Keywords
- reasoning 推理
- Deductive reasoning(for a basic logic) 演绎推理
- analogy 类比;比喻 /əˈnælədʒi/
- definition of terminology /ˌtɜːmɪˈnɒlədʒi/术语的定义
- proposition/ˌprɒpəˈzɪʃn/命题
- distinction/dɪˈstɪŋkʃn/n. 区别;差别
- arithmetic /əˈrɪθmətɪk/ 算术,算法
- anthropomorphize/,ænθrəpəʊ'mɔːfaɪz/vt. 赋与人性,人格化
- knowledge base(KB) 知识库
- connectionism /kə'nekʃənizəm/ 联结主义
- retrieval /rɪˈtriːvl/n. 检索;恢复;取回;拯救
- inference: 推理
- entailment:蕴含
- syntax: /ˈsɪntæks/n. 语法;句法;
- semantic: /sɪˈmæntɪk/adj. 语义的;语义学的
- falsity: /ˈfɔːlsəti/n. 虚伪;错误;谎言;不真实
- notation /nəʊˈteɪʃn/n. 符号
- terminology:/ˌtɜːmɪˈnɒlədʒi/n. 术语,术语学;用辞
- theorem/ˈθɪərəm/n. [数] 定理;原理
- axiom: /ˈæksiəm/n. [数] 公理
- iff: 当且仅当
- K |= a是语义蕴含,K |- b是形式推演
What's all the Fuss about?
- Resources required to solve a problem
- Time(computational complexity)
- Memory
- Some problem are easy to solve
- 1+1=?
- This is good!
- Some problems are difficult to solve
- Playing chess, scheduling/timetabling...
- Is this bad?
- Some problems cannot be solved!
- Reasoning, planning,...
What is knowledge?
- taking the world to be one way and not another
- the propositions for the true or false encode what you know about the world.
What is representation?
- symbolic encoding of propositions believed by some agent 命题的符号编码,由某些行为者相信
- symbols standing for things in the world
What is reasoning?
- Manipulation of symbols encoding propositions to produce representations of new propositions.对编码命题的符号进行操作,以产生新命题的表示。
Why knowledge?
- taking an intentional stance
Why representation?
- intentional stance says nothing about what is / is not represented symbolically
Why reasoning?
- Want knowledge to affect action
- We don't want to do action A if sentence P is in KB,
- But rather do action A if world believed in satisfies P
- Difference:
- P may not be explicitly represented
- Need to apply what is known to particulars of given situation
- Usually need more than just DB-style retrieval of facts in the KB
Entailment
- Sentences P1, P2, ..., Pn entail sentence P iff the truth of P is implicit in the truth of P1, P2, ..., Pn
- Inference: the process of calculating entailments
- sound: get only entailment
- complete: get all entailment
- Sometimes want unsound / incomplete reasoning
- Logic: study of entailment relations
Using Logic
- No universal language / semantics
- No universal reasoning scheme
- Start with first-order predicate calculus(FOL)
Why do we need formal Knowledge Representation?
- Natural languages exhibit ambiguity
- ambiguity make it difficult to make any inferences
Syntax vs Semantics
- Syntax: Describe the legal sentences in a knowledge representation language.
- Semantics: Refers to the meaning of sentences. Semantics talks about truth and falsity.
Propositions
- Propositions are statements of fact.
- We shall use single letters to represent propositions
- P: Socrates is bald.
Formulae in Propositional Logic
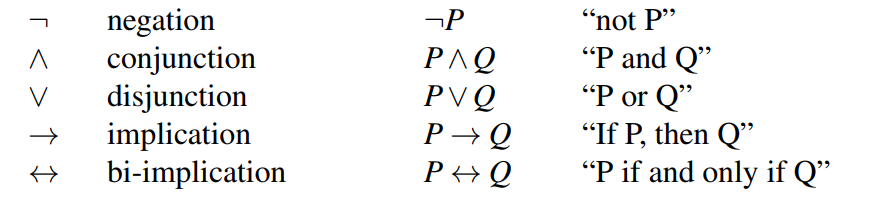
Syntax
- BNF grammar
- Sentence ::= AtomicSentence || ComplexSentence
- AtomicSentence ::= True || False || P || Q || R || . .
- ComplexSentence ::= ( Sentence ) || Sentence Connective Sentence || ¬ Sentence
- Connective ::= ∧ || ∨ || → || ↔
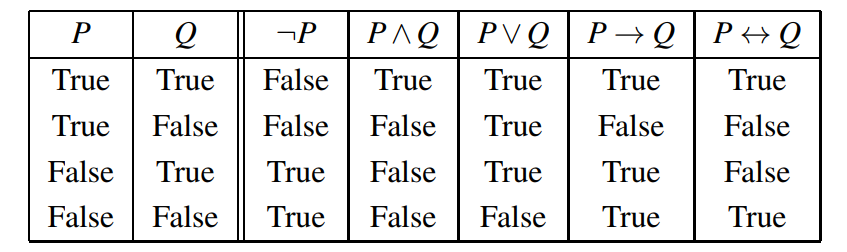
Semantics
- The semantics of the connectives can be given by truth tables. It determines the semantics for complex formulae.
What is a logic?
- A logic consists of:
- A formal system for expressing knowledge about a domain consisting of
- Syntax: Sentences(well formed formulae)
- Semantics: Meaning
- A proof theory: rules of inference for deducing sentences from a knowledge base
Provability
- λ ⊢ ρ: we can construct a proof for ρ from λ using axioms and rules of inference
- If λ is empty (i.e., 0⊢ρ) and ρ is a single formula, then we say that ρ is a theorem of the logic
Entailment
- λ |= ρ: whenever the formula(s) λ are true, one of the formula(s) in ρ is true
- In the case where ρ is a single formula, we can determine whether λ |= ρ by constructing a truth table for λ and ρ. If, in any row of the truth table where all the formulae in λ are true, ρ is also true, then λ |= ρ.
- If λ is empty, we say that ρ is a tautology
Soundness and Completeness
- λ |= a是语义蕴含, λ |- b是形式推演
- An inference procedure (and hence a logic) is sound if and only if it preserves truth
- In other words ⊢ is sound iff whenever λ ⊢ ρ, then λ |= ρ
- Soundness 是说右侧推演的知识都是被λ蕴含的(推出来的知识都是正确的)
- A logic is complete if and only if it is capable of proving all truths
- In other words, whenever λ |= ρ, then λ ⊢ ρ
- Completeness 是说,左侧蕴含出来的知识都可以推演出来
- A logic is decidable if and only if we can write a mechanical procedure (computer program) which when asked λ ⊢ ρ it can eventually halt and answer “yes” or answer “no”