如果一个spring项目是使用xml方式配置的,那就不用关注ConfigurationClassPostProcessor因为不写@Configuration注解,ConfigurationClassPostProcessor是不会生效的。
但是,在spring boot里,这个类太重要了。可以说是最重要的,自动装配就靠它实现的。
本文就浅析一下ConfigurationClassPostProcessor。
一 概述
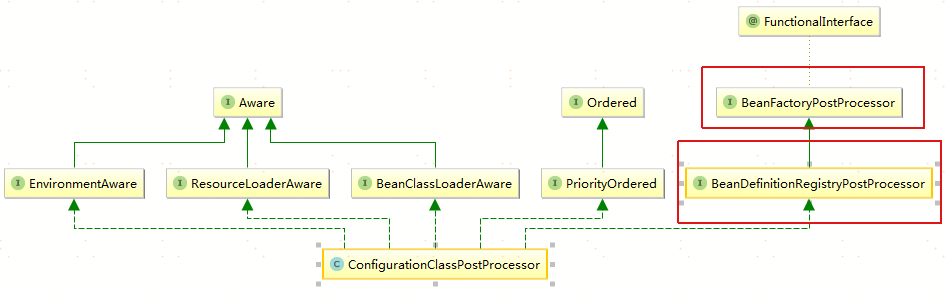
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 是实现了 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口的
同时实现了它的接口方法 public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
二 调用地点
先抛开SpringBoot回到Spring,AbstractApplicationContext中最重要的方法refresh()
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
中间的一些环节省略,继续看 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) { // Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any. Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>(); if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) { BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory; List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new LinkedList<>(); List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new LinkedList<>(); for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) { if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) { BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor = (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor; registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor); }
在这里 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 就会被调用,我们继续看
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { int registryId = System.identityHashCode(registry); if (this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) { throw new IllegalStateException( "postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry already called on this post-processor against " + registry); } if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) { throw new IllegalStateException( "postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + registry); } this.registriesPostProcessed.add(registryId); processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry); }
开始正式解析
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>(); String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();//去拿当前所有的BeanDefinition,看下面的截图 for (String beanName : candidateNames) { BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName); if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef) || ConfigurationClassUtils.isLiteConfigurationClass(beanDef)) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef); } } else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) { configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName)); } } // Return immediately if no @Configuration classes were found 在这里只会过滤出来注解@Configuration
if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) { return; }
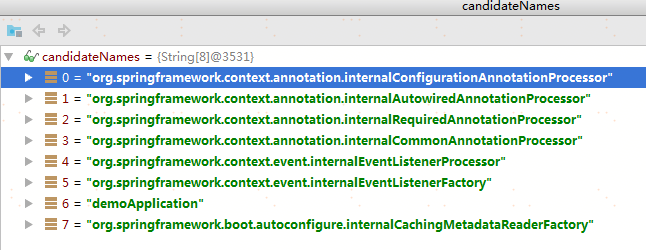
前几个就不看了,主要看6号,这个就是我们SpringBoot的启动类,这个启动类会在Spring框架启动前就把自己注册进去,代码在
SpringApplication.prepareContext
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) { context.setEnvironment(environment); postProcessApplicationContext(context); applyInitializers(context); listeners.contextPrepared(context); if (this.logStartupInfo) { logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null); logStartupProfileInfo(context); } // Add boot specific singleton beans context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments); if (printedBanner != null) { context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner); } // Load the sources Set<Object> sources = getAllSources(); Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty"); load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));/在这里把启动类作为一个BeanDefinition注册进去 listeners.contextLoaded(context); }
好了,准备工作都做完了,@Configuration也找到了,接下来就是正式的解析了。解析我有空之后会详细的来解析
三 总结
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 有两个最重要的方法
1 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry (接口BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的方法)
2 postProcessBeanFactory (接口BeanFactoryPostProcessor的方法)
而这两个方法都是通过调用 processConfigBeanDefinitions来完成的
===================== 2020-12-24 ===========================================
又跟了一次代码,发现上面的说法有误
SpringApplication类中applyInitializers(context);,它会将三个默认的内部类加入到 spring 容器DefaultListableBeanFactory中,如下:
ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer$ConfigurationWarningsPostProcessor
SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer$CachingMetadataReaderFactoryPostProcessor
ConfigFileApplicationListener$PropertySourceOrderingPostProcessor
而在方法
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors)
上面的 beanFactoryPostProcessors 就是上面的三个默认内部类
也就是说容器启动的时候其实是走不到
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) { BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory; List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new LinkedList<>(); List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new LinkedList<>(); for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {//这里面就没有ConfigurationClassPostProcessor if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) { BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor = (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor; registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor); } else { regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor); } }
而是要往下走
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));//在这里实例化ConfigurationClassPostProcessor processedBeans.add(ppName); } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);//调用 currentRegistryProcessors.clear();