所谓序列化,就是讲内存数据保存为磁盘数据的过程,反序列化就是反过来理解。对于图像处理程序来说,最主要的变量是图片,然后还有相关的参数或运算结果。这里区分4个部分、由简单到复杂,分享一下自己的研究成果,希望能够给需要的工程师提供一些帮助。
一、基本操作
OpenCV本身提供了FileStorage的序列化保存方法,这对于保存参数来说非常适合;但是如果用来保存图片,会将原始图片的体积多倍增大,速度也比较慢。Mfc本身也提供了序列化的操作,但是使用起来的话,需要注意的地方比较多,比不上OpenCV来的直接。
我们最终想要通过保存得到,并且能够被图像处理程序读取的,是一个单一的文件。这个文件不仅包含了图片数据,而且包括相关的参数和运算结果,同时这个文件不能太大。所以我想到采用zip压缩/解压的方式来打包原始图片和运算结果。实验证明,效果是能够符合要求的。
在打包代码的选择上,找到了比较好的实现。zip.c++/unzip.c++中提供了稳定并且便于使用的压缩解压过程(具体使用参考对应的.h文件,压缩文件可以设定密码)。实际使用中,保存的时候参数保存为.xml文件,图片保存为.jpg图片,而后统一压缩成.go文件;读取的时候反过来操作。
为了说明问题,编写例程。现在把使用说明一下,具体细节可以参考代码。
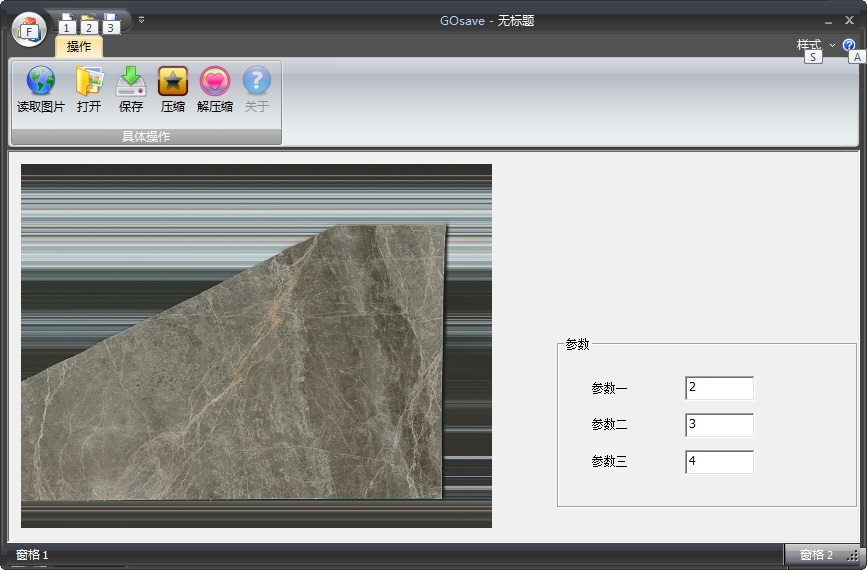
1、点击读取图片,可以读入jpg或bmp图片,同时手工设置参数一到三
2、点击保存,保存为.go文件
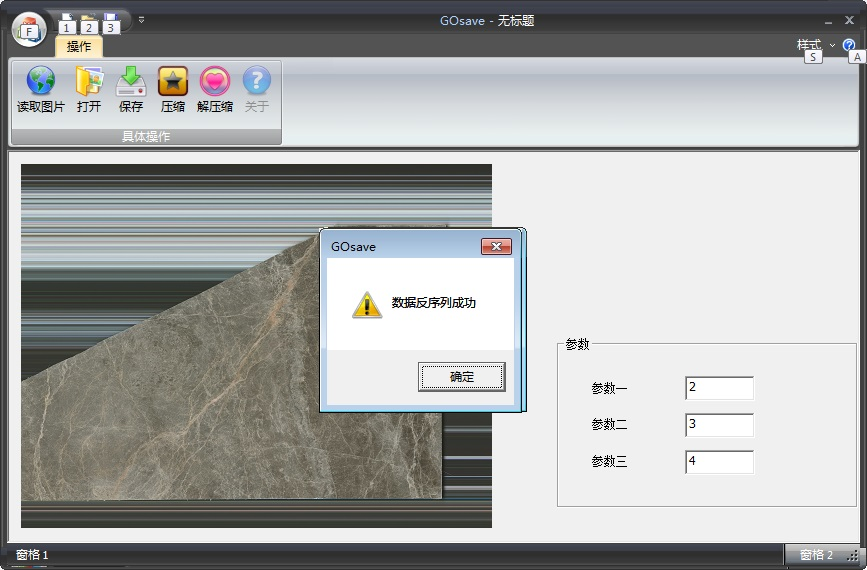
3、点击打开,打开相应的.go文件,同时解压缩后,图片和参数分别显示出来。
本例程主要展现的是“图像处理程序的序列化和反序列化”,而后结合实际使用过程中发现的问题进行衍生。希望能够有类似需求的工程师提供一些帮助。


主要代码://保存序列化结果
void CGOsaveView::OnButtonSave()
{
CString str1;string s1;
CString str2;string s2;
CString str3;string s3;
CString szFilters= _T("go(*.go)|*.go|*(*.*)|*.*||");
CString FilePathName = "";
CFileDialog dlg(FALSE,NULL,NULL,0,szFilters,this);
if(dlg.DoModal()==IDOK){
FilePathName=dlg.GetPathName();
}
if (m_fimage.rows <= 0)
{
AfxMessageBox("m_fimage为空!");
return;
}
GetDlgItemText(IDC_EDIT1,str1);
GetDlgItemText(IDC_EDIT2,str2);
GetDlgItemText(IDC_EDIT3,str3);
s1 = str1.GetBuffer(0);
s2 = str2.GetBuffer(0);
s3 = str3.GetBuffer(0);
string filename = "params.xml";
FileStorage fs(filename, FileStorage::WRITE);
fs << "str1" << s1;
fs << "str2" << s2;
fs << "str3" << s3;
fs.release();
imwrite("m_fimage.jpg",m_fimage);
AfxMessageBox("数据保存成功!");
HZIP hz = CreateZip(FilePathName,"GreenOpen");//可以设定密码
ZipAdd(hz,"params.xml", "params.xml");
ZipAdd(hz,"m_fimage.jpg", "m_fimage.jpg");
CloseZip(hz);
AfxMessageBox("数据压缩成功!");
}
//打开序列化结果
void CGOsaveView::OnButtonOpen()
{
string s1;
string s2;
string s3;
CString szFilters= _T("*(*.*)|*.*|go(*.go)|*.go||");
CString FilePathName = "";
CFileDialog dlg(TRUE,NULL,NULL,0,szFilters,this);
if(dlg.DoModal()==IDOK){
FilePathName=dlg.GetPathName();
}
HZIP hz = OpenZip(FilePathName,"GreenOpen");
ZIPENTRY ze; GetZipItem(hz,-1,&ze); int numitems=ze.index;
if (numitems <=0)
{
AfxMessageBox("文件读取错误!");
return;
}
for (int i=0; i<numitems; i++)
{
GetZipItem(hz,i,&ze);
UnzipItem(hz,i,ze.name);
}
CloseZip(hz);
AfxMessageBox("数据解压缩成功");
m_fimage = imread("m_fimage.jpg");
if (m_fimage.rows <=0 )
{
AfxMessageBox("文件读取错误!");
return;
}
string filename = "params.xml";
FileStorage fs(filename, FileStorage::READ);
fs["str1"]>>s1;
fs["str2"]>>s2;
fs["str3"]>>s3;
SetDlgItemText(IDC_EDIT1,s1.c_str());
SetDlgItemText(IDC_EDIT2,s2.c_str());
SetDlgItemText(IDC_EDIT3,s3.c_str());
AfxMessageBox("数据反序列成功");
SOURSHOW;
}
{
CString str1;string s1;
CString str2;string s2;
CString str3;string s3;
CString szFilters= _T("go(*.go)|*.go|*(*.*)|*.*||");
CString FilePathName = "";
CFileDialog dlg(FALSE,NULL,NULL,0,szFilters,this);
if(dlg.DoModal()==IDOK){
FilePathName=dlg.GetPathName();
}
if (m_fimage.rows <= 0)
{
AfxMessageBox("m_fimage为空!");
return;
}
GetDlgItemText(IDC_EDIT1,str1);
GetDlgItemText(IDC_EDIT2,str2);
GetDlgItemText(IDC_EDIT3,str3);
s1 = str1.GetBuffer(0);
s2 = str2.GetBuffer(0);
s3 = str3.GetBuffer(0);
string filename = "params.xml";
FileStorage fs(filename, FileStorage::WRITE);
fs << "str1" << s1;
fs << "str2" << s2;
fs << "str3" << s3;
fs.release();
imwrite("m_fimage.jpg",m_fimage);
AfxMessageBox("数据保存成功!");
HZIP hz = CreateZip(FilePathName,"GreenOpen");//可以设定密码
ZipAdd(hz,"params.xml", "params.xml");
ZipAdd(hz,"m_fimage.jpg", "m_fimage.jpg");
CloseZip(hz);
AfxMessageBox("数据压缩成功!");
}
//打开序列化结果
void CGOsaveView::OnButtonOpen()
{
string s1;
string s2;
string s3;
CString szFilters= _T("*(*.*)|*.*|go(*.go)|*.go||");
CString FilePathName = "";
CFileDialog dlg(TRUE,NULL,NULL,0,szFilters,this);
if(dlg.DoModal()==IDOK){
FilePathName=dlg.GetPathName();
}
HZIP hz = OpenZip(FilePathName,"GreenOpen");
ZIPENTRY ze; GetZipItem(hz,-1,&ze); int numitems=ze.index;
if (numitems <=0)
{
AfxMessageBox("文件读取错误!");
return;
}
for (int i=0; i<numitems; i++)
{
GetZipItem(hz,i,&ze);
UnzipItem(hz,i,ze.name);
}
CloseZip(hz);
AfxMessageBox("数据解压缩成功");
m_fimage = imread("m_fimage.jpg");
if (m_fimage.rows <=0 )
{
AfxMessageBox("文件读取错误!");
return;
}
string filename = "params.xml";
FileStorage fs(filename, FileStorage::READ);
fs["str1"]>>s1;
fs["str2"]>>s2;
fs["str3"]>>s3;
SetDlgItemText(IDC_EDIT1,s1.c_str());
SetDlgItemText(IDC_EDIT2,s2.c_str());
SetDlgItemText(IDC_EDIT3,s3.c_str());
AfxMessageBox("数据反序列成功");
SOURSHOW;
}
我们需要注意到的是这里的Mat是可以直接序列化的,这种方法对于存储OpenCV一类的变量来说,非常方便。但是如果是自己设定的结构体了?
二、存储自己的结构体
这里给出一个新的例子,值得参考:
//另存当前模板数据
BOOL CGOImageShopDoc::OutPutElementItems(string filename)
{
FileStorage fs(filename, FileStorage::WRITE);
////具体写下内容,注意OpenCV支持Rect等基础结构的序列化
int iElementStruct = m_rctTracker.size();//数量
fs << "iElementStruct" << iElementStruct;
//按照openCV推荐的方法来写入和读取数据。
fs << "ElementContent" << "[";
for (int i = 0; i < iElementStruct; i++)
{
string strName(CW2A(m_rctTracker[i].name.GetString()));
string strTypeName(CW2A(m_rctTracker[i].typeName.GetString()));
int iLeft = m_rctTracker[i].AreaTracker.m_rect.left;
int iTop = m_rctTracker[i].AreaTracker.m_rect.top;
int iWidth = m_rctTracker[i].AreaTracker.m_rect.Width();
int iHeight = m_rctTracker[i].AreaTracker.m_rect.Height();
fs<<"{:"<<"strName"<<strName<<"strTypeName"<<strTypeName<<"rectLeft"<<iLeft<<"rectTop"<<iTop<<"rectWidth"<<iWidth<<"rectHeight"<<iHeight<<"}";
}
fs << "]";
////书写内容结束
fs.release();
return TRUE;
}
BOOL CGOImageShopDoc::OutPutElementItems(string filename)
{
FileStorage fs(filename, FileStorage::WRITE);
////具体写下内容,注意OpenCV支持Rect等基础结构的序列化
int iElementStruct = m_rctTracker.size();//数量
fs << "iElementStruct" << iElementStruct;
//按照openCV推荐的方法来写入和读取数据。
fs << "ElementContent" << "[";
for (int i = 0; i < iElementStruct; i++)
{
string strName(CW2A(m_rctTracker[i].name.GetString()));
string strTypeName(CW2A(m_rctTracker[i].typeName.GetString()));
int iLeft = m_rctTracker[i].AreaTracker.m_rect.left;
int iTop = m_rctTracker[i].AreaTracker.m_rect.top;
int iWidth = m_rctTracker[i].AreaTracker.m_rect.Width();
int iHeight = m_rctTracker[i].AreaTracker.m_rect.Height();
fs<<"{:"<<"strName"<<strName<<"strTypeName"<<strTypeName<<"rectLeft"<<iLeft<<"rectTop"<<iTop<<"rectWidth"<<iWidth<<"rectHeight"<<iHeight<<"}";
}
fs << "]";
////书写内容结束
fs.release();
return TRUE;
}
//读取模板书
BOOL CGOImageShopDoc::ReadElementsItems(string filename)
{
//读取数据
FileStorage fs(filename, FileStorage::READ);
if (fs.isOpened())
{
//清空现有数据
m_rctTracker.clear();
//具体业务
int iElementStruct = -1;
Rect rect;
fs["iElementStruct"] >> iElementStruct;
cv::FileNode features = fs["ElementContent"];
cv::FileNodeIterator it = features.begin(), it_end = features.end();
int idx = 0;
for (; it != it_end; ++it, idx++)
{
string strName;string strTypeName;
int iLeft;
int iTop;
int iWidth;
int iHeight;
strName = (string)(*it)["strName"]; //获得strName
strTypeName=(string)(*it)["strTypeName"];
iLeft = (int)(*it)["rectLeft"];
iTop = (int)(*it)["rectTop"];
iWidth = (int)(*it)["rectWidth"];
iHeight = (int)(*it)["rectHeight"];
CRect rect = CRect(iLeft, iTop, iLeft+iWidth, iTop+iHeight);//获得rect
//生成识别区域
Mat matROI = m_imageRaw(Rect(iLeft,iTop,iWidth,iHeight));
vector<CRect> vecFindRect ;
if (strTypeName == "定位")
{
vecFindRect = findRect(matROI);
}
……
}
}
fs.release();
return TRUE;
}
BOOL CGOImageShopDoc::ReadElementsItems(string filename)
{
//读取数据
FileStorage fs(filename, FileStorage::READ);
if (fs.isOpened())
{
//清空现有数据
m_rctTracker.clear();
//具体业务
int iElementStruct = -1;
Rect rect;
fs["iElementStruct"] >> iElementStruct;
cv::FileNode features = fs["ElementContent"];
cv::FileNodeIterator it = features.begin(), it_end = features.end();
int idx = 0;
for (; it != it_end; ++it, idx++)
{
string strName;string strTypeName;
int iLeft;
int iTop;
int iWidth;
int iHeight;
strName = (string)(*it)["strName"]; //获得strName
strTypeName=(string)(*it)["strTypeName"];
iLeft = (int)(*it)["rectLeft"];
iTop = (int)(*it)["rectTop"];
iWidth = (int)(*it)["rectWidth"];
iHeight = (int)(*it)["rectHeight"];
CRect rect = CRect(iLeft, iTop, iLeft+iWidth, iTop+iHeight);//获得rect
//生成识别区域
Mat matROI = m_imageRaw(Rect(iLeft,iTop,iWidth,iHeight));
vector<CRect> vecFindRect ;
if (strTypeName == "定位")
{
vecFindRect = findRect(matROI);
}
……
}
}
fs.release();
return TRUE;
}
如果我们打开这里保存的文件,可以发现这种模式:
%YAML:1.0
---
iElementStruct: 15
ElementContent:
- { strName:"定位", rectLeft:37, rectTop:73, rectWidth:241,
rectHeight:120 }
- { strName:"定位", rectLeft:1556, rectTop:107, rectWidth:130,
rectHeight:70 }
- { strName:"定位", rectLeft:3127, rectTop:99, rectWidth:93,
rectHeight:70 }
- { strName:"定位", rectLeft:19, rectTop:2187, rectWidth:95,
rectHeight:77 }
- { strName:"定位", rectLeft:1592, rectTop:2203, rectWidth:95,
rectHeight:44 }
- { strName:"定位", rectLeft:3151, rectTop:2184, rectWidth:84,
rectHeight:68 }
- { strName:"考号", rectLeft:1042, rectTop:419, rectWidth:300,
rectHeight:121 }
- { strName:"主观分数", rectLeft:161, rectTop:678, rectWidth:929,
rectHeight:63 }
- { strName:"主观分数", rectLeft:1789, rectTop:203, rectWidth:869,
rectHeight:76 }
- { strName:"主观分数", rectLeft:1777, rectTop:717, rectWidth:868,
rectHeight:64 }
- { strName:"主观分数", rectLeft:1785, rectTop:1713, rectWidth:388,
rectHeight:66 }
- { strName:"主观题", rectLeft:76, rectTop:825, rectWidth:1450,
rectHeight:1246 }
- { strName:"主观题", rectLeft:1692, rectTop:367, rectWidth:1524,
rectHeight:323 }
- { strName:"主观题", rectLeft:1696, rectTop:864, rectWidth:1518,
rectHeight:749 }
- { strName:"主观题", rectLeft:1696, rectTop:1787, rectWidth:1534,
rectHeight:307 }
---
iElementStruct: 15
ElementContent:
- { strName:"定位", rectLeft:37, rectTop:73, rectWidth:241,
rectHeight:120 }
- { strName:"定位", rectLeft:1556, rectTop:107, rectWidth:130,
rectHeight:70 }
- { strName:"定位", rectLeft:3127, rectTop:99, rectWidth:93,
rectHeight:70 }
- { strName:"定位", rectLeft:19, rectTop:2187, rectWidth:95,
rectHeight:77 }
- { strName:"定位", rectLeft:1592, rectTop:2203, rectWidth:95,
rectHeight:44 }
- { strName:"定位", rectLeft:3151, rectTop:2184, rectWidth:84,
rectHeight:68 }
- { strName:"考号", rectLeft:1042, rectTop:419, rectWidth:300,
rectHeight:121 }
- { strName:"主观分数", rectLeft:161, rectTop:678, rectWidth:929,
rectHeight:63 }
- { strName:"主观分数", rectLeft:1789, rectTop:203, rectWidth:869,
rectHeight:76 }
- { strName:"主观分数", rectLeft:1777, rectTop:717, rectWidth:868,
rectHeight:64 }
- { strName:"主观分数", rectLeft:1785, rectTop:1713, rectWidth:388,
rectHeight:66 }
- { strName:"主观题", rectLeft:76, rectTop:825, rectWidth:1450,
rectHeight:1246 }
- { strName:"主观题", rectLeft:1692, rectTop:367, rectWidth:1524,
rectHeight:323 }
- { strName:"主观题", rectLeft:1696, rectTop:864, rectWidth:1518,
rectHeight:749 }
- { strName:"主观题", rectLeft:1696, rectTop:1787, rectWidth:1534,
rectHeight:307 }
那么,这种方式是OpenCV支持的结构保存方式,每一个
- { strName:"主观题", rectLeft:1696, rectTop:1787, rectWidth:1534,
rectHeight:307 }
rectHeight:307 }
是一个可以存储读取的结构。
三、FileNode支持哪些结构
在这个例子中,我们非常丑陋地使用了4个int值来定义一个Rect。为什么不能直接定义?
比如编写代码
string filename = "序列化.yml";
FileStorage fs(filename, FileStorage::WRITE);
fs << "str1" <<1;
cv::Rect cvRect(10,10,10,10);
fs<<"cvRect"<<cvRect;
fs.release();
return 0;
fs << "str1" <<1;
cv::Rect cvRect(10,10,10,10);
fs<<"cvRect"<<cvRect;
fs.release();
return 0;
生成这样的结果:
%YAML:1.0
---
str1: 1
cvRect: [ 10, 10, 10, 10 ]
---
str1: 1
cvRect: [ 10, 10, 10, 10 ]
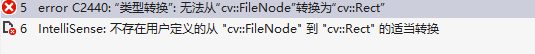
但是,如果我们读取这个Rect,并且编写这样的代码

则会报错:
为了进一步解析这个问题,翻看OpenCV的代码:
class CV_EXPORTS_W_SIMPLE FileNode
{
public:
//! type of the file storage node
enum Type
{
NONE = 0, //!< empty node
INT = 1, //!< an integer
REAL = 2, //!< floating-point number
FLOAT = REAL, //!< synonym or REAL
STR = 3, //!< text string in UTF-8 encoding
STRING = STR, //!< synonym for STR
REF = 4, //!< integer of size size_t. Typically used for storing complex dynamic structures where some elements reference the others
SEQ = 5, //!< sequence
MAP = 6, //!< mapping
TYPE_MASK = 7,
FLOW = 8, //!< compact representation of a sequence or mapping. Used only by YAML writer
USER = 16, //!< a registered object (e.g. a matrix)
EMPTY = 32, //!< empty structure (sequence or mapping)
NAMED = 64 //!< the node has a name (i.e. it is element of a mapping)
};
{
public:
//! type of the file storage node
enum Type
{
NONE = 0, //!< empty node
INT = 1, //!< an integer
REAL = 2, //!< floating-point number
FLOAT = REAL, //!< synonym or REAL
STR = 3, //!< text string in UTF-8 encoding
STRING = STR, //!< synonym for STR
REF = 4, //!< integer of size size_t. Typically used for storing complex dynamic structures where some elements reference the others
SEQ = 5, //!< sequence
MAP = 6, //!< mapping
TYPE_MASK = 7,
FLOW = 8, //!< compact representation of a sequence or mapping. Used only by YAML writer
USER = 16, //!< a registered object (e.g. a matrix)
EMPTY = 32, //!< empty structure (sequence or mapping)
NAMED = 64 //!< the node has a name (i.e. it is element of a mapping)
};
那么的确是不可能直接转换为所有的OpenCV类型,这里只是保存为了其他节点的序列,通过代码测试也的确是这样。
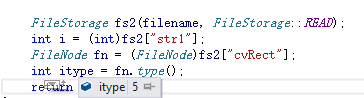
在这种情况下,我们可以首先将序列读入vector中,非常有用。

而后再根据实际情况进行封装。
四、更进一步,进行类封装
如果想更进一步,自然需要采用类的方法,这里是一个很好的例子。
#include <opencv2opencv.hpp>
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
class ColletorMat
{
private:
int indexFrame;
bool found;
Mat frame;
public:
ColletorMat(int index, bool found, Mat frame)
{
this->indexFrame = index;
this->found = found;
this->frame = frame;
}
~ColletorMat()
{
}
// settors
void set_indexFrame(int index)
{
this->indexFrame = index;
}
void set_found(bool found)
{
this->found = found;
}
void set_frame(Mat frame)
{
this->frame = frame;
}
// accessors
int get_indexFrame()
{
return this->indexFrame;
}
bool get_found()
{
return this->found;
}
Mat get_frame()
{
return this->frame;
}
};
void matwrite(ofstream& fs, const Mat& mat, int index, bool checking)
{
// Data Object
int indexFrame = index;
bool found = checking;
fs.write((char*)&indexFrame, sizeof(int)); // indexFrame
fs.write((char*)&found, sizeof(bool)); // bool checking
// Header
int type = mat.type();
int channels = mat.channels();
fs.write((char*)&mat.rows, sizeof(int)); // rows
fs.write((char*)&mat.cols, sizeof(int)); // cols
fs.write((char*)&type, sizeof(int)); // type
fs.write((char*)&channels, sizeof(int)); // channels
// Data
if (mat.isContinuous())
{
fs.write(mat.ptr<char>(0), (mat.dataend - mat.datastart));
}
else
{
int rowsz = CV_ELEM_SIZE(type) * mat.cols;
for (int r = 0; r < mat.rows; ++r)
{
fs.write(mat.ptr<char>(r), rowsz);
}
}
}
ColletorMat matread(ifstream& fs)
{
// Data Object
int indexFrame;
bool found;
fs.read((char*)&indexFrame, sizeof(int)); //
fs.read((char*)&found, sizeof(bool)); //
// Header
int rows, cols, type, channels;
fs.read((char*)&rows, sizeof(int)); // rows
fs.read((char*)&cols, sizeof(int)); // cols
fs.read((char*)&type, sizeof(int)); // type
fs.read((char*)&channels, sizeof(int)); // channels
// Data
Mat mat(rows, cols, type);
fs.read((char*)mat.data, CV_ELEM_SIZE(type) * rows * cols);
ColletorMat ojbectMat(indexFrame, found, mat);
return ojbectMat;
}
int main()
{
// Save the random generated data
{
Mat image1, image2, image3;
image1 = imread("C:\opencvVid\data_seq\Human3\0001.jpg");
image2 = imread("C:\opencvVid\data_seq\Human3\0002.jpg");
image3 = imread("C:\opencvVid\data_seq\Human3\0003.jpg");
if (image1.empty() || image2.empty() || image3.empty()) {
std::cout << "error: image not readed from file ";
return(0);
}
imshow("M1",image1);
imshow("M2",image2);
imshow("M3",image3);
(char)cvWaitKey(0);
ofstream fs("azdoudYoussef.bin", fstream::binary);
matwrite(fs, image1, 100, true);
matwrite(fs, image2, 200, true);
matwrite(fs, image3, 300, true);
fs.close();
double tic = double(getTickCount());
ifstream loadFs("azdoudYoussef.bin", ios::binary);
if(!loadFs.is_open()){
cout << "error while opening the binary file" << endl;
}
ColletorMat lcolletorMat1 = matread(loadFs);
ColletorMat lcolletorMat2 = matread(loadFs);
ColletorMat lcolletorMat3 = matread(loadFs);
cout << "frames loaded up " << endl;
vector<ColletorMat> setFrames;
setFrames.push_back(lcolletorMat1);
setFrames.push_back(lcolletorMat2);
setFrames.push_back(lcolletorMat3);
imshow("1", lcolletorMat1.get_frame());
imshow("2", lcolletorMat2.get_frame());
imshow("3", lcolletorMat3.get_frame());
(char)cvWaitKey(0);
cout << "indexFrame" <<lcolletorMat1.get_indexFrame() << "found" << lcolletorMat1.get_found();
double toc = (double(getTickCount()) - tic) * 1000. / getTickFrequency();
cout << "Using Raw: " << toc << endl;
loadFs.close();
}
return 0;
}
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
class ColletorMat
{
private:
int indexFrame;
bool found;
Mat frame;
public:
ColletorMat(int index, bool found, Mat frame)
{
this->indexFrame = index;
this->found = found;
this->frame = frame;
}
~ColletorMat()
{
}
// settors
void set_indexFrame(int index)
{
this->indexFrame = index;
}
void set_found(bool found)
{
this->found = found;
}
void set_frame(Mat frame)
{
this->frame = frame;
}
// accessors
int get_indexFrame()
{
return this->indexFrame;
}
bool get_found()
{
return this->found;
}
Mat get_frame()
{
return this->frame;
}
};
void matwrite(ofstream& fs, const Mat& mat, int index, bool checking)
{
// Data Object
int indexFrame = index;
bool found = checking;
fs.write((char*)&indexFrame, sizeof(int)); // indexFrame
fs.write((char*)&found, sizeof(bool)); // bool checking
// Header
int type = mat.type();
int channels = mat.channels();
fs.write((char*)&mat.rows, sizeof(int)); // rows
fs.write((char*)&mat.cols, sizeof(int)); // cols
fs.write((char*)&type, sizeof(int)); // type
fs.write((char*)&channels, sizeof(int)); // channels
// Data
if (mat.isContinuous())
{
fs.write(mat.ptr<char>(0), (mat.dataend - mat.datastart));
}
else
{
int rowsz = CV_ELEM_SIZE(type) * mat.cols;
for (int r = 0; r < mat.rows; ++r)
{
fs.write(mat.ptr<char>(r), rowsz);
}
}
}
ColletorMat matread(ifstream& fs)
{
// Data Object
int indexFrame;
bool found;
fs.read((char*)&indexFrame, sizeof(int)); //
fs.read((char*)&found, sizeof(bool)); //
// Header
int rows, cols, type, channels;
fs.read((char*)&rows, sizeof(int)); // rows
fs.read((char*)&cols, sizeof(int)); // cols
fs.read((char*)&type, sizeof(int)); // type
fs.read((char*)&channels, sizeof(int)); // channels
// Data
Mat mat(rows, cols, type);
fs.read((char*)mat.data, CV_ELEM_SIZE(type) * rows * cols);
ColletorMat ojbectMat(indexFrame, found, mat);
return ojbectMat;
}
int main()
{
// Save the random generated data
{
Mat image1, image2, image3;
image1 = imread("C:\opencvVid\data_seq\Human3\0001.jpg");
image2 = imread("C:\opencvVid\data_seq\Human3\0002.jpg");
image3 = imread("C:\opencvVid\data_seq\Human3\0003.jpg");
if (image1.empty() || image2.empty() || image3.empty()) {
std::cout << "error: image not readed from file ";
return(0);
}
imshow("M1",image1);
imshow("M2",image2);
imshow("M3",image3);
(char)cvWaitKey(0);
ofstream fs("azdoudYoussef.bin", fstream::binary);
matwrite(fs, image1, 100, true);
matwrite(fs, image2, 200, true);
matwrite(fs, image3, 300, true);
fs.close();
double tic = double(getTickCount());
ifstream loadFs("azdoudYoussef.bin", ios::binary);
if(!loadFs.is_open()){
cout << "error while opening the binary file" << endl;
}
ColletorMat lcolletorMat1 = matread(loadFs);
ColletorMat lcolletorMat2 = matread(loadFs);
ColletorMat lcolletorMat3 = matread(loadFs);
cout << "frames loaded up " << endl;
vector<ColletorMat> setFrames;
setFrames.push_back(lcolletorMat1);
setFrames.push_back(lcolletorMat2);
setFrames.push_back(lcolletorMat3);
imshow("1", lcolletorMat1.get_frame());
imshow("2", lcolletorMat2.get_frame());
imshow("3", lcolletorMat3.get_frame());
(char)cvWaitKey(0);
cout << "indexFrame" <<lcolletorMat1.get_indexFrame() << "found" << lcolletorMat1.get_found();
double toc = (double(getTickCount()) - tic) * 1000. / getTickFrequency();
cout << "Using Raw: " << toc << endl;
loadFs.close();
}
return 0;
}