基于注解的Spring AOP开发
简单案例快速入门
定义目标类接口和实现类
/** * Created by zejian on 2017/2/19.*/ //接口类 public interface UserDao { int addUser(); void updateUser(); void deleteUser(); void findUser(); } //实现类 import com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; /** * Created by zejian on 2017/2/19.*/ @Repository public class UserDaoImp implements UserDao { @Override public int addUser() { System.out.println("add user ......"); return 6666; } @Override public void updateUser() { System.out.println("update user ......"); } @Override public void deleteUser() { System.out.println("delete user ......"); } @Override public void findUser() { System.out.println("find user ......"); } }
使用Spring 2.0引入的注解方式,编写Spring AOP的aspect 类:
@Aspect public class MyAspect { /** * 前置通知 */ @Before("execution(* com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao.addUser(..))") public void before(){ System.out.println("前置通知...."); } /** * 后置通知 * returnVal,切点方法执行后的返回值 */ @AfterReturning(value="execution(* com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao.addUser(..))",returning = "returnVal") public void AfterReturning(Object returnVal){ System.out.println("后置通知...."+returnVal); } /** * 环绕通知 * @param joinPoint 可用于执行切点的类 * @return * @throws Throwable */ @Around("execution(* com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao.addUser(..))") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable { System.out.println("环绕通知前...."); Object obj= (Object) joinPoint.proceed(); System.out.println("环绕通知后...."); return obj; } /** * 抛出通知 * @param e */ @AfterThrowing(value="execution(* com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao.addUser(..))",throwing = "e") public void afterThrowable(Throwable e){ System.out.println("出现异常:msg="+e.getMessage()); } /** * 无论什么情况下都会执行的方法 */ @After(value="execution(* com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao.addUser(..))") public void after(){ System.out.println("最终通知...."); } }
编写配置文件交由Spring IOC容器管理
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 启动@aspectj的自动代理支持--> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy /> <!-- 定义目标对象 --> <bean id="userDaos" class="com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.daoimp.UserDaoImp" /> <!-- 定义aspect类 --> <bean name="myAspectJ" class="com.zejian.spring.springAop.AspectJ.MyAspect"/> </beans>
编写测试类
/** * Created by zejian on 2017/2/19.*/ @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(locations= "classpath:spring/spring-aspectj.xml") public class UserDaoAspectJ { @Autowired UserDao userDao; @Test public void aspectJTest(){ userDao.addUser(); } }
简单说明一下,定义了一个目标类UserDaoImpl,利用Spring2.0引入的aspect注解开发功能定义aspect类即MyAspect,在该aspect类中,编写了5种注解类型的通知函数,分别是前置通知@Before、后置通知@AfterReturning、环绕通知@Around、异常通知@AfterThrowing、最终通知@After,在注解通知上使用execution关键字定义的切点表达式,即指明该通知要应用的目标函数,当只有一个execution参数时,value属性可以省略,当含两个以上的参数,value必须注明,例如存在返回值时。当然除了把切点表达式直接传递给通知注解类型外,还可以使用@pointcut来定义切点匹配表达式。目标类和aspect类定义完成后,所有类的创建都交由SpringIOC容器处理,注意,使用Spring AOP 的aspectJ功能时,需要引用 aspectJ 的 jar 包: aspectjweaver.jar aspectjrt.jar aspectj.jar aopalliance.jar,另外需要使用以下代码启动aspect的注解功能支持:
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
ok~,运行程序,结果符合预期:
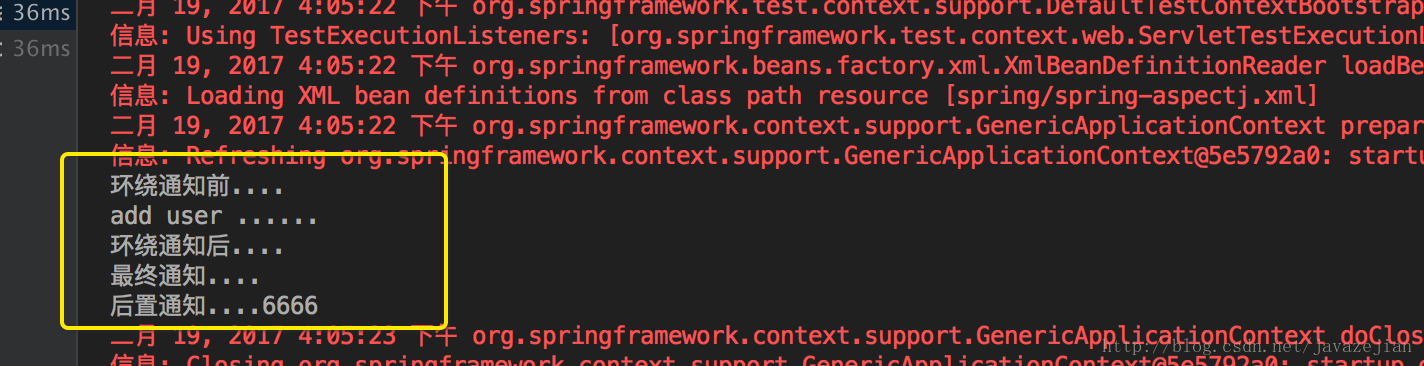
定义切入点函数
在案例中,定义过滤切入点函数时,是直接把execution以定义匹配表达式作为值传递给通知类型的如下:
@After(value="execution(* com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao.addUser(..))") public void after(){ System.out.println("最终通知...."); }
除了上述方式外,还可采用与ApectJ中使用pointcut关键字类似的方式定义切入点表达式如下,使用@Pointcut注解:
/** * 使用Pointcut定义切点 */ @Pointcut("execution(* com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao.addUser(..))") private void myPointcut(){} /** * 应用切入点函数 */ @After(value="myPointcut()") public void afterDemo(){ System.out.println("最终通知...."); }
使用@Pointcut注解进行定义,应用到通知函数afterDemo()时直接传递切点表达式的函数名称myPointcut()即可。
切入点指示符
为了方法通知应用到相应过滤的目标方法上,SpringAOP提供了匹配表达式,这些表达式也叫切入点指示符,在前面的案例中,它们已多次出现。
通配符
在定义匹配表达式时,通配符几乎随处可见,如*、.. 、+ ,它们的含义如下:
-
.. :匹配方法定义中的任意数量的参数,此外还匹配类定义中的任意数量包
//任意返回值,任意名称,任意参数的公共方法 execution(public * *(..)) //匹配com.zejian.dao包及其子包中所有类中的所有方法 within(com.zejian.dao..*) -
+ :匹配给定类的任意子类
//匹配实现了DaoUser接口的所有子类的方法 within(com.zejian.dao.DaoUser+) -
* :匹配任意数量的字符
//匹配com.zejian.service包及其子包中所有类的所有方法 within(com.zejian.service..*) //匹配以set开头,参数为int类型,任意返回值的方法 execution(* set*(int))
类型签名表达式
为了方便类型(如接口、类名、包名)过滤方法,Spring AOP 提供了within关键字。其语法格式如下:
within(<type name>)
type name 则使用包名或者类名替换即可,来点案例吧。
//匹配com.zejian.dao包及其子包中所有类中的所有方法
@Pointcut("within(com.zejian.dao..*)")
//匹配UserDaoImpl类中所有方法
@Pointcut("within(com.zejian.dao.UserDaoImpl)")
//匹配UserDaoImpl类及其子类中所有方法
@Pointcut("within(com.zejian.dao.UserDaoImpl+)")
//匹配所有实现UserDao接口的类的所有方法
@Pointcut("within(com.zejian.dao.UserDao+)")
方法签名表达式
如果想根据方法签名进行过滤,关键字execution可以帮到我们,语法表达式如下
//scope :方法作用域,如public,private,protect //returnt-type:方法返回值类型 //fully-qualified-class-name:方法所在类的完全限定名称 //parameters 方法参数 execution(<scope> <return-type> <fully-qualified-class-name>.*(parameters))
对于给定的作用域、返回值类型、完全限定类名以及参数匹配的方法将会应用切点函数指定的通知,这里给出模型案例:
//匹配UserDaoImpl类中的所有方法
@Pointcut("execution(* com.zejian.dao.UserDaoImpl.*(..))")
//匹配UserDaoImpl类中的所有公共的方法
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.zejian.dao.UserDaoImpl.*(..))")
//匹配UserDaoImpl类中的所有公共方法并且返回值为int类型
@Pointcut("execution(public int com.zejian.dao.UserDaoImpl.*(..))")
//匹配UserDaoImpl类中第一个参数为int类型的所有公共的方法
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.zejian.dao.UserDaoImpl.*(int , ..))")
其他指示符
-
bean:Spring AOP扩展的,AspectJ没有对于指示符,用于匹配特定名称的Bean对象的执行方法;
//匹配名称中带有后缀Service的Bean。 @Pointcut("bean(*Service)") private void myPointcut1(){} -
this :用于匹配当前AOP代理对象类型的执行方法;请注意是AOP代理对象的类型匹配,这样就可能包括引入接口也类型匹配
//匹配了任意实现了UserDao接口的代理对象的方法进行过滤 @Pointcut("this(com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao)") private void myPointcut2(){} -
target :用于匹配当前目标对象类型的执行方法;
//匹配了任意实现了UserDao接口的目标对象的方法进行过滤 @Pointcut("target(com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao)") private void myPointcut3(){} -
@within:用于匹配所以持有指定注解类型内的方法;请注意与within是有区别的, within是用于匹配指定类型内的方法执行;
//匹配使用了MarkerAnnotation注解的类(注意是类) @Pointcut("@within(com.zejian.spring.annotation.MarkerAnnotation)") private void myPointcut4(){} -
@annotation(com.zejian.spring.MarkerMethodAnnotation) : 根据所应用的注解进行方法过滤
//匹配使用了MarkerAnnotation注解的方法(注意是方法) @Pointcut("@annotation(com.zejian.spring.annotation.MarkerAnnotation)") private void myPointcut5(){}
ok~,关于表达式指示符就介绍到这,我们主要关心前面几个常用的即可,不常用过印象即可。这里最后说明一点,切点指示符可以使用运算符语法进行表达式的混编,如and、or、not(或者&&、||、!),如下一个简单例子:
//匹配了任意实现了UserDao接口的目标对象的方法并且该接口不在com.zejian.dao包及其子包下 @Pointcut("target(com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao) !within(com.zejian.dao..*)") private void myPointcut6(){} //匹配了任意实现了UserDao接口的目标对象的方法并且该方法名称为addUser @Pointcut("target(com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao)&&execution(* com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao.addUser(..))") private void myPointcut7(){}
通知函数以及传递参数
5种通知函数
通知在前面的Spring AOP的入门案例已见过面,在Spring中,通知主要分5种类型,分别是前置通知、后置通知、异常通知、最终通知以及环绕通知,下面分别介绍。
-
前置通知@Before
前置通知通过@Before注解进行标注,并可直接传入切点表达式的值,该通知在目标函数执行前执行,注意JoinPoint,是Spring提供的静态变量,通过joinPoint 参数,可以获取目标对象的信息,如类名称,方法参数,方法名称等,,该参数是可选的。
/**
* 前置通知
* @param joinPoint 该参数可以获取目标对象的信息,如类名称,方法参数,方法名称等
*/
@Before("execution(* com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao.addUser(..))")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("我是前置通知");
}
- 后置通知@AfterReturning
通过@AfterReturning注解进行标注,该函数在目标函数执行完成后执行,并可以获取到目标函数最终的返回值returnVal,当目标函数没有返回值时,returnVal将返回null,必须通过returning = “returnVal”注明参数的名称而且必须与通知函数的参数名称相同。请注意,在任何通知中这些参数都是可选的,需要使用时直接填写即可,不需要使用时,可以完成不用声明出来。如下
/**
* 后置通知,不需要参数时可以不提供
*/
@AfterReturning(value="execution(* com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao.*User(..))")
public void AfterReturning(){
System.out.println("我是后置通知...");
}
/**
* 后置通知
* returnVal,切点方法执行后的返回值
*/
@AfterReturning(value="execution(* com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao.*User(..))",returning = "returnVal")
public void AfterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object returnVal){
System.out.println("我是后置通知...returnVal+"+returnVal);
}
- 异常通知 @AfterThrowing
该通知只有在异常时才会被触发,并由throwing来声明一个接收异常信息的变量,同样异常通知也用于Joinpoint参数,需要时加上即可,如下:
/** * 抛出通知 * @param e 抛出异常的信息 */ @AfterThrowing(value="execution(* com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao.addUser(..))",throwing = "e") public void afterThrowable(Throwable e){ System.out.println("出现异常:msg="+e.getMessage()); }
- 最终通知 @After
该通知有点类似于finally代码块,只要应用了无论什么情况下都会执行。
/** * 无论什么情况下都会执行的方法 * joinPoint 参数 */ @After("execution(* com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao.*User(..))") public void after(JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.println("最终通知...."); }
- 环绕通知@Around
环绕通知既可以在目标方法前执行也可在目标方法之后执行,更重要的是环绕通知可以控制目标方法是否指向执行,但即使如此,我们应该尽量以最简单的方式满足需求,在仅需在目标方法前执行时,应该采用前置通知而非环绕通知。案例代码如下第一个参数必须是ProceedingJoinPoint,通过该对象的proceed()方法来执行目标函数,proceed()的返回值就是环绕通知的返回值。同样的,ProceedingJoinPoint对象也是可以获取目标对象的信息,如类名称,方法参数,方法名称等等。
@Around("execution(* com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao.*User(..))")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("我是环绕通知前....");
//执行目标函数
Object obj= (Object) joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("我是环绕通知后....");
return obj;
}
通知传递参数
在Spring AOP中,除了execution和bean指示符不能传递参数给通知方法,其他指示符都可以将匹配的方法相应参数或对象自动传递给通知方法。获取到匹配的方法参数后通过”argNames”属性指定参数名。如下,需要注意的是args(指示符)、argNames的参数名与before()方法中参数名 必须保持一致即param。
@Before(value="args(param)", argNames="param") //明确指定了 public void before(int param) { System.out.println("param:" + param); }
当然也可以直接使用args指示符不带argNames声明参数,如下:
@Before("execution(public * com.zejian..*.addUser(..)) && args(userId,..)")
public void before(int userId) {
//调用addUser的方法时如果与addUser的参数匹配则会传递进来会传递进来
System.out.println("userId:" + userId);
}
args(userId,..)该表达式会保证只匹配那些至少接收一个参数而且传入的类型必须与userId一致的方法,记住传递的参数可以简单类型或者对象,而且只有参数和目标方法也匹配时才会有值传递进来。
Aspect优先级
在不同的切面中,如果有多个通知需要在同一个切点函数指定的过滤目标方法上执行,那些在目标方法前执行(”进入”)的通知函数,最高优先级的通知将会先执行,在执行在目标方法后执行(“退出”)的通知函数,最高优先级会最后执行。而对于在同一个切面定义的通知函数将会根据在类中的声明顺序执行。如下:
package com.zejian.spring.springAop.AspectJ; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; /** * Created by zejian on 2017/2/20.*/ @Aspect public class AspectOne { /** * Pointcut定义切点函数 */ @Pointcut("execution(* com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao.deleteUser(..))") private void myPointcut(){} @Before("myPointcut()") public void beforeOne(){ System.out.println("前置通知....执行顺序1"); } @Before("myPointcut()") public void beforeTwo(){ System.out.println("前置通知....执行顺序2"); } @AfterReturning(value = "myPointcut()") public void AfterReturningThree(){ System.out.println("后置通知....执行顺序3"); } @AfterReturning(value = "myPointcut()") public void AfterReturningFour(){ System.out.println("后置通知....执行顺序4"); } }
在同一个切面中定义多个通知响应同一个切点函数,执行顺序为声明顺序:
如果在不同的切面中定义多个通知响应同一个切点,进入时则优先级高的切面类中的通知函数优先执行,退出时则最后执行,如下定义AspectOne类和AspectTwo类并实现org.springframework.core.Ordered 接口,该接口用于控制切面类的优先级,同时重写getOrder方法,定制返回值,返回值(int 类型)越小优先级越大。其中AspectOne返回值为0,AspectTwo的返回值为3,显然AspectOne优先级高于AspectTwo。
/** * Created by zejian on 2017/2/20.*/ @Aspect public class AspectOne implements Ordered { /** * Pointcut定义切点函数 */ @Pointcut("execution(* com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao.deleteUser(..))") private void myPointcut(){} @Before("myPointcut()") public void beforeOne(){ System.out.println("前置通知..AspectOne..执行顺序1"); } @Before("myPointcut()") public void beforeTwo(){ System.out.println("前置通知..AspectOne..执行顺序2"); } @AfterReturning(value = "myPointcut()") public void AfterReturningThree(){ System.out.println("后置通知..AspectOne..执行顺序3"); } @AfterReturning(value = "myPointcut()") public void AfterReturningFour(){ System.out.println("后置通知..AspectOne..执行顺序4"); } /** * 定义优先级,值越低,优先级越高 * @return */ @Override public int getOrder() { return 0; } } //切面类 AspectTwo.java @Aspect public class AspectTwo implements Ordered { /** * Pointcut定义切点函数 */ @Pointcut("execution(* com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.UserDao.deleteUser(..))") private void myPointcut(){} @Before("myPointcut()") public void beforeOne(){ System.out.println("前置通知....执行顺序1--AspectTwo"); } @Before("myPointcut()") public void beforeTwo(){ System.out.println("前置通知....执行顺序2--AspectTwo"); } @AfterReturning(value = "myPointcut()") public void AfterReturningThree(){ System.out.println("后置通知....执行顺序3--AspectTwo"); } @AfterReturning(value = "myPointcut()") public void AfterReturningFour(){ System.out.println("后置通知....执行顺序4--AspectTwo"); } /** * 定义优先级,值越低,优先级越高 * @return */ @Override public int getOrder() { return 2; } }
运行结果如下:
案例中虽然只演示了前置通知和后置通知,但其他通知也遵循相同的规则,有兴趣可自行测试。到此基于注解的Spring AOP 分析就结束了,但请注意,在配置文件中启动@Aspect支持后,Spring容器只会尝试自动识别带@Aspect的Bean,前提是任何定义的切面类都必须已在spring容器中声明。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!--<context:component-scan base-package=""--> <!-- 启动@aspectj的自动代理支持--> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy /> <!-- 定义目标对象 --> <bean id="userDaos" class="com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.daoimp.UserDaoImp" /> <!-- 定义aspect类 --> <bean name="myAspectJ" class="com.zejian.spring.springAop.AspectJ.MyAspect"/> <bean name="aspectOne" class="com.zejian.spring.springAop.AspectJ.AspectOne" /> <bean name="aspectTwo" class="com.zejian.spring.springAop.AspectJ.AspectTwo" /> </beans>
基于XML的开发
前面分析完基于注解支持的开发是日常应用中最常见的,即使如此我们还是有必要了解一下基于xml形式的Spring AOP开发,这里会以一个案例的形式对xml的开发形式进行简要分析,定义一个切面类
/** * Created by zejian on 2017/2/20.*/ public class MyAspectXML { public void before(){ System.out.println("MyAspectXML====前置通知"); } public void afterReturn(Object returnVal){ System.out.println("后置通知-->返回值:"+returnVal); } public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable { System.out.println("MyAspectXML=====环绕通知前"); Object object= joinPoint.proceed(); System.out.println("MyAspectXML=====环绕通知后"); return object; } public void afterThrowing(Throwable throwable){ System.out.println("MyAspectXML======异常通知:"+ throwable.getMessage()); } public void after(){ System.out.println("MyAspectXML=====最终通知..来了"); } }
通过配置文件的方式声明如下(spring-aspectj-xml.xml):
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!--<context:component-scan base-package=""--> <!-- 定义目标对象 --> <bean name="productDao" class="com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.daoimp.ProductDaoImpl" /> <!-- 定义切面 --> <bean name="myAspectXML" class="com.zejian.spring.springAop.AspectJ.MyAspectXML" /> <!-- 配置AOP 切面 --> <aop:config> <!-- 定义切点函数 --> <aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.ProductDao.add(..))" /> <!-- 定义其他切点函数 --> <aop:pointcut id="delPointcut" expression="execution(* com.zejian.spring.springAop.dao.ProductDao.delete(..))" /> <!-- 定义通知 order 定义优先级,值越小优先级越大--> <aop:aspect ref="myAspectXML" order="0"> <!-- 定义通知 method 指定通知方法名,必须与MyAspectXML中的相同 pointcut 指定切点函数 --> <aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pointcut" /> <!-- 后置通知 returning="returnVal" 定义返回值 必须与类中声明的名称一样--> <aop:after-returning method="afterReturn" pointcut-ref="pointcut" returning="returnVal" /> <!-- 环绕通知 --> <aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pointcut" /> <!--异常通知 throwing="throwable" 指定异常通知错误信息变量,必须与类中声明的名称一样--> <aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowing" pointcut-ref="pointcut" throwing="throwable"/> <!-- method : 通知的方法(最终通知) pointcut-ref : 通知应用到的切点方法 --> <aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> </beans>
声明方式和定义方式在代码中已很清晰了,了解一下即可,在实际开发中,会更倾向与使用注解的方式开发,毕竟更简单更简洁。
参考资料
http://blog.csdn.net/javazejian/article/details/56267036#基于aspect-spring-aop-开发
http://shouce.jb51.net/spring/aop.html

