本文转自边缘计算k3s社区
前 言
随着Kubernetes生态系统的发展,新的技术正在被开发出来,以实现更广泛的应用和用例。边缘计算的发展推动了对其中一些技术的需求,以实现将Kubernetes部署到网络边缘资源受限的基础设施上。在这篇文章中,我们将向你介绍一种将k3OS部署到边缘的方法。你可以使用这种方法将你的边缘机自动注册到Rancher实例中作为控制平面。我们还将讨论自动部署到物理机的一些好处。
k3OS于2019年4月由业界应用最为广泛的Kubernetes管理平台创建者Rancher Labs(以下简称Rancher)推出,它是一个轻量的、专注于边缘的Kubernetes操作系统,同时也是业界首个Kubernetes操作系统。它与K3s打包,使得应用程序能够轻松地部署到资源受限的环境中,如部署在边缘设备上。
虽然k3OS仍处于起步阶段,但它已经通过了实战测试,并被用于各种生产环境中。为了充分掌握边缘计算的全部优势,你需要在你部署的基础设施上尽可能地节省空间。
Argo简介
Argo是云原生计算基金会(CNCF)的一个项目,旨在减轻在容器原生环境中运行计算密集型工作负载的一些痛苦。子项目Argo workflow是一个开源的容器原生workflow引擎,用于协调Kubernetes中的并行job。它以Kubernetes自定义资源(CRD)的形式实现,本质上是Kubernetes API的扩展。
通过Argo workflow,我们可以定义workflow,其中的每一步都是一个容器,并将多步工作流建模为任务序列,或使用有向无环图(DAG)捕获任务之间的依赖关系。这在自动化部署和配置边缘原生服务时非常有用。我们将在本次demo的后面看到Argo Workflows的许多方面将会发挥作用。
Step 1 设置一个demo环境
为了模拟一个工作边缘站点,我们需要在本地虚拟机上启动k3OS,然后使用Argo工作流呼叫到远程Rancher实例。在本节中,我们将:
-
下载k3OS
iso -
部署Rancher
-
安装Argo Workflows
设置本地VM(边缘端)
安装VirtualBox不在本次演示的范围内,因此默认你已经安装完成。然后,我们将其启动并完成设置虚拟机和附加k3OS iso的初始过程。完成之后,我们将启动机器并看到介绍屏幕:
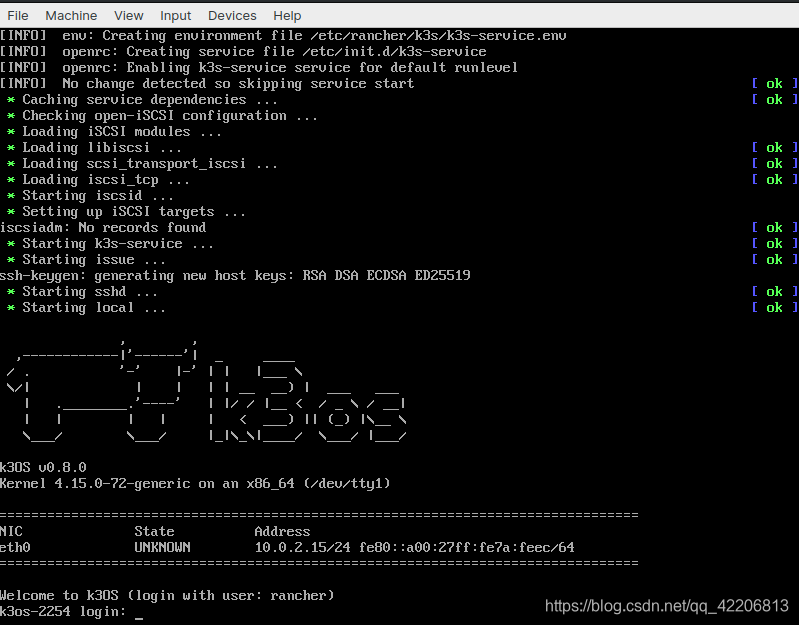
此时,我们将打开一个terminal并添加k3OS VM到我们的config.yaml文件。我们可以使用这个方便的帮忙脚本:
# Pull k3OS credentials
get_vm() {
gsed -i '/127.0.0.1/d' ~/.ssh/known_hosts
scp -P 3022 rancher@127.0.0.1:/etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml ~/.kube/current_k3os_vm.yaml
sed 's/6443/4443/g' ~/.kube/current_k3os_vm.yaml > ~/.kube/current_k3os_master.yaml
export KUBECONFIG=~/.kube/current_k3os_master.yaml
rm ~/.kube/current_k3os_vm.yaml
}
请注意:需要转发3022和4443端口
我们成功拉取.kubeconfig文件之后,我们应该准备好部署控制平面。
部署Rancher(云端)
要部署Rancher到云端环境,请执行以下步骤:
-
Clone或下载该仓库(https://github.com/rancher/quickstart)到本地文件夹
-
选择一个云提供商并导航到提供商的文件夹中
-
将terraform.tfvars.example复制或重命名为terraform.tfvars并填入所有必要的变量
-
运行terraform init
-
运行terraform apply
当配置完成之后,Terraform将输出连接到Rancher服务器的URL。还会生成两套Kubernetes配置:
Apply complete! Resources: 16 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Outputs:
rancher_node_ip = xx.xx.xx.xx
rancher_server_url = https://xx-xx-xx-xx.nip.io
workload_node_ip = yy.yy.yy.yy
kube_config_server.yaml包含了访问支持Rancher server的RKE集群的凭证, kube_config_workload.yaml包含了访问配置工作负载集群的凭证。
有关每个云提供商的更多详情,请参阅 repo 中各自文件夹中的文档。
Step 2 安装Argo Workflow
安装Argo CLI:
你可以从Argo release页面下载最新的Argo CLI:
https://github.com/argoproj/argo/releases
安装controller:
在这一步中,我们将安装Argo Workflows,通过workflow CRD扩展Kubernetes API。这将允许我们将多个“job”依次链在一起。安装Argo Workflows就像切换到k3OS集群并运行一样简单:
kubectl create namespace argo
kubectl apply -n argo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo/stable/manifests/install.yaml
请注意:在GKE上,你可能需要授予你的账户创建新集群角色的能力。
kubectl create clusterrolebinding YOURNAME-cluster-admin-binding --clusterrole=cluster-admin --user=YOUREMAIL@gmail.com
Step 3 配置服务账户以运行workflows
角色、角色绑定以及ServiceAccount
为了让Argo支持工件、输出、访问secret等功能,它需要使用Kubernetes API与Kubernetes资源进行通信。为了做到这一点,Argo使用ServiceAccount来验证自己与Kubernetes API的关系。你可以通过使用RoleBinding将一个Role绑定到ServiceAccount上,指定Argo使用的ServiceAccount是哪个Role(即哪个权限)。
然后,在提交workflow时,指定Argo使用哪个ServiceAccount:
argo submit --serviceaccount <name>
当没有提供ServiceAccount时,Argo将使用运行的命名空间的默认ServiceAccount,默认情况下它的权限几乎总是不够的。
授予管理员权限
在本次demo中,我们将授予defaultServiceAccount管理员权限(即我们将绑定adminRole到当前命名空间的defaultServiceAccount中):
kubectl create rolebinding default-admin --clusterrole=admin --serviceaccount=argo:default -n argo
请注意:这将向命令运行的命名空间中的default ServiceAccount授予管理权限,因此你将只能在制作RoleBinding的命名空间中运行workflows。
Step 4 运行workflow
从这里,你可以通过CLI以多种方式提交Argo workflow:
argo submit -n argo --watch https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo/master/examples/hello-world.yaml
argo submit -n argo --watch https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo/master/examples/coinflip.yaml
argo submit -n argo --watch https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo/master/examples/loops-maps.yaml
argo list -n argo
argo get xxx-workflow-name-xxx -n argo
argo logs xxx-pod-name-xxx -n argo #from get command above
你也能使用kubectl直接创建Workflow,但是Argo CLI会提供诸如YAML验证、workflow可视化、参数传递、重试以及重新提交、暂停和恢复等额外的功能:
kubectl create -n argo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo/master/examples/hello-world.yaml
kubectl get wf -n argo
kubectl get wf hello-world-xxx -n argo
kubectl get po -n argo --selector=workflows.argoproj.io/workflow=hello-world-xxx
kubectl logs hello-world-yyy -c main -n argo
所以,我们创建一个workflow.yaml文件并把这里的内容全部加进去:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
name: cluster-up
spec:
serviceAccountName: argo-serviceaccount
entrypoint: main
templates:
- name: main
steps:
- - name: rancher-dance
template: rancher-dance
- name: rancher-dance
inputs:
artifacts:
- name: kubectl
path: /bin/kubectl
mode: 0755
http:
url: https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v1.18.0/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
container:
image: giantswarm/tiny-tools:3.10
command:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- |
echo "Log in to Rancher"
LOGIN_RESPONSE=$(curl -s "https://$RANCHER_URI/v3-public/localProviders/local?action=login"
-H 'content-type: application/json'
--data-binary '{"username":"'$RANCHER_USER'","password":"'$RANCHER_PASS'"}')
LOGIN_TOKEN=$(echo $LOGIN_RESPONSE | jq -r .token)
echo "Obtain Rancher API token"
API_RESPONSE=$(curl -s "https://$RANCHER_URI/v3/token"
-H 'content-type: application/json'
-H "Authorization: Bearer $LOGIN_TOKEN"
--data-binary '{"type":"token","description":"automation"}')
API_TOKEN=$(echo $API_RESPONSE | jq -r .token)
echo "Configure server-url"
RANCHER_SERVER_URL="https://$RANCHER_URI/latest/meta-data/public-ipv4"
curl -s 'https://$RANCHER_URI/v3/settings/server-url'
-H 'content-type: application/json' -H "Authorization: Bearer $API_TOKEN"
-X PUT --data-binary '{"name":"server-url","value":"'$RANCHER_SERVER_URL'"}'
echo "Create the cluster, or get the info on an existing cluster"
CLUSTER_RESPONSE=$(curl -sf "https://$RANCHER_URI/v3/cluster"
-H 'content-type: application/json' -H "Authorization: Bearer $API_TOKEN"
--data-binary '{"type": "cluster",
"name": "'$CLUSTER_NAME'",
"enableClusterAlerting":true,
"enableClusterMonitoring":false}'
|| curl -s "https://$RANCHER_URI/v3/cluster?name=$CLUSTER_NAME"
-H 'content-type: application/json'
-H "Authorization: Bearer $API_TOKEN"
| jq ".data | .[]" )
echo "Extract the cluster ID"
CLUSTER_ID=$(echo $CLUSTER_RESPONSE | jq -r .id)
echo "Generate the cluster registration token"
CLUSTER_JSON=$(curl -s "https://$RANCHER_URI/v3/clusterregistrationtoken"
-H 'content-type: application/json' -H "Authorization: Bearer $API_TOKEN"
--data-binary '{"type":"clusterRegistrationToken","clusterId":"'$CLUSTER_ID'"}')
echo "Extract the cluster registration token"
CLUSTER_TOKEN=$(echo $CLUSTER_JSON | jq -r .token)
echo "Notify Slack of import"
curl -s "https://$RANCHER_URI/v3/notifiers"
-H 'content-type: application/json'
-H "Authorization: Bearer $API_TOKEN"
--data-binary '{"clusterId":"'$CLUSTER_ID'",
"name":"slack-alerter",
"namespaceId":"",
"pagerdutyConfig":null,
"sendResolved":true,
"slackConfig":{"url":"'$SLACK_WEBHOOK_URI'"},
"smtpConfig":null,
"webhookConfig":null,
"wechatConfig":null}'
echo "Retrieve and Apply Manifests"
kubectl apply -f "https://$RANCHER_URI/v3/import/$CLUSTER_TOKEN.yaml"
env:
- name: RANCHER_URI
value: "x.x.x.x.x.x"
- name: CLUSTER_NAME
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: cluster-name
key: CLUSTER_NAME
- name: RANCHER_USER
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: rancher-credentials
key: RANCHER_USER
- name: RANCHER_PASS
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: rancher-credentials
key: RANCHER_PASS
- name: SLACK_WEBHOOK_URI
value: https://hooks.slack.com/services/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
在一个较高的层次上,这个workflow本质上是将一个脚本作为一个pod在我们的集群中运行,并允许它使用某些变量。
-
登录到Rancher API
-
cURL,一个Rancher API令牌,使用TinyTools -
将Rancher server的URL设置为一个变量。
-
提取集群ID
-
检索和应用manifest
接下来,我们要把workflow cd到目录中,然后运行:
argo submit -n argo workflow.yaml
你可以看到workflow在你的集群中配置一个名为cluster-up的pod,它将会与Rancher连接:
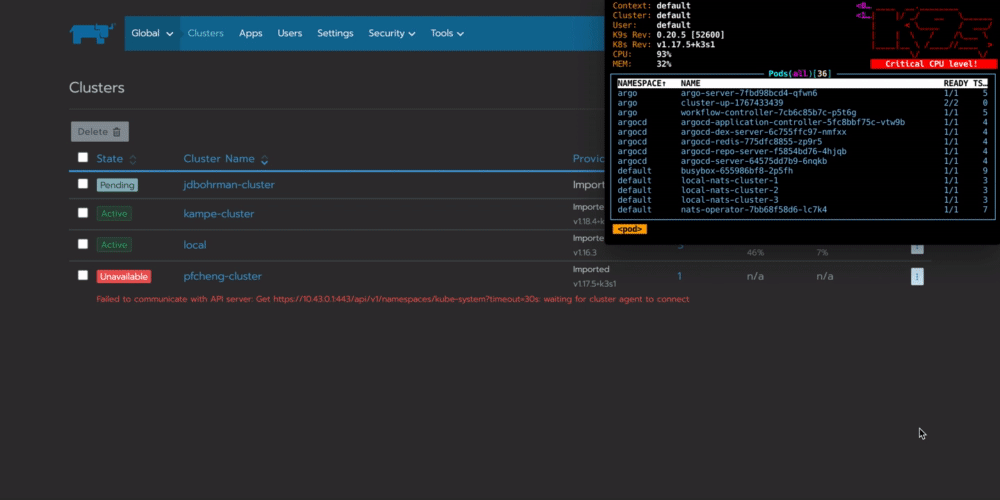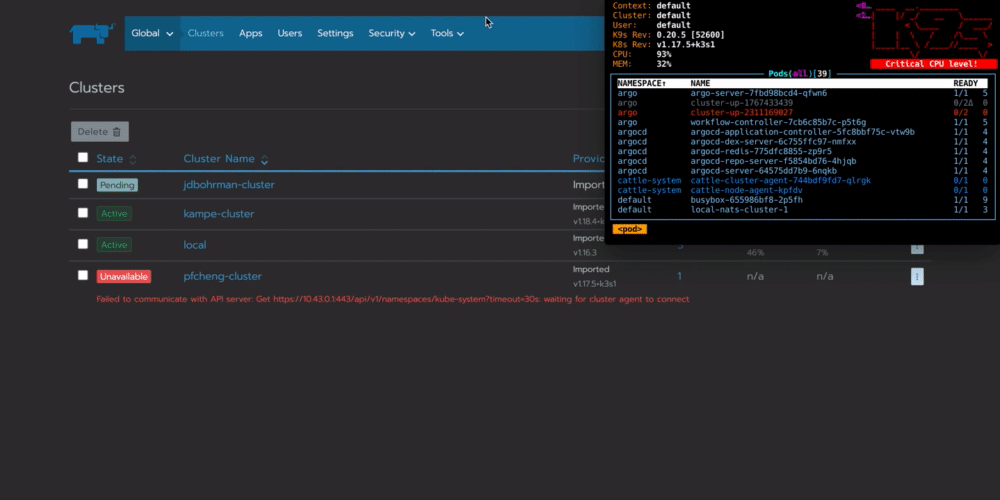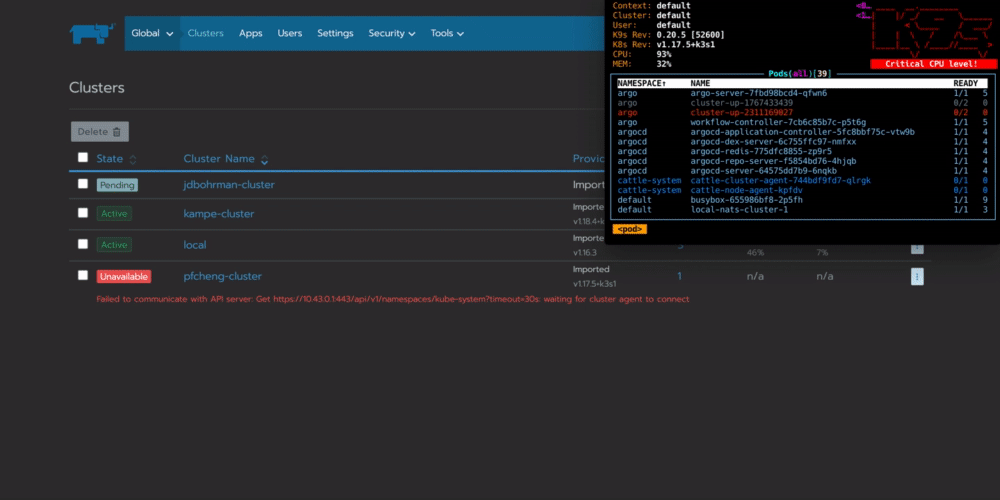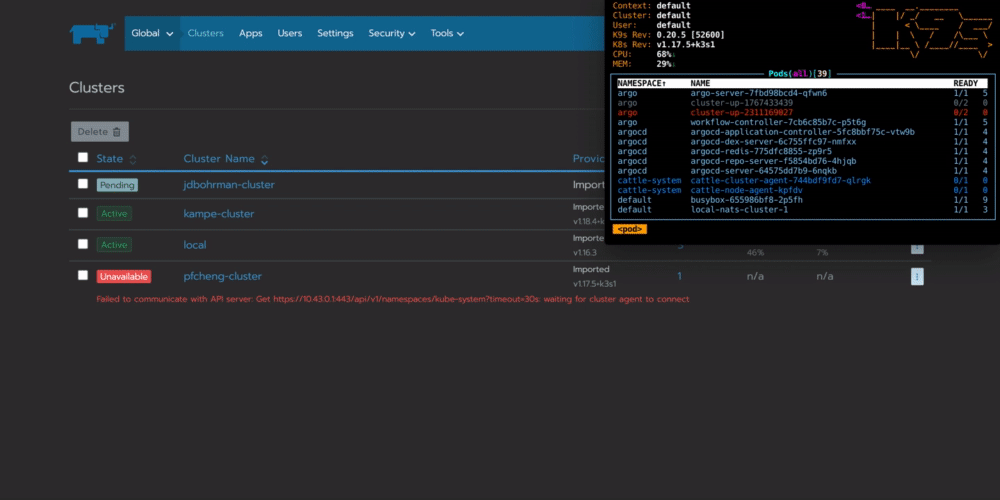
总结:为什么要在边缘自动执行任务
现在你已经了解了如何使用k3OS和Argo进行自动化边缘部署,让我们来讨论一下为什么这种类型的自动化如此重要。在为工业物联网(IIOT)等业务启动物理机器时,自动化这些任务是有益的,与机器交互的人是硬件技术人员,而不是云工程师。
在边缘,往往物理机器的配置是很费力的——但不应该一次只配置一台。通过这种方法,技术人员可以简单地插入类似USB的东西,它会启动一个ISO,然后运行一个脚本来启动机器的配置,然后注册到控制平面。