1.大纲
aqs的思路
为什么要学aqs
aqs的作用
aqs的重要性
aqs的原理
应用实例,源码解析
aqs实现自己的门闩
一:AQS的思路
1.
先从应用层面理解为什么需要他,如何使用
了解使用场景
再去分析它的结构
二:为什么要学习
1.锁与协作类的共同点
闸门
2.协作同步功能
类似的还有CountDownLatch
他们的底层都有一个共同的基类,就是AQS
三:为什么要学AQS
1.
很多工作都是类似的,如果能提起一个工具类,对于一些类而言,就可以屏蔽很多细节,只要关注业务逻辑了
四:AQS的重要性
1.Semaphore与AQS的关系
Semaphore内部有一个Sync类,Sync类继承了AQS
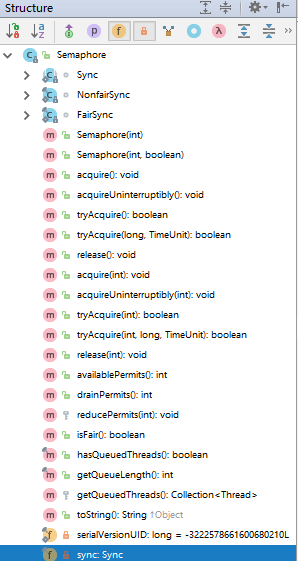
2.CountDownLatch与AQS的关系
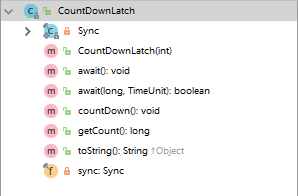
3.ReenTractLock与AQS
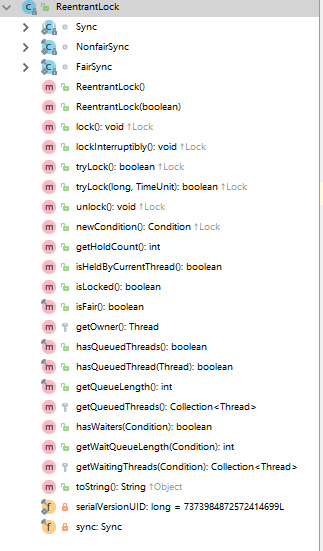
4.AQS的作用
是一个用于构建锁,同步器,协作工具类的工具类。有了AQS,很多协作工具类都可以被方便的写出来
五:AQS原理
1.核心三大部分
state
控制线程抢锁和配合的FIFO队列
协作工具类去实现的获取与释放的重要方法
2.state
根据具体的实现类的不同而不同,例如在信号量中,表示剩余的许可证的数量,而countDownLatch里,它表示还需要倒数的数量
state是volatile修饰的,会被并发的修改,所以都需要保证线程安全。getState,setState,compareAndSetState操作读取更新,都是依赖于atomic的支持。
其中,在AbstractQueueSynchronizer中的方法:
protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) {
// See below for intrinsics setup to support this
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, expect, update);
}
可以发现,底层是保证线程安全的。
在ReentractLock中,state是锁的占有情况,包括可重入计数,当state是0的时候,表示lock不被任何线程占有
2.FIFO队列
这个队列是存在等待的线程,AQS就是排队管理器。
当多个线程用同一个锁时,必须有排队机制将没能拿到锁的线程串在一起。当锁释放的时候,锁管理器就会挑选一个合适的线程来占有这个刚刚释放的锁
是一个双向队列
3.需要实现的释放获取的方法
获取方法:
会依赖state变量,经常会阻塞
在Semaphore中,获取就是acquire方法,作用是获取许可证
在CountDownLatch中,获取就是await方法,作用是等待,知道结束
释放方法:
释放不会阻塞
4.需要重写tryAcquire和tryRelease方法
5.Aqs用法

六:AQS在CountDownLatch中的应用
1.构造函数
public CountDownLatch(int count) {
if (count < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("count < 0");
this.sync = new Sync(count);
}
然后,进入Sync:
private static final class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4982264981922014374L;
Sync(int count) {
setState(count);
}
int getCount() {
return getState();
}
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
return (getState() == 0) ? 1 : -1;
}
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
// Decrement count; signal when transition to zero
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
if (c == 0)
return false;
int nextc = c-1;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
return nextc == 0;
}
}
}
然后进入的是aqs的setState方法:
protected final void setState(int newState) {
state = newState;
}
2.getCount方法
public long getCount() {
return sync.getCount();
}
进入getCount:
private static final class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4982264981922014374L;
Sync(int count) {
setState(count);
}
int getCount() {
return getState();
}
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
return (getState() == 0) ? 1 : -1;
}
进入aqs中:
/**
* The synchronization state.
*/
private volatile int state;
/**
* Returns the current value of synchronization state.
* This operation has memory semantics of a {@code volatile} read.
* @return current state value
*/
protected final int getState() {
return state;
}
3.await方法
public void await() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
}
然后进入acquireSharedInterruptibly
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}
然后,进入tryAcquireShared方法,在CountDownLatch里已经实现了:
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
return (getState() == 0) ? 1 : -1;
}
当不等于0的时候,表示需要进行等待,具体的doAcquireSharedInterruptibly,在aqs中:
/**
* Acquires in shared interruptible mode.
* @param arg the acquire argument
*/
private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
这个方法是入队列进行等待,然后进行阻塞。
先对当前的线程包装成Node节点,如下:
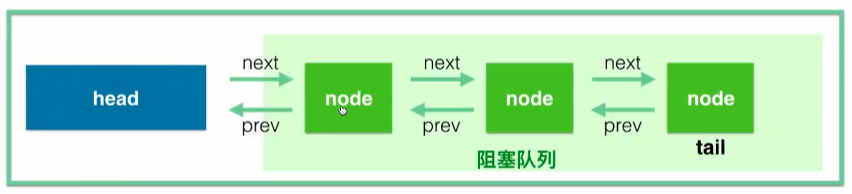
阻塞是parkAndCheckInterrupt方法做的,进入看一下源码:
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
再进入park方法:
public static void park(Object blocker) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
setBlocker(t, blocker);
UNSAFE.park(false, 0L);
setBlocker(t, null);
}
在上面可以知道UNSAFE.park是一个native方法,就是讲当前线程进行挂起。
总结:
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly就是讲当前的线程进行挂起
4.countDown方法
public void countDown() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
进入releaseShared方法:
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
分析tryReleaseShared方法
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
// Decrement count; signal when transition to zero
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
if (c == 0)
return false;
int nextc = c-1;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
return nextc == 0;
}
}
返回false,表示这次不需要进行释放,已经被释放过了。进行state-1,使用cas进行更新;如果不成功,再进行for循环,进行更新,一旦等于0,则返回true
然后,在返回true的时候,会进行doReleaseShared方法,这个方法是唤醒等待的线程
七::AQS在Semaphore中的应用
1.state
表示许可证的剩余数量
2.acquire方法
public void acquire() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
}
进入acqiureSharedInterruptibly:
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}
发现和上面的countDownLatch使用的一样
针对参数不同,有公平与不公平两种方式:
/**
* NonFair version
*/
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2694183684443567898L;
NonfairSync(int permits) {
super(permits);
}
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquireShared(acquires);
}
}
这个是不公平的方式,进入nonfairTryAcquireShared
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1192457210091910933L;
Sync(int permits) {
setState(permits);
}
final int getPermits() {
return getState();
}
final int nonfairTryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
for (;;) {
int available = getState();
int remaining = available - acquires;
if (remaining < 0 ||
compareAndSetState(available, remaining))
return remaining;
}
}
获取当前可用许可证,然后进行计算。如果小于0,则返回一个负数,外面的方法就是进行等待阻塞;如果不小于0,则使用cas将剩余的许可证给设置进去,如果成功,同时返回一个正数,说明有可用的许可证;如果cas失败,则新一轮的循环
八:AQS在ReenTrantLock中的应用
1.unlock方法
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
进入release方法
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
进入tryRelease方法:
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
如果,当前线程没有持有锁,则抛出异常
计算一个c,其中getState是已经重入的次数
如果不等于0,则将c设置
如果等于0,则要释放锁,让free为true,同时,将当前的线程不再持有锁,null即可
再回到上面的代码。
unparkSuccessor方法,后面的节点会被唤醒
2.lock方法
public void lock() {
sync.lock();
}
然后进行lock
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}
/**
* Acquires the lock.
*
* <p>Acquires the lock if it is not held by another thread and returns
* immediately, setting the lock hold count to one.
*
* <p>If the current thread already holds the lock then the hold
* count is incremented by one and the method returns immediately.
*
* <p>If the lock is held by another thread then the
* current thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling
* purposes and lies dormant until the lock has been acquired,
* at which time the lock hold count is set to one.
*/
public void lock() {
sync.lock();
}
因为有公平与非公平的不同实现方式,具体是那一个,可以看到上面有一个sync的判断
先看不公平的实现:
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
进行cas操作,如果是0,表示没有锁,将当前的线程进行加锁
如果失败,则进入else:
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
然后看非公平的tryAcquire
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
在sync中,看nobfairTryAcquire:
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
如果是0,表示没有线程持有锁,则加锁就行
否则,如果线程恰好是这个锁的持有者,就是一个重入的操作,在当前的基础上加上acquire,如果小于0,表示溢出了。不然就setState。
· 再继续,如果又不是当前持有的锁,返回false。
所以,返回上一层,tryAcquire表示获取锁失败,因为是取非,则执行acquireQueued,当前的线程被包装,放入等待队列进行等待
九:实现一个自己的门闩
1.程序
package com.jun.juc.aqs;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer;
/**
* 使用aqs实现一个简单的门闩
*/
public class OneShotLatch {
// 不知道是使用独占的还是共享的,所以,不强制重写
private class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer{
@Override
protected int tryAcquireShared(int arg) {
return (getState()==1) ? 1 : -1;
}
@Override
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int arg) {
setState(1);
return true;
}
}
private final Sync sync = new Sync();
/**
* 等待
*/
public void await(){
sync.acquireShared(0);
}
public void signal(){
sync.releaseShared(0);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
OneShotLatch oneShotLatch = new OneShotLatch();
for (int i=0; i<10; i++){
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("尝试获取");
oneShotLatch.await();
System.out.println("门闩开了");
}
}).start();
}
Thread.sleep(5000);
oneShotLatch.signal();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("尝试获取");
oneShotLatch.await();
System.out.println("门闩开了");
}
}).start();
}
}
效果:
Connected to the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:64474', transport: 'socket' 尝试获取 尝试获取 尝试获取 尝试获取 尝试获取 尝试获取 尝试获取 尝试获取 尝试获取 尝试获取 Disconnected from the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:64474', transport: 'socket' 门闩开了 门闩开了 门闩开了 门闩开了 门闩开了 门闩开了 门闩开了 门闩开了 门闩开了 门闩开了 尝试获取 门闩开了 Process finished with exit code 0