finall关键字:

 →
→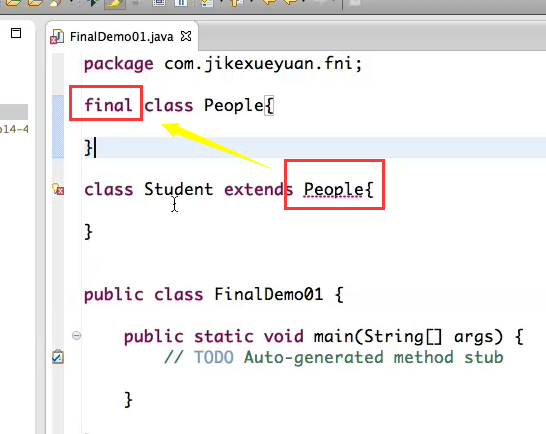 final声明的类不能被继承,类似太监
final声明的类不能被继承,类似太监
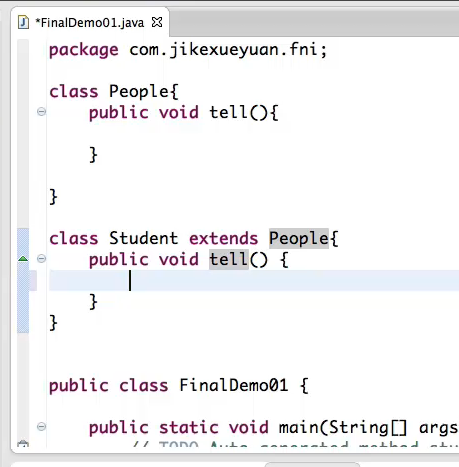
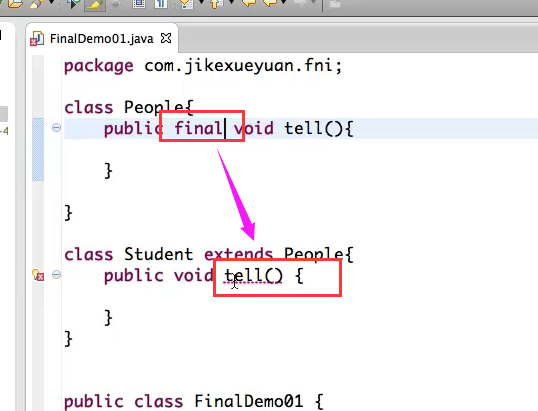
final声明的类不能被重写:
 →
→
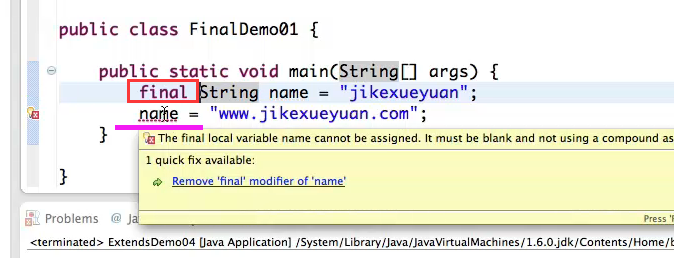
使用final声明的变量变成常量,常量不可以被修改:
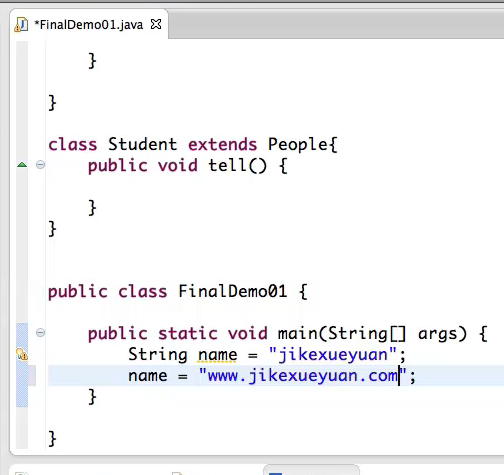 →
→
JAVA抽象类:

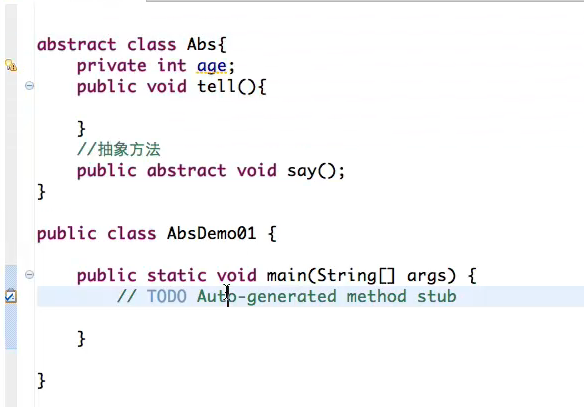
抽象类不能直接被实例化:

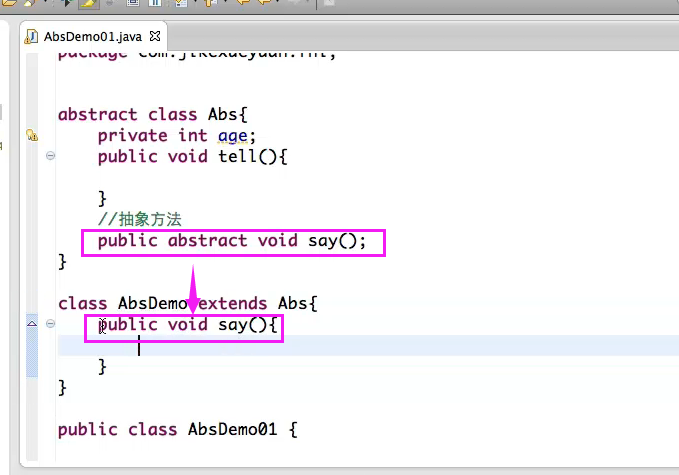

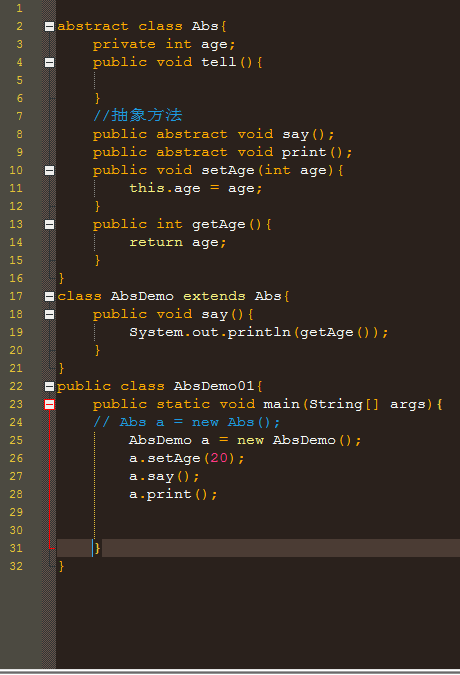
abstract class Abs{ private int age; public void tell(){ } //抽象方法 public abstract void say(); public abstract void print(); public void setAge(int age){ this.age = age; } public int getAge(){ return age; } } class AbsDemo extends Abs{ public void say(){ System.out.println(getAge()); } } public class AbsDemo01{ public static void main(String[] args){ // Abs a = new Abs(); AbsDemo a = new AbsDemo(); a.setAge(20); a.say(); a.print(); } }

接口的实现也必须通过子类,使用关键字implements:
package com.jikexueyuan.fin; interface Inter{ public static final int AGE = 100; public abstract void tell(); } class A implements Inter{ public void tell(){ } } public class InterDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args){ //Inter i = new Inter(); //不能直接而是要通过子类implements来使用 A a = new A(); a.tell(); System.out.println(Inter.AGE); } }
接口也是可以多实现:
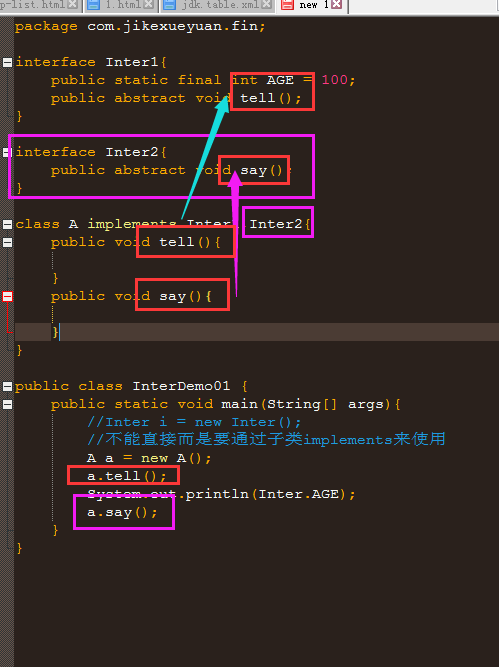
package com.jikexueyuan.fin; interface Inter1{ public static final int AGE = 100; public abstract void tell(); } interface Inter2{ public abstract void say(); } class A implements Inter1,Inter2{ public void tell(){ } public void say(){ } } public class InterDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args){ //Inter i = new Inter(); //不能直接而是要通过子类implements来使用 A a = new A(); a.tell(); System.out.println(Inter.AGE); a.say(); } }
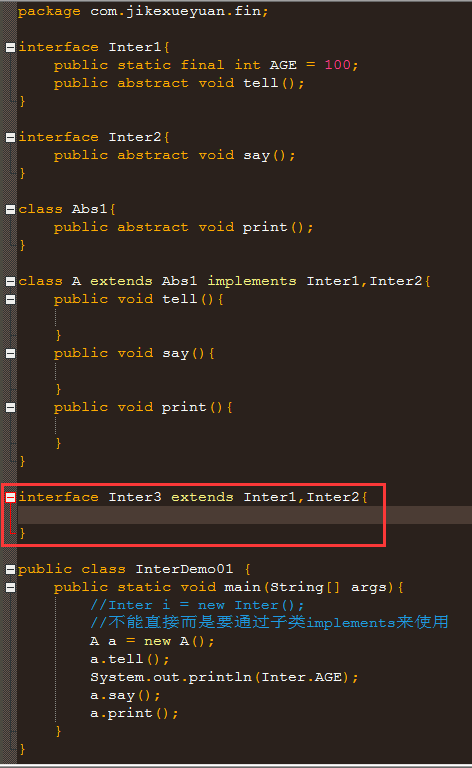
一个子类可以同时继承抽象类和实现接口:
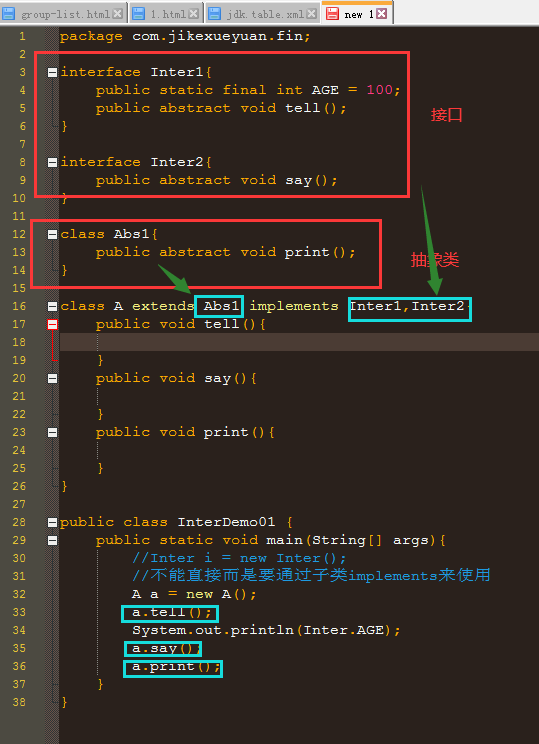
package com.jikexueyuan.fin; interface Inter1{ public static final int AGE = 100; public abstract void tell(); } interface Inter2{ public abstract void say(); } class Abs1{ public abstract void print(); } class A extends Abs1 implements Inter1,Inter2{ public void tell(){ } public void say(){ } public void print(){ } } public class InterDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args){ //Inter i = new Inter(); //不能直接而是要通过子类implements来使用 A a = new A(); a.tell(); System.out.println(Inter.AGE); a.say(); a.print(); } }
一个接口不能继承一个抽象类,但是可以通过extends关键字同时继承多个接口,实现接口的多继承: