一.安装目前最流行的包之一 matplotlib
1.绘制简单的折线图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt input_values = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8] squares = [1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64] #linewidth线条粗细 plt.plot(input_values, squares, linewidth=5) #设置图标标题,fontproperties字体变量 plt.title("平方数图形",fontproperties='SimHei', fontsize=14) #给x轴设置标题 plt.xlabel("数字", fontproperties='SimHei',fontsize=14) #给y轴设置标题 plt.ylabel("数的平方", fontproperties='SimHei',fontsize=14) #设置刻度标记的大小 plt.tick_params(axis='both', labelsize=14) plt.show()
运行之后

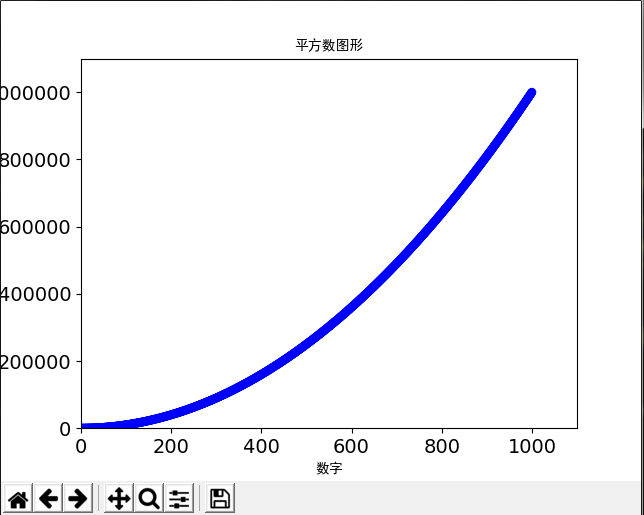
2.绘制散点图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #x轴是一个列表 x_values = list(range(1, 1001)) #y轴用x的值遍历之后平方 y_values = [x**2 for x in x_values] #使用scatter函数生成散点图,参数c设置要使用的颜色 plt.scatter(x_values, y_values, c='blue', edgecolor='none', s=40) plt.title("平方数图形",fontproperties='SimHei',fontsize=10) plt.xlabel("数字", fontproperties='SimHei',fontsize=10) plt.ylabel("数的平方", fontproperties='SimHei',fontsize=10) # 设置刻度标记 plt.tick_params(axis='both', which='major', labelsize=14) # 设置x,y轴的坐标范围 plt.axis([0, 1100, 0, 1100000]) plt.show()
如果要保存图表可以将
plt.show( )改为 plt.savefig('shu.png',bbox_inches='tight')
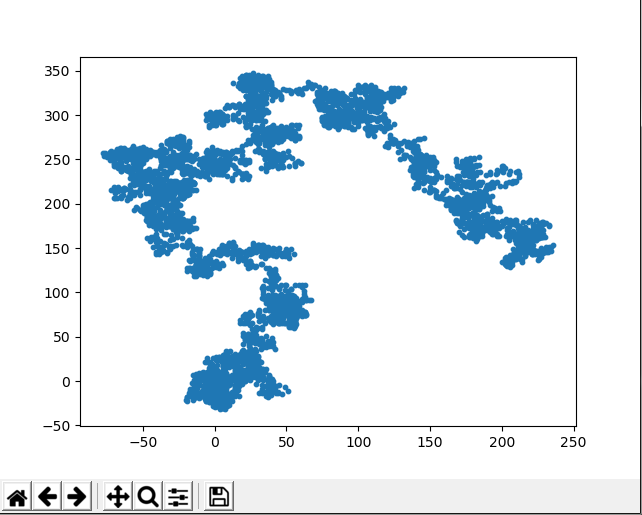
3.随机漫步
随机漫步是又一系列随机决策决定的,模拟随机漫步要先创建RandomWalk( )类
from random import choice class RandomWalk(): def __init__(self, num_points=5000): #设置5000个随机点 self.num_points = num_points # 所有随机点都是从(0,0)开始. self.x_values = [0] self.y_values = [0] def fill_walk(self): #判断x轴有没有到达设置的长度 while len(self.x_values) < self.num_points: #判断随机点的发现是前进还是后退 x_direction = choice([1, -1]) #每一次走多远,随机产生一个 x_distance = choice([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]) #x轴移动距离 x_step = x_direction * x_distance y_direction = choice([1, -1]) y_distance = choice([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]) y_step = y_direction * y_distance # 判断是否原地不动 if x_step == 0 and y_step == 0: continue # 计算下一个点 next_x = self.x_values[-1] + x_step next_y = self.y_values[-1] + y_step #将下一个点添加到列表x_values,y_values后面 self.x_values.append(next_x) self.y_values.append(next_y)
下面将随机慢点所有的点都绘制出来
from random_walk import RandomWalk
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
rw=RandomWalk() rw.fill_walk() plt.scatter(rw.x_values,rw.y_values,s=10) plt.show()