B. Eastern Exhibition
题目:
You and your friends live in n houses.
Each house is located on a 2D plane, in a point with integer coordinates.
There might be different houses located in the same point.
The mayor of the city is asking you for places for the building of the Eastern exhibition.
You have to find the number of places (points with integer coordinates),
so that the summary distance from all the houses to the exhibition is minimal.
The exhibition can be built in the same point as some house.
The distance between two points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) is |x1−x2|+|y1−y2|,
where |x| is the absolute value of x.
Input
First line contains a single integer t (1 ≤ t ≤ 1000) — the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer n (1≤n≤1000).
Next n lines describe the positions of the houses (xi,yi) (0≤xi,yi≤109).
It's guaranteed that the sum of all n does not exceed 1000.
Output
For each test case output a single integer - the number of different positions for the exhibition.
The exhibition can be built in the same point as some house.
Example:
input
6
3
0 0
2 0
1 2
4
1 0
0 2
2 3
3 1
4
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
2
0 0
1 1
2
0 0
2 0
2
0 0
0 0
output
1
4
4
4
3
1

解题思路:
题目给出了计算距离为曼哈顿距离(|x_1 - x_2| + |y_1 - y_2|)
图中的红色、蓝色、黄色的线的距离均相同,这就是曼哈顿距离,而绿线为两点之间的真实距离,也是最短距离。
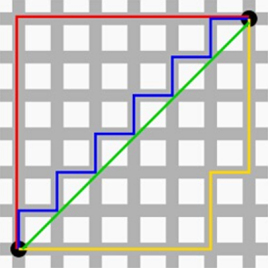
图片来自百度百科词条
在曼哈顿距离中,横向移动只会改变两点的(|x_1 - x_2|)的距离,不会对两点的y的距离有影响
所以我们可以分步讨论,先计算可以放置绿点的x的坐标的长度,再计算y坐标的长度,然后相乘即可。
注意:以上算法思路是对蓝点个数为偶数的情况考虑的,如果蓝点个数为奇数,那么只能有一个绿点符合条件,可以在上图中画画模拟一下。
所以如果点数为偶数,那么在讨论x的范围时,x的个数也为偶数,同样,y的个数也为偶数

如上图(x_1<x_2<x_3<x_4)且(y_2=y_3<y_1=y_4)
当选取(x)坐标时,因为有偶数个点,所以选取中间两点,即 (n÷2) 和 (n÷2+1) 两点
所以这两点间的距离为(x_{(n÷2+1)} - x_{(n÷2)} + 1),上图(n = 4)
选取y坐标时同理
依上图,可计算出x的范围为2,y的范围为2,绿点即为打叉的位置。
如果还不明白,请私信我哦
代码如下:
注意,long long哦
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1010;
ll x[N], y[N];
void solve ( void )
{
ll n;
cin >> n;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i++ )
{
cin >> x[i] >> y[i];
}
sort ( x + 1, x + n + 1 ); // 将x和y按大小排序,这样能方便取中位数
sort ( y + 1, y + n + 1 );
if ( n % 2 != 0 )
{
cout << 1 << endl;
return ;
} else {
cout << ( x[n / 2 + 1] - x[n / 2] + 1 ) * ( y[n / 2 + 1] - y[n / 2] + 1 ) << endl;
return ;
}
}
int main ( void )
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while ( T-- ) solve();
return 0;
}