this.name.CompareTo(rhs.name);
}
public bool Equals(Employee rhs)
{
return this.name == rhs.name;
}
}
public class Node<T>:IComparable<Node<T>>
where T : IComparable<T> //约束,使得T必须实现IComparable接口,从而一定有CompareTo方法
{
private T data;
private Node<T> next = null;
private Node<T> prev = null;
public Node(T data)
{
this.data = data;
}
public T Data { get { return data; } }
public Node<T> Next { get { return this.next; } }
public Node<T> Prev { get { return this.prev; } }
public int CompareTo(Node<T> rhs)
{
return this.data.CompareTo(rhs.data);//data属于类型T,由约束可知,一定有CompareTo方法
}
public bool Equals(Node<T> rhs)
{
return this.data.Equals(rhs.data);
}
public Node<T> Add(Node<T> newNode)
{
if (this.CompareTo(newNode) > 0) //在我之前
{
newNode.next = this;//安插在我前面,首先更改newNode的next,然后根据我的prev有无来做安排
if (this.prev != null) //我之前有结点
{
this.prev.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.prev;
}
this.prev = newNode;
return newNode;
}
else //在我之后
{
if (this.next != null)
{
this.next.Add(newNode);
}
else
{
this.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this;
}
return this;
}
}
public override string ToString()
{
string output = data.ToString();
if (next != null)
{
output += "," + next.ToString();
}
return output;
}
}
public class LinkedList<T>
where T : IComparable<T>
{
private Node<T> headNode = null;
public LinkedList() { }
public void Add(T data)
{
if (headNode == null)
{
headNode = new Node<T>(data);
}
else
{
headNode = headNode.Add(new Node<T>(data));
}
}
public override string ToString()
{
if (this.headNode != null)
{
return this.headNode.ToString();
}
else
{
return string.Empty;
}
}
public T this[int index]
{
get
{
int ctr = 0;
Node<T> node = headNode;
while(node!=null && ctr <= index)
{
if (ctr == index)
{
return node.Data;
}
else
{
node = node.Next;
}
ctr++;
}
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException();
}
}
}
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
var myLinkedList = new LinkedList<int>();
Random rand = new Random();
Console.WriteLine("Adding...");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
int nextInt = rand.Next(10);
myLinkedList.Add(nextInt);
}
Console.WriteLine("integers:" + myLinkedList.ToString());
var employees = new LinkedList<Employee>();
employees.Add(new Employee("John"));
employees.Add(new Employee("Paul"));
employees.Add(new Employee("George"));
employees.Add(new Employee("Ringo"));
employees.Add(new Employee("Ahad"));
Console.WriteLine("Emplyees:" + employees);
Console.WriteLine($"employees[2]:{employees[2]}");
}
}
}

List<T> 和ArrayList
与所有集合一样,List也要实现IComparable接口,从而可以调用Sort方法,其接口要求实现CompareTo(T rhs)方法。当调用Sort方法时,会调用IComparer的默认实现,它会使用QuickSort调用List中每个元素的CompareTo()的IComparable实现。
当要控制排序顺序如何定义时,特别是多种排序定义时候,可以自行创建IComparer实现,它要求实现Compare(T rhs,T lhs)。
- 通过List
中元素T实现 IComparable,向Sort()传入实现IComparer的类进行排序
public class Employee : IComparable<Employee>
{
private int empID;
private int yearsOfSvc;
public Employee(int empID)
{
this.empID = empID;
}
public Employee(int empID,int yearsOfSvc)
{
this.empID = empID;
this.yearsOfSvc = yearsOfSvc;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return "ID:" + empID.ToString()+
".Years of Svc" + yearsOfSvc.ToString();
}
public int CompareTo(Employee rhs, Employee.EmployeeComparer.ComparisonType which) //该方法是EmployeeCompareer类的Compare方法的要求
{
switch (which)
{
case Employee.EmployeeComparer.ComparisonType.EmpID:
return this.empID.CompareTo(rhs.empID);
case Employee.EmployeeComparer.ComparisonType.Yrs:
return this.yearsOfSvc.CompareTo(rhs.yearsOfSvc);
}
return 0;
}
public int CompareTo(Employee rhs) //该方法是IComparable的硬性要求
{
return this.empID.CompareTo(rhs.empID);
}
public static EmployeeComparer GetComparer()
{
return new EmployeeComparer();
}
public class EmployeeComparer : IComparer<Employee>
{
public enum ComparisonType
{
EmpID,
Yrs
};
private ComparisonType whichComparison;
public ComparisonType WhichComparison
{
get { return whichComparison; }
set { whichComparison = value; }
}
public int Compare(Employee rhs,Employee lhs)
{
return rhs.CompareTo(lhs, whichComparison);
}
}
}
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
List<Employee> empArray = new List<Employee>();
Random r = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
empArray.Add(new Employee(r.Next(10) + 100, r.Next(20)));
}
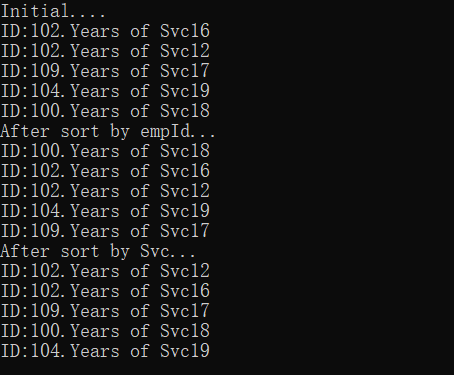
Console.WriteLine("Initial....");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(empArray[i]);
}
var comparer = Employee.GetComparer();//创建EmployeeComparer实例
comparer.WhichComparison = Employee.EmployeeComparer.ComparisonType.EmpID;//为实例的WhichComparison属性赋值
empArray.Sort(comparer);//Sort方法调用,将实现IComparer的comparer实例传入
Console.WriteLine("After sort by empId...");
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(empArray[i]);
}
comparer.WhichComparison = Employee.EmployeeComparer.ComparisonType.Yrs;
empArray.Sort(comparer);
Console.WriteLine("After sort by Svc...");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(empArray[i]);
}
}
}
IComparer,Comparer
Comparer主要用来对有序字典和集合进行排序。需要注意的是,它对无序字典类,如Dictionary和Hashtable来讲是没有什么用的,这些无序字典类主要还是侧重于hashcode。
public interface IComparer
{
int Comparer(object x,object y);
}
public interface IComparer<T>
{
int Comparer(T x,T,y);
}
正如equality comparer一样,也有一个可以用来继承的抽象类,而不是实现这些接口:
public abstract class Comparer<T>:ICompare,ICompare<T>
{
public static Comparer<T> Default{get;}
public abstract int Comparer(T x,T y);//Implemented by you
int IComparer.Compare(object x,object y);//Implemented for you
}
- 通过传入
Sort()继承Comparer<T>的类来实现排序:
class Wish
{
public string Name;
public int Priority;
public Wish(string name,int priority)
{
Name = name;Priority = priority;
}
}
class PriorityComparer : Comparer<Wish>
{
public override int Compare(Wish x, Wish y)
{
if (object.Equals(x, y)) return 0;//保证了不与Equals方法冲突,这里object.Equals
//要比x.Equals方法好,因为它对null仍然有效
return x.Priority.CompareTo(y.Priority);
}
}
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
var wishList = new List<Wish>();
wishList.Add(new Wish("Peace", 2));
wishList.Add(new Wish("Wealth", 3));
wishList.Add(new Wish("Love", 2));
wishList.Add(new Wish("Helth", 1));
wishList.Add(new Wish("3 more wishes", 1));
wishList.Sort(new PriorityComparer());
foreach (var w in wishList) Console.Write(w.Name + " | ");
}
}

class SurnameComparer : Comparer<string>
{
string Normalize(string s)
{
s = s.Trim().ToUpper();
if (s.StartsWith("MC")) s = "MAC" + s.Substring(2);
return s;
}
public override int Compare(string x, string y)
{
return Normalize(x).CompareTo(Normalize(y));
}
}
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
var dic = new SortedDictionary<string, string>(new SurnameComparer());
dic.Add("MacPhail", "second");
dic.Add("MacWilliam", "third");
dic.Add("McDonald", "first");
foreach (var s in dic.Values)
Console.Write(s + " ");
}
}

- 传入
Sort()委托j进行排序:
public class b
{
public int x;
public b(int x)
{
this.x = x;
}
}
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
var c = new List<b>()
{
new b(10),new b(2),new b(1),new b(3),new b(4)
};
c.Sort((l, r) => l.x.CompareTo(r.x));
foreach (var ele in c) Console.WriteLine(ele.x);
}
}

ConvertAll
List<string> words = new List<string>();
words.Add("melon");
words.Add("apple");
words.AddRange(new[] { "banana", "plum" });//注意list也可以直接加Array,实际上是AddRange(IEnumerable<T> collection)
words.Insert(0, "lemon");
words.InsertRange(0, new[] { "peach", "nashi" });
words.Remove("melon");
words.RemoveAt(3);//去掉第四个元素
words.RemoveRange(0, 2);//去掉前两个元素
words.RemoveAll(s => s.StartsWith("n"));
List<string> subset = words.GetRange(1, 2);//得到第二个和第三个元素组成的List<string>
string[] wordsString = words.ToArray(); //得到新的包含其中元素的string[]
string[] existing = new string[1000];
words.CopyTo(0,existing, 2, 2);//从words的0索引开始,复制到existing的索引2开始,复制2个元素过去
List<string> upperCase = words.ConvertAll(s => s.ToUpper());
List<int> lengths = words.ConvertAll(s => s.Length);
Console.WriteLine();
- 创建列表
使用默认的构造函数创建一个空列表,元素添加到列表后,列表的容量就会扩大为可接纳4个元素,如果添加了第5个元素,列表的大小就重新设置为包含8个元素,如果8个还不够,那么就重新设置为16个元素,每次都会将列表的容量重新设置为原来的2倍。
为了节省时间,如果事先知道列表中元素的个数,就可以用构造函数定义其容量。
List<int> intList=new List<int>(10);//创建了一个容量为10个元素的集合,如果不足,则自动重新设置为20,40个元素
ArrayList主要用来保持兼容性,需要臃肿的cast,但它也有优点,那就是它可以混装各种类型的元素,在功能上与List