了解异步操作与回调,是学习网络请求必不可少的
回调(Callback)
当执行一个耗时操作或者等待某些触发性事件时,我们得保证耗时操作完成或者事件触发后才能进行下一步动作,这就是回调的应用场景(MDN文档居然说回调过时了QAQ)
截图为证

一个经典的例子便是监听器
var action = function(){}
btn.addEventListener("click", action);
以上代码即是为btn注册了一个监听器,当btn被点击后,执行action函数
action函数即是一个回调函数,它既没有被coder直接调用,也不会在被传参为btn的回调函数时立即执行
- XMLHttpRequest方式的网络请求中异步回调的使用
function loadAsset(url, type, callback) {
let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('GET', url);
xhr.responseType = type;
xhr.onload = function() {
callback(xhr.response);
};
xhr.send();
}
function displayImage(blob) {
let objectURL = URL.createObjectURL(blob);
let image = document.createElement('img');
image.src = objectURL;
document.body.appendChild(image);
}
loadAsset('coffee.jpg', 'blob', displayImage);displayImage作为回调函数传入
并非所有回调都是异步的
比如 Array.prototype.forEach(function) 遍历数组执行function操作 就是立即执行的
Promise
Promise是您在现代Web API中使用的新的异步代码样式
Promise允许推迟进一步的操作,直到上一个操作完成或响应其失败,Promise就是表示上一步操作结果,来调用下一步操作的对象,起承上启下的过渡作用
一个经典的应用是fetch()API,它是XMLHTTPRequest的现代版本
以下是一个从服务器获取数据的简单示例
fetch('products.json').then(function(response) {
return response.json();
}).then(function(json) {
products = json;
initialize();
}).catch(function(err) {
console.log('Fetch problem: ' + err.message);
});
- fetch()返回一个Promise对象,这个对象是表示异步操作完成或失败的对象;
- .then()函数中定义了一个回调函数,可以接收上一步成功操作的结果,进行下一个异步操作;
- 每一个.then()也返回该操作的Promise对象,因此我们可以根据需要链接多个异步操作;(听起来就很爽)
- 如果任何.then()块失败,可以由.catch()捕捉异常
像promises这样的异步操作被放入一个事件队列中,该事件队列不会阻止后续的JavaScript代码运行。排队的操作将尽快完成,然后将结果返回到JavaScript环境
Promise与回调
Promise本质上是将异步操作的结果以对象的形式返回到主过程,在主过程中将回调函数附加到这个对象上,再去异步执行,再返回操作结果;而回调则是将回调函数交给异步过程,在异步过程中进行调用
Promise与回调相比有一些优点
- 可以使用多个.then()块链接多个异步操作,这种方式远比多个嵌套的回调直观、可读
- Promise总是严格按照它们放置在事件队列中的顺序调用
- 只需一个.catch块处理异常,比在嵌套回调的每一层中处理错误方便
Promise与监听器有相似之处,但又有些许不同
- Promise只能成功(fulfilled)或失败(rejected)一次。它不能成功或失败两次。一旦操作完成,就不能从成功转为失败,反之亦然
- 当获取到一个Promise对象后,不做任何处理,在以后的时间为它添加.then()回调,也会调用正确的回调方法(就是说,在得到一个Promise后,可以在适当的时候增加.then()执行下一步动作)
异步操作像是多车道行车,不会阻塞主车道。同步操作则都是行驶在主车道上
async/await 关键字
async 和 await是基于Promise的
使用async关键字修饰函数声明,使该函数变成一个异步函数,返回一个Promise
使用await关键字,仅可在async函数中使用,表示等待一个Promise的返回,如果修饰的表达式的返回值并不是Promise对象,那么就返回该值本身
- async
以下几种方式都是定义了一个异步函数hello,返回函数执行完后的Promise
async function hello() { return "Hello" };
let hello = async function() { return "Hello" };
let hello = async () => { return "Hello" };
- await
使用await在async函数中等待任何返回Promise对象的表达式
fetch('coffee.jpg')
.then(response => response.blob())
.then(myBlob => {
let objectURL = URL.createObjectURL(myBlob);
let image = document.createElement('img');
image.src = objectURL;
document.body.appendChild(image);
})
.catch(e => {
console.log('There has been a problem with your fetch operation: ' + e.message);
});
用async/await改写
async function myFetch() {
let response = await fetch('coffee.jpg');
let myBlob = await response.blob();
let objectURL = URL.createObjectURL(myBlob);
let image = document.createElement('img');
image.src = objectURL;
document.body.appendChild(image);
}
或是
async function myFetch() {
let response = await fetch('coffee.jpg');
return await response.blob();
}
myFetch().then((blob) => {
let objectURL = URL.createObjectURL(blob);
let image = document.createElement('img');
image.src = objectURL;
document.body.appendChild(image);
});
await 会暂停myFetch函数(当然允许其他代码执行),等到异步操作返回结果后继续向下运行
为 async/await 添加错误处理
- 使用同步形式的 try…catch…
async function myFetch() {
try {
let response = await fetch('coffee.jpg');
let myBlob = await response.blob();
let objectURL = URL.createObjectURL(myBlob);
let image = document.createElement('img');
image.src = objectURL;
document.body.appendChild(image);
} catch(e) {
console.log(e);
}
}
- 使用.catch()块
async function myFetch() {
let response = await fetch('coffee.jpg');
return await response.blob();
}
myFetch().then((blob) => {
let objectURL = URL.createObjectURL(blob);
let image = document.createElement('img');
image.src = objectURL;
document.body.appendChild(image);
})
.catch((e) =>
console.log(e)
);
在以上的代码中,不能使用 try…catch…来包裹myFetch()和.then()块捕获异常
因为 try…catch…没法捕获异步函数中抛出的异常
而.catch()块可以捕获异步函数调用中抛出的异常,也能捕获promise链中的异常
为什么使用 async/await
.then()块的链接远比多层Callback清晰可读,而 async 中的 await 使得异步程序完全可以以同步代码的形式编写,这是其他异步操作不可比的
等待多个Promise
如果一个操作需要等待多个异步操作完成
可以使用Promise.all()方法
function fetchAndDecode(url, type) {
// Returning the top level promise, so the result of the entire chain is returned out of the function
return fetch(url).then(response => {
// Depending on what type of file is being fetched, use the relevant function to decode its contents
if(type === 'blob') {
return response.blob();
} else if(type === 'text') {
return response.text();
}
})
.catch(e => {
console.log(`There has been a problem with your fetch operation for resource "${url}": ` + e.message);
});
}
async function displayContent() {
// Call the fetchAndDecode() method to fetch the images and the text, and store their promises in variables
let coffee = fetchAndDecode('coffee.jpg', 'blob');
let tea = fetchAndDecode('tea.jpg', 'blob');
let description = fetchAndDecode('description.txt', 'text');
// Use Promise.all() to run code only when all three function calls have resolved
let values = await Promise.all([coffee, tea, description]);
console.log(values);
// Store each value returned from the promises in separate variables; create object URLs from the blobs
let objectURL1 = URL.createObjectURL(values[0]);
let objectURL2 = URL.createObjectURL(values[1]);
let descText = values[2];
// Display the images in <img> elements
let image1 = document.createElement('img');
let image2 = document.createElement('img');
image1.src = objectURL1;
image2.src = objectURL2;
document.body.appendChild(image1);
document.body.appendChild(image2);
// Display the text in a paragraph
let para = document.createElement('p');
para.textContent = descText;
document.body.appendChild(para);
}
displayContent()
.catch((e) =>
console.log(e)
);
用 async/await 改写 fetchAndDecode
async function fetchAndDecode(url, type) {
try {
// Returning the top level promise, so the result of the entire chain is returned out of the function
let response = await fetch(url);
let content;
// Depending on what type of file is being fetched, use the relevant function to decode its contents
if(type === 'blob') {
content = await response.blob();
} else if(type === 'text') {
content = await response.text();
}
return content;
} finally {
console.log(`fetch attempt for "${url}" finished.`);
};
}
Promise.all()后也可以跟.then()块处理
Promise.all([coffee, tea, description]).then(values => {
console.log(values);
// Store each value returned from the promises in separate variables; create object URLs from the blobs
let objectURL1 = URL.createObjectURL(values[0]);
......
......
});
async/await 使用中的问题
如果有一系列操作接连进行 await,那么你的异步函数就频频阻塞,等待Promise返回,真的变成了"同步代码"
function timeoutPromise(interval) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(function(){
resolve("done");
}, interval);
});
};
async function timeTest() {
await timeoutPromise(3000);
await timeoutPromise(3000);
await timeoutPromise(3000);
}
let startTime = Date.now();
timeTest().then(() => {
let finishTime = Date.now();
let timeTaken = finishTime - startTime;
alert("Time taken in milliseconds: " + timeTaken);
})
以上代码运行结果
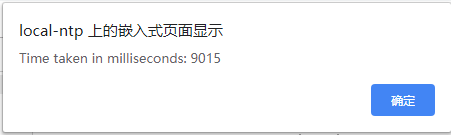
可见每个timeTest()都必须等待上一个timeTest()执行完成
这显然不是我们想要的
我们可是异步操作!
那么
修改 timeTest() 函数如下
async function timeTest() {
let a = timeoutPromise(3000);
let b = timeoutPromise(3000);
let c = timeoutPromise(3000);
await a;
await b;
await c;
}
结果如下
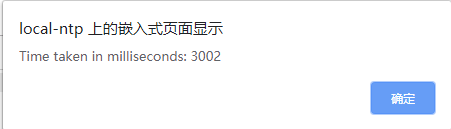
如何理解这个问题呢
await 三连好像是开一个线程去执行任务1,任务1执行完后,再开一个线程执行任务2,任务2执行完后,开线程执行任务3
而将返回的Promise先用变量保存,再一一 await,像是连开了三个线程去分别做三个任务,最后等待三个任务都完成
所以要考虑一系列任务间的同步关系,选择合适的 await 方式
另外需要注意的一点是:await 只能在 async 函数中使用
async/await 在OO中的使用
class Person {
constructor(first, last, age, gender, interests) {
this.name = {
first,
last
};
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
this.interests = interests;
}
async greeting() {
return await Promise.resolve(`Hi! I'm ${this.name.first}`);
};
farewell() {
console.log(`${this.name.first} has left the building. Bye for now!`);
};
}
let han = new Person('Han', 'Solo', 25, 'male', ['Smuggling']);
就可以写出这样的代码
han.greeting().then(console.log);
2019/5/27
最后编辑
2019/6/2