1.Overview
这篇文章主要分享从源代码角度解读wpf中xaml。由于源码查看起来错综复杂“随便找一个对象按下F12就是一个新的世界”,看源码的感觉就是在盗梦空间里来回穿梭;所以也是耗费很长的时间去阅读源码然后根据自己的理解编写文章和贴出部分关键源码。
2.Detail
大概将从编写、保存、编译、读取、加载这几个维度来解读。以防后面看源码会晕,先直接讲结果;
- 编写

- 编译

- 读取、加载
有的帅气的观众就会问了,这些研究在实际在项目中应用场景是什么?
选择性的加载xaml(baml)文件来达到更改UI的操作。
- 动态换肤,大家都用过手机app每到过年过节都会看到界面上会出现对应的主题,那么我们就可以在程序内设定到了某个节日直接加载对应主题界面的xaml(baml)文件来达到这种效果,对于动态皮肤场景来说,在运行时加载和解析XAML是有意义的。
- 适应不同分辨率的布局
- 简单固定的UI美工人员将设计稿转换为位图,可使用blend或者 expression design转成对应的wpf界面
还可以适配不同的业务要求。可能这种延伸就是研究的意义吧
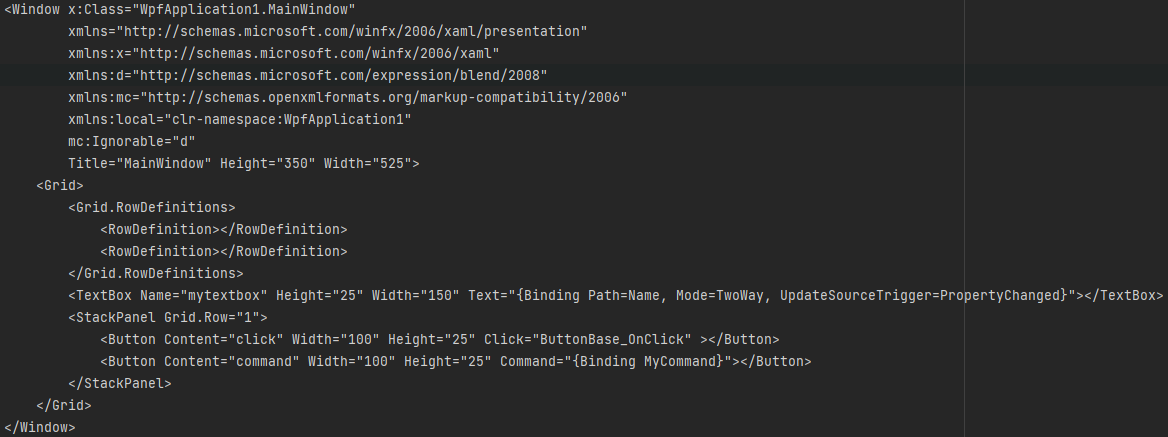
(1)编写xaml
XAML 文档中的每个元素都映射为.NET 类的一个实例。元素的名称也完全对应于类 名。例如,元素指示 WPF 创建 Button 对象。
(2)保存xaml
(3)编译xaml
XAML不仅要能够解决涉及协作问题,它还需要快速运行。尽管基于XML格式可以很灵活并且很容易地迁移到其他平台和工具,但未必是有效的选择。XML的涉及目标是具有逻辑性、易读而且简单,没有被压缩。WPF 使用 BAML(Binaiy Application Markup Language,二进制应用程序标记语言)来克服这 个缺点。BAML 并非新事物,它实际上就是 XAML 的二进制表示,当在 Visual Studio 中编译 WPF 应用程序时,所有 XAML 文件都被转换为 BAML这些 BAML 然后作为资源被嵌入到最 终的 DLL 或 EXE 程序集中。BAML 是标记化的,这意味着较长的 XAML 被较短的标记替代。 BAML 不仅明显小一些,还对其进行了优化,从而使它在运行时能够更快地解析。并成为一个内嵌资源;
BAML由VS编译生成存在,obj目录的debug下;
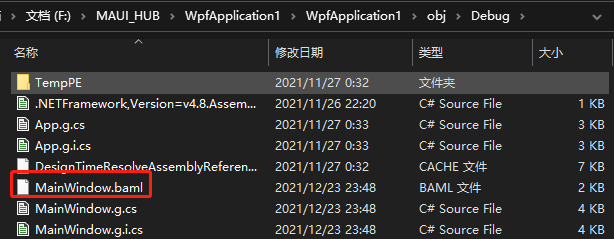
通过IL反编译项目文件之后,可以看到编译完成之后将会被连接到工程的“资源清单”当中。
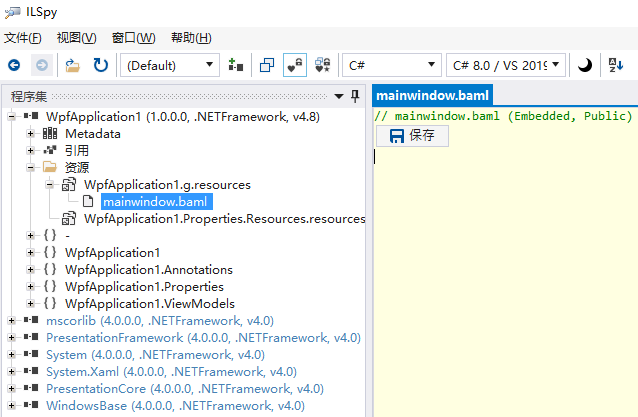
使用Assembly的GetManifestResourceStream方法,可以在运行期获取到这个二进制流
Assembly asm = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly( );
Stream s = asm.GetManifestResourceStream("StreamName");
(4)读取、加载xaml(baml)
使用代码和未经编译的标记(XAML),这种具体方式对于某些特殊情况是很苻意义的* 例如创建高度动态化的用户界面。这种方式在运行时使用 System.Windows.Markup 名 称空间中的 从 XAML 文件中加载部分用户界面。 使用代码和编译过的标记(BAML),对于 WPF 而言这是一种更好的方式,也是 Visual Studio 支持的一种方式。这种方式为每个窗口创建一个 XAML 橫板,这个 XAML 模板 被编译为 BAML,并嵌入到最终的程序集中。编译过的 BAML 在运行时被提取出来, 用于重新生成用户界面。
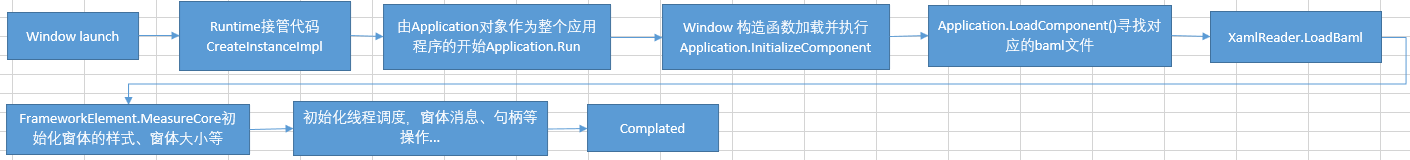
- 1.当客户端程序被启动时Runtime接管代码来创建window实例
internal object CreateInstanceImpl(
BindingFlags bindingAttr,
Binder binder,
object[] args,
CultureInfo culture,
object[] activationAttributes,
ref StackCrawlMark stackMark)
{
this.CreateInstanceCheckThis();
object obj = (object) null;
try
{
try
{
if (activationAttributes != null)
ActivationServices.PushActivationAttributes((Type) this, activationAttributes);
if (args == null)
args = EmptyArray<object>.Value;
int length = args.Length;
if (binder == null)
binder = Type.DefaultBinder;
if (length == 0 && (bindingAttr & BindingFlags.Public) != BindingFlags.Default && (bindingAttr & BindingFlags.Instance) != BindingFlags.Default && (this.IsGenericCOMObjectImpl() || this.IsValueType))
{
obj = this.CreateInstanceDefaultCtor((bindingAttr & BindingFlags.NonPublic) == BindingFlags.Default, false, true, ref stackMark);
}
else
{
ConstructorInfo[] constructors = this.GetConstructors(bindingAttr);
List<MethodBase> methodBaseList = new List<MethodBase>(constructors.Length);
Type[] argumentTypes = new Type[length];
for (int index = 0; index < length; ++index)
{
if (args[index] != null)
argumentTypes[index] = args[index].GetType();
}
for (int index = 0; index < constructors.Length; ++index)
{
if (RuntimeType.FilterApplyConstructorInfo((RuntimeConstructorInfo) constructors[index], bindingAttr, CallingConventions.Any, argumentTypes))
methodBaseList.Add((MethodBase) constructors[index]);
}
MethodBase[] methodBaseArray = new MethodBase[methodBaseList.Count];
methodBaseList.CopyTo(methodBaseArray);
if (methodBaseArray != null && methodBaseArray.Length == 0)
methodBaseArray = (MethodBase[]) null;
if (methodBaseArray == null)
{
if (activationAttributes != null)
{
ActivationServices.PopActivationAttributes((Type) this);
activationAttributes = (object[]) null;
}
throw new MissingMethodException(Environment.GetResourceString("MissingConstructor_Name", (object) this.FullName));
}
object state = (object) null;
MethodBase methodBase;
try
{
methodBase = binder.BindToMethod(bindingAttr, methodBaseArray, ref args, (ParameterModifier[]) null, culture, (string[]) null, out state);
}
catch (MissingMethodException ex)
{
methodBase = (MethodBase) null;
}
if (methodBase == (MethodBase) null)
{
if (activationAttributes != null)
{
ActivationServices.PopActivationAttributes((Type) this);
activationAttributes = (object[]) null;
}
throw new MissingMethodException(Environment.GetResourceString("MissingConstructor_Name", (object) this.FullName));
}
if (RuntimeType.DelegateType.IsAssignableFrom(methodBase.DeclaringType))
new SecurityPermission(SecurityPermissionFlag.UnmanagedCode).Demand();
if (methodBase.GetParametersNoCopy().Length == 0)
{
if (args.Length != 0)
throw new NotSupportedException(string.Format((IFormatProvider) CultureInfo.CurrentCulture, Environment.GetResourceString("NotSupported_CallToVarArg")));
obj = Activator.CreateInstance((Type) this, true);
}
else
{
obj = ((ConstructorInfo) methodBase).Invoke(bindingAttr, binder, args, culture);
if (state != null)
binder.ReorderArgumentArray(ref args, state);
}
}
}
finally
{
if (activationAttributes != null)
{
ActivationServices.PopActivationAttributes((Type) this);
activationAttributes = (object[]) null;
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw;
}
return obj;
}
- 2.Window构造函数调用Application.LoadComponent读取创建.xaml(baml)
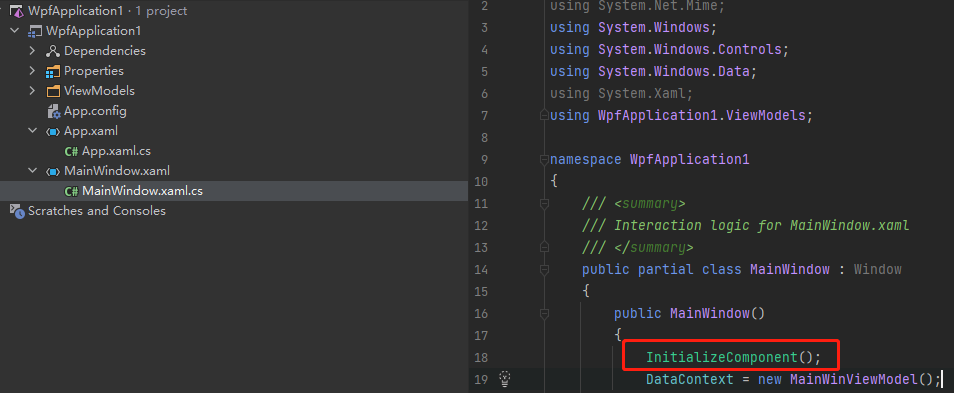
IL反编译后的代码
/// <summary>
/// MainWindow
/// </summary>
public partial class MainWindow : System.Windows.Window, System.Windows.Markup.IComponentConnector {
#line 10 "..\..\..\MainWindow.xaml"
[System.Diagnostics.CodeAnalysis.SuppressMessageAttribute("Microsoft.Performance", "CA1823:AvoidUnusedPrivateFields")]
internal System.Windows.Controls.TextBox textBox;
#line default
#line hidden
private bool _contentLoaded;
/// <summary>
/// InitializeComponent
/// </summary>
[System.Diagnostics.DebuggerNonUserCodeAttribute()]
[System.CodeDom.Compiler.GeneratedCodeAttribute("PresentationBuildTasks", "6.0.0.0")]
public void InitializeComponent() {
if (_contentLoaded) {
return;
}
_contentLoaded = true;
System.Uri resourceLocater = new System.Uri("/WpfApp1;component/mainwindow.xaml", System.UriKind.Relative);
#line 1 "..\..\..\MainWindow.xaml"
System.Windows.Application.LoadComponent(this, resourceLocater);
#line default
#line hidden
}
[System.Diagnostics.DebuggerNonUserCodeAttribute()]
[System.CodeDom.Compiler.GeneratedCodeAttribute("PresentationBuildTasks", "6.0.0.0")]
[System.ComponentModel.EditorBrowsableAttribute(System.ComponentModel.EditorBrowsableState.Never)]
[System.Diagnostics.CodeAnalysis.SuppressMessageAttribute("Microsoft.Design", "CA1033:InterfaceMethodsShouldBeCallableByChildTypes")]
[System.Diagnostics.CodeAnalysis.SuppressMessageAttribute("Microsoft.Maintainability", "CA1502:AvoidExcessiveComplexity")]
[System.Diagnostics.CodeAnalysis.SuppressMessageAttribute("Microsoft.Performance", "CA1800:DoNotCastUnnecessarily")]
void System.Windows.Markup.IComponentConnector.Connect(int connectionId, object target) {
switch (connectionId)
{
case 1:
this.textBox = ((System.Windows.Controls.TextBox)(target));
return;
}
this._contentLoaded = true;
}
}
- 3.Application.LoadComponent()加载baml
public static void LoadComponent(object component, Uri resourceLocator)
{
if (component == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (component));
if (resourceLocator == (Uri) null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (resourceLocator));
if (resourceLocator.OriginalString == null)
throw new ArgumentException(SR.Get("ArgumentPropertyMustNotBeNull", (object) nameof (resourceLocator), (object) "OriginalString"));
Uri curComponentUri = !resourceLocator.IsAbsoluteUri ? new Uri(BaseUriHelper.PackAppBaseUri, resourceLocator) : throw new ArgumentException(SR.Get("AbsoluteUriNotAllowed"));
ParserContext parserContext = new ParserContext();
parserContext.BaseUri = curComponentUri;
Stream stream;
bool closeStream;
if (Application.IsComponentBeingLoadedFromOuterLoadBaml(curComponentUri))
{
NestedBamlLoadInfo nestedBamlLoadInfo = Application.s_NestedBamlLoadInfo.Peek();
stream = nestedBamlLoadInfo.BamlStream;
stream.Seek(0L, SeekOrigin.Begin);
parserContext.SkipJournaledProperties = nestedBamlLoadInfo.SkipJournaledProperties;
nestedBamlLoadInfo.BamlUri = (Uri) null;
closeStream = false;
}
else
{
PackagePart resourceOrContentPart = Application.GetResourceOrContentPart(resourceLocator);
ContentType contentType = new ContentType(resourceOrContentPart.ContentType);
stream = resourceOrContentPart.GetStream();
closeStream = true;
if (!MimeTypeMapper.BamlMime.AreTypeAndSubTypeEqual(contentType))
throw new Exception(SR.Get("ContentTypeNotSupported", (object) contentType));
}
if (!(stream is IStreamInfo streamInfo) || streamInfo.Assembly != component.GetType().Assembly)
throw new Exception(SR.Get("UriNotMatchWithRootType", (object) component.GetType(), (object) resourceLocator));
XamlReader.LoadBaml(stream, parserContext, component, closeStream);
}
XamlReader.LoadBaml细节代码
internal static object LoadBaml(
Stream stream,
ParserContext parserContext,
object parent,
bool closeStream)
{
object p1 = (object) null;
EventTrace.EasyTraceEvent(EventTrace.Keyword.KeywordPerf | EventTrace.Keyword.KeywordXamlBaml, EventTrace.Event.WClientParseBamlBegin, (object) parserContext.BaseUri);
if (TraceMarkup.IsEnabled)
TraceMarkup.Trace(TraceEventType.Start, TraceMarkup.Load);
try
{
if (stream is IStreamInfo streamInfo2)
parserContext.StreamCreatedAssembly = streamInfo2.Assembly;
Baml2006ReaderSettings bamlReaderSettings = XamlReader.CreateBamlReaderSettings();
bamlReaderSettings.BaseUri = parserContext.BaseUri;
bamlReaderSettings.LocalAssembly = streamInfo2.Assembly;
if (bamlReaderSettings.BaseUri == (Uri) null || string.IsNullOrEmpty(bamlReaderSettings.BaseUri.ToString()))
bamlReaderSettings.BaseUri = BaseUriHelper.PackAppBaseUri;
Baml2006ReaderInternal baml2006ReaderInternal = new Baml2006ReaderInternal(stream, new Baml2006SchemaContext(bamlReaderSettings.LocalAssembly), bamlReaderSettings, parent);
Type type = (Type) null;
if (streamInfo2.Assembly != (Assembly) null)
{
try
{
type = XamlTypeMapper.GetInternalTypeHelperTypeFromAssembly(parserContext);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
if (CriticalExceptions.IsCriticalException(ex))
throw;
}
}
if (type != (Type) null)
{
XamlAccessLevel xamlAccessLevel = XamlAccessLevel.AssemblyAccessTo(streamInfo2.Assembly);
new XamlLoadPermission(xamlAccessLevel).Assert();
try
{
p1 = WpfXamlLoader.LoadBaml((System.Xaml.XamlReader) baml2006ReaderInternal, parserContext.SkipJournaledProperties, parent, xamlAccessLevel, parserContext.BaseUri);
}
finally
{
CodeAccessPermission.RevertAssert();
}
}
else
p1 = WpfXamlLoader.LoadBaml((System.Xaml.XamlReader) baml2006ReaderInternal, parserContext.SkipJournaledProperties, parent, (XamlAccessLevel) null, parserContext.BaseUri);
if (p1 is DependencyObject dependencyObject2)
dependencyObject2.SetValue(BaseUriHelper.BaseUriProperty, (object) bamlReaderSettings.BaseUri);
if (p1 is Application application2)
application2.ApplicationMarkupBaseUri = XamlReader.GetBaseUri(bamlReaderSettings.BaseUri);
}
finally
{
if (TraceMarkup.IsEnabled)
TraceMarkup.Trace(TraceEventType.Stop, TraceMarkup.Load, p1);
EventTrace.EasyTraceEvent(EventTrace.Keyword.KeywordPerf | EventTrace.Keyword.KeywordXamlBaml, EventTrace.Event.WClientParseBamlEnd, (object) parserContext.BaseUri);
if (closeStream && stream != null)
stream.Close();
}
return p1;
}
- 4.加载控件对象
提取BAML(编译过的XAML)解析并创建每个定义的控件对象,设置属性、关联事件等内容。
internal static object LoadBamlStreamWithSyncInfo(Stream stream, ParserContext pc)
{
if (Application.s_NestedBamlLoadInfo == null)
Application.s_NestedBamlLoadInfo = new Stack<NestedBamlLoadInfo>();
NestedBamlLoadInfo nestedBamlLoadInfo = new NestedBamlLoadInfo(pc.BaseUri, stream, pc.SkipJournaledProperties);
Application.s_NestedBamlLoadInfo.Push(nestedBamlLoadInfo);
try
{
return XamlReader.LoadBaml(stream, pc, (object) null, true);
}
finally
{
Application.s_NestedBamlLoadInfo.Pop();
if (Application.s_NestedBamlLoadInfo.Count == 0)
Application.s_NestedBamlLoadInfo = (Stack<NestedBamlLoadInfo>) null;
}
}
循环遍历所有xaml里的标签节点生成窗体内的内容。
private static object Load(
System.Xaml.XamlReader xamlReader,
IXamlObjectWriterFactory writerFactory,
bool skipJournaledProperties,
object rootObject,
XamlObjectWriterSettings settings,
Uri baseUri)
{
XamlContextStack<WpfXamlFrame> stack = new XamlContextStack<WpfXamlFrame>((Func<WpfXamlFrame>) (() => new WpfXamlFrame()));
int persistId = 1;
settings.AfterBeginInitHandler = (EventHandler<XamlObjectEventArgs>) ((sender, args) =>
{
if (EventTrace.IsEnabled(EventTrace.Keyword.KeywordPerf | EventTrace.Keyword.KeywordXamlBaml, EventTrace.Level.Verbose))
{
IXamlLineInfo xamlLineInfo = xamlReader as IXamlLineInfo;
int num1 = -1;
int num2 = -1;
if (xamlLineInfo != null && xamlLineInfo.HasLineInfo)
{
num1 = xamlLineInfo.LineNumber;
num2 = xamlLineInfo.LinePosition;
}
int num3 = (int) EventTrace.EventProvider.TraceEvent(EventTrace.Event.WClientParseXamlBamlInfo, EventTrace.Keyword.KeywordPerf | EventTrace.Keyword.KeywordXamlBaml, EventTrace.Level.Verbose, (object) (args.Instance == null ? 0L : PerfService.GetPerfElementID(args.Instance)), (object) num1, (object) num2);
}
if (args.Instance is UIElement instance3)
{
int num = persistId++;
instance3.SetPersistId(num);
}
XamlSourceInfoHelper.SetXamlSourceInfo(args.Instance, args, baseUri);
if (args.Instance is DependencyObject instance4 && stack.CurrentFrame.XmlnsDictionary != null)
{
XmlnsDictionary xmlnsDictionary = stack.CurrentFrame.XmlnsDictionary;
xmlnsDictionary.Seal();
XmlAttributeProperties.SetXmlnsDictionary(instance4, xmlnsDictionary);
}
stack.CurrentFrame.Instance = args.Instance;
});
XamlObjectWriter xamlWriter = writerFactory == null ? new XamlObjectWriter(xamlReader.SchemaContext, settings) : writerFactory.GetXamlObjectWriter(settings);
IXamlLineInfo xamlLineInfo1 = (IXamlLineInfo) null;
try
{
xamlLineInfo1 = xamlReader as IXamlLineInfo;
IXamlLineInfoConsumer xamlLineInfoConsumer = (IXamlLineInfoConsumer) xamlWriter;
bool shouldPassLineNumberInfo = false;
if (xamlLineInfo1 != null && xamlLineInfo1.HasLineInfo && xamlLineInfoConsumer != null && xamlLineInfoConsumer.ShouldProvideLineInfo)
shouldPassLineNumberInfo = true;
IStyleConnector styleConnector = rootObject as IStyleConnector;
WpfXamlLoader.TransformNodes(xamlReader, xamlWriter, false, skipJournaledProperties, shouldPassLineNumberInfo, xamlLineInfo1, xamlLineInfoConsumer, stack, styleConnector);
xamlWriter.Close();
return xamlWriter.Result;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
if (CriticalExceptions.IsCriticalException(ex) || !XamlReader.ShouldReWrapException(ex, baseUri))
{
throw;
}
else
{
XamlReader.RewrapException(ex, xamlLineInfo1, baseUri);
return (object) null;
}
}
}
// Get the XAML content from an external file.
DependencyObject rootElement;
using (FileStream fs = new FileStrearn(xamlFile, FileMode Open)){
rootElement = (DependencyObject)XamlReader.Load(fs);
}
// Insert the markup into this window.
this.Content = rootElement;
// Find the control with the appropriate
buttonl = (Button)LogicalTreeHelper.FindLogicalNode(rootElement, ibuttonl");
name.
// Wire up the event handler.
buttonl.Click += buttonl 'Click
【截选内容1,这一段引用lindexi文章内的内容,原文地址在文章末尾】在 WPF 中,在 XAML 里面定义的对象的创建,实际上不是完全通过反射来进行创建的,在WPF框架里面,有进行了一系列的优化。将会通过 XamlTypeInvoker 的 CreateInstance 方法来进行对象的创建,而默认的 XamlTypeInvoker 的 CreateInstance 定义如下。还有其他精彩内容在原文里可以查看;
public virtual object CreateInstance(object[] arguments)
{
ThrowIfUnknown();
if (!_xamlType.UnderlyingType.IsValueType && (arguments == null || arguments.Length == 0))
{
object result = DefaultCtorXamlActivator.CreateInstance(this);
if (result != null)
{
return result;
}
}
return CreateInstanceWithActivator(_xamlType.UnderlyingType, arguments);
}
private object CreateInstanceWithActivator(Type type, object[] arguments)
{
return SafeReflectionInvoker.CreateInstance(type, arguments);
}
【截选内容2,这一段引用lindexi文章内的内容,原文地址在文章末尾】
在 EnsureConstructorDelegate 方法里面将会判断如果对象是公开的,那么尝试获取默认构造函数,将默认构造函数做成委托。此时的性能将会是类型第一次进入的时候的速度比较慢,但是后续进入的时候就能使用委托创建,此时性能将会比较好。通过反射创建委托提升性能的方法,详细请看 .NET Core/Framework 创建委托以大幅度提高反射调用的性能 - walterlv
private static bool EnsureConstructorDelegate(XamlTypeInvoker type)
{
// 如果类型初始化过构造函数创建,那么返回,这是缓存的方法
if (type._constructorDelegate != null)
{
return true;
}
// 如果不是公开的方法,那么将无法使用反射创建委托的科技
if (!type.IsPublic)
{
return false;
}
// 反射获取对象的构造函数
Type underlyingType = type._xamlType.UnderlyingType.UnderlyingSystemType;
// Look up public ctors only, for equivalence with Activator.CreateInstance
ConstructorInfo tConstInfo = underlyingType.GetConstructor(Type.EmptyTypes);
IntPtr constPtr = tConstInfo.MethodHandle.GetFunctionPointer();
// 反射创建委托,这样下次访问就不需要使用反射,可以提升性能
// This requires Reflection Permission
Action<object> ctorDelegate = ctorDelegate =
(Action<object>)s_actionCtor.Invoke(new object[] { null, constPtr });
type._constructorDelegate = ctorDelegate;
return true;
}
也就是说只有第一次的类型进入才会调用反射创建委托用来提升性能,之后的进入将会使用第一次创建出来的委托来创建对象,这样能提升性能。
4.Reference
dotnet/wpf: WPF is a .NET Core UI framework for building Windows desktop applications. (github.com)